Overview of ITIL Lifecycle
Information technology infrastructure library (ITIL) is a planned structure, the main purpose of which is to improve the efficiency of the IT department of a company. This department does not just remain back-office support but the IT officers are service partners of the business. In this topic, we are going to learn about ITIL Lifecycle.
The ITIL is designed in such a way that the planning, selection, maintenance, and delivery of IT services of any business is systematized and standardized.
When a company decides to adopt ITIL, it requires trained and certified personnel to maintain it and also to guide the company and its IT department. Microsoft, IBM, and Hewlett Packard Enterprise are Company which is already using ITIL successfully.
Evolution of ITIL
- In 1989 ITIL was introduced to standardize IT service management. This helped in streamlining services in organizations.
- In 2001 ITIL v2 was introduced which included actual processes and a sound support system to benefit organizations.
- 2007 brought us ITIL v3 which provided guidelines to design, service and operation. Feedback for improvement was also started for continuous improvement.
- In 2011, ITIL v3 gave a broader perspective and added more focus on strategy,
- 2019 gives us ITIL v4 which hopes to provide an improved role of IT management in a service economy. It ensures to give practical guidance and while drawing connections between ITIL and new technologies like DevOps.
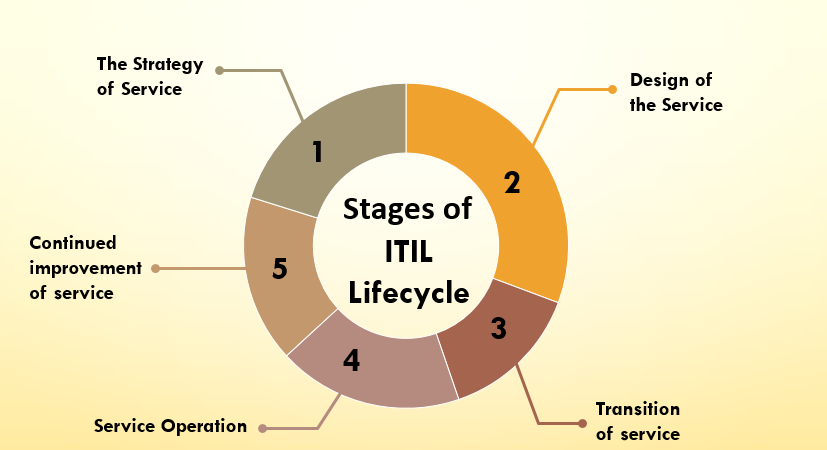
Stages of ITIL Lifecycle
For IT services to run smoothly, it is necessary to follow the principles of ITIL Lifecycles. This Lifecycle is divided into 5 stages. These are interconnected so that the end goal is always the focus.
1. The Strategy of Service
This stage is of most importance as it is the crux of ITIL Lifecycle services. A uniform and rational strategy is the key to superior service management provided by any organization. The business goals of a company and the procedures followed by the IT department should be in sync. The objectives should be in alignment with the strategies.
So, the initial step to be taken here is :
To find out who the customers are?
What are the services required?+
What sort of skill or qualifications are needed?
From where will the funds come and how will the delivery be done?
How will the monetary worth be determined?
Who will take the responsibility of the business relations?
What is the purpose of IT service management?
2. Design of the Service
In this stage, the strategies of stage 1 are converted into activity. Now the ideas are taken to the next step and planning and designing takes place. A time period is also pre-decided within which the service needs to be executed.
This process includes:
Understanding the strategy.
Creating a prospectus for the service
Ensuring that the policies and services are cost-efficient
Short-listing efficient suppliers
Look into the security system
3. Transition of Service
Once designed, the strategy is tested so that it is ready to be actually performed or we can say ready to be executed. This is the stage where the procedure is thoroughly checked so that there is no issue when it is finally presented to the customer.
This transition includes:
A new service to be implemented for every design.
Every design to be tested and displayed.
Any changes required for services to be managed.
Any risks to the services also are looked into.
Accomplishing the business target.
4. Service Operation
This is where the service is presented to the customer and is ready for operation. Customer satisfaction should be ensured by the service provider here and it is his duty to see how the service is performing. If there are any issues, they need to be reported.
The steps can be summarised as:
Services are delivered to sanctioned users.
The cost should be effective and quality enhanced.
The satisfaction of the user.
Business Enhancement.
5. Continued Improvement of Service
Though the planning, designing and implementing services is done meticulously, continuous monitoring is required so that all the strategic targets of that IT service are reached. Once these are reached, new targets can be set and the process can start again.
By ensuring the proper execution of each stage of the ITIL lifecycle, the company knows that their services and their business strategies are on the same page.
Guiding Principles of ITIL
These are a few rules of ITIL which might be common to other methods too.
- Focusing on creating value directly or indirectly
- Acknowledge what is good and work on the weaker aspects
- Work on small projects, improvising while the job is being done and measuring the work done for future reference.
- Transparency amongst the team members as well as the shareholders and owners of the company as always proves beneficial to all concerned.
- The undertaking of a project until its completion should have a holistic approach to it as this is the responsibility of the service value system (SVS)
- The employment of resources, tools, procedures should be optimum and practical as time and finances both matter.
- Human Resources should be involved only when necessary as it is easier with software.
ITIL looks at how the knowledge of the admins can be utilized for the benefit of the organization at a larger scale.
ITIL is beneficial as stated under:
- The business and its IT department are aligned better as far as the goal is concerned.
- Service is provided within the timeline and there are happy customers.
- Resources are optimally utilized resulting in cost reduction.
- There is more clarity on the cost and assets of IT.
- The environment is more adjustable and open to changes which are very helpful.
ITIL proves to be a good infrastructure for businesses that don’t have a fixed service foundation but can pursue specialists to do the job in the best way possible.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to ITIL Lifecycle. Here we discuss the Evolution, Stages, Principles and the main purpose of using ITIL in an IT department of a company. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –