Definition of ITIL Service Design
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is the best suit framework providing information related to the best practices of delivering IT services. Its methodical approach helps IT services mitigate the risk level in businesses, build up strong customer relationships, and establish cost-effective practices that ensure to construct a stable and flexible IT environment that influences career growth and the company’s progression, accepting changes bringing up new innovation. In this topic, we are going to learn about ITIL Service Design.
What is Service Design?
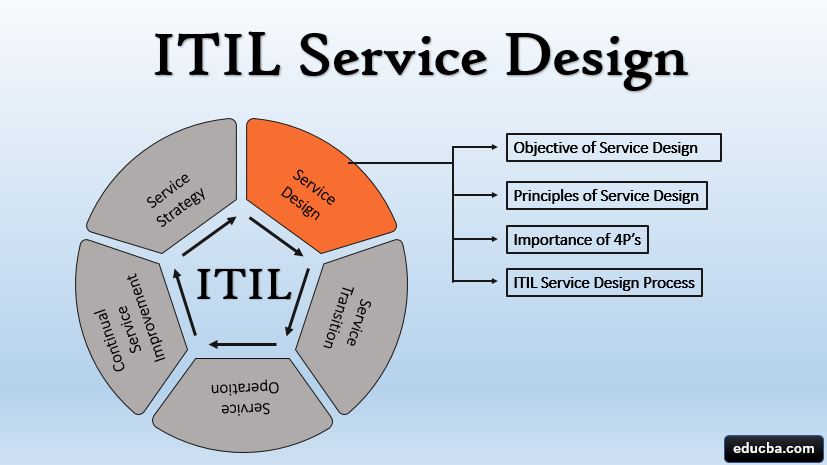
The ITIL Service Lifecycle comprises of five consecutive stages, such as Service Strategy, ITIL Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement are closely entangled with one another that the service cannot be effectively completed without any of a single stage. Service Design (SD) is the second process group of ITIL Service Management Lifecycle which begins after determining the strategy by the service team. The service management team needs guidelines for designing and developing the new services, and these are established in the Service Designing stage. The ITIL Service Design process includes guidelines for designing new IT services, processes and other aspects of IT Service Management. It assimilates design principles and methods for transforming strategic business objectives into portfolios of services and service assets.
Objective
The ultimate purpose of the Service Design process is to present new, innovative and appropriate IT services, processes and other aspects of ITIL Service management to fulfill present and future business requirements.
Principles
The overall approach of ITIL Service Design is to represent the fundamentals of designing services. The five key aspects of the Service Design process are as follows –
- Designing Service Solution: At the planning stage, the service team chalks a plan of producing services with balancing cost, deadline, budget and business requirements.
- Designing Management Information Systems and Tools: ITIL service design defines some important Management Information Systems (MIS), such as service portfolio, configuration management system, capacity management information system and security management information system.
- Designing of Technology and Architecture: Designing technology brings in technological competencies which take care of designs, plans, and processes aligning with IT policies and strategies.
- Designing Processes: The process model is one of the elaborate paradigms in ITIL, and it helps in the transition, operation, and improvement of services.
- Designing Measurements and Metrics: Process metrics must be aligned with organizational goals and drilled down to each individual role as in balanced scorecard metrics.
Importance of 4P’s
The entire ITIL Service Design process depends on 4 P’s – Product, People, Process and Partner.
The efficient and effective use of 4Ps will deliver the benefits of the Service Design process. It also mitigates the risk factor; because many designs, plans and projects fail for lack of preparation and management.
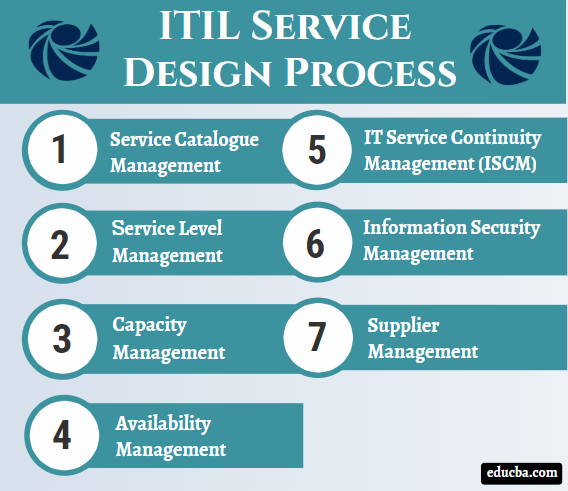
ITIL Service Design Process
The Service Design processes are as follows –
1. Service Catalogue Management
Service catalog management ensures that a service catalog or a list of all the services is produced or maintained for all those who are parts of IT service management or have the authorization to see it. In addition, it contains accurate information on all operational services.
The key purposes of service catalog management are –
- To ascertain that the agreed services are well-defined, documented and accurate.
- To make sure that the business requisites supported by the IT service team are defined in the service catalog, and this catalog has to be maintained in conjunction with the service portfolio.
The service catalog supports in two ways –
- It helps customers to choose services based on their needs.
- It helps IT personnel to assume what kind of technical services they should provide to support business services.
2. Service Level Management
This important design process emphasizes business requirements and then defines, negotiates, and agrees upon the IT services target. The purpose of negotiation is to control and monitor the Service Level Agreement (SLA) with precise measures to provide better quality service or product. The services are regularly checked to measure whether it meets up the expectation level. It also authorizes the accuracy of Operational Level Agreements (OLA). The main mission of service level management is to ensure effective communication between the service provider and business. That is why service level management should meet customers face-to-face on a regular basis.
3. Capacity Management
The objective of Capacity Management is to focus on business requirements, the organization’s operation, and IT infrastructure. It ensures that the IT organization is able to deliver the services in a timely manner without compromising quality and budget. Different processes associate with capacity management is technology, business plan, requirements, and incidents. Effective capacity management helps to diminish the risk factor of unnecessary investment in technology.
4. Availability Management
Availability management ensures that the infrastructure, roles, tools are appropriate to meet the target or exceed the need of the business. It also works with the design team and observes the processes, roles, and tools to meet the target. The primary objectives of Availability Management are as follows –
- To manage the availability of requirements in association with customer’s demands.
- To ascertain and monitor the availability of services.
- To propose any change available in IT services for improvement.
5. IT Service Continuity Management (ISCM)
IT Service Continuity Management is responsible for the alignment of IT services to Business Continuity Management. Generally, it is the process responsible for managing the risk that may directly impact IT services. ISCM closely works with the business continuity management process to risk analysis and business impact analysis. This analysis helps to understand different types of risk factor’s impact on business. ITSCM is responsible for the development as well as the deployment of the plan, including regular testing and training of all personnel associated with the plan. The lifecycle of the ITSCM process includes four stages –
- Initiation
- Requirements and strategy
- Implementation
- Ongoing operation
6. Information Security Management
The objective of the Information Security Management process is to align business security with information security and ensures that it protects data, databases and all IT-related information effectively. It also maintains and enforces the security policy. The information which is very critical for any organization should maintain confidentiality, availability, and integrity.
7. Supplier Management
Supplier management ensures that all the dealers or suppliers adhere to the terms mentioned in the contract. The key objective of Supplier Management is the alignment of the contract with the needs of the business.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ITIL Service Design. Here we discuss the objective, Principles, Importance of 4P’s and the Process of ITIL Service Design. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –