Overview of ITIL Service Operation
ITIL or Information technology infrastructure library is an IT practice that fulfills the requirements of customers as well as the needs of the business. An ITIL Lifecycle has 5 phases, and service operation is the fourth phase. To run a business smoothly, there are certain activities and procedures done on a daily basis so that the customer demands can be fulfilled efficiently and timely. ITIL service operation focuses on such daily business activities.
When a customer wants a particular service, his main concern is the cost of the service, its reliability, and timely delivery. The type of technology used is not their concern. A capable service operating team minimizes issues and quick resolution when they arise. Delivering excellent service makes the next stage of ongoing service more efficient.
The key factor in service operation is the increased consumption of goods and service experience. Effectively manage everyday affairs so that there are no issues and, if an issue arises, settle it at the priority level.
Why Service Operation should be used?
Service operation is an important phase of the ITIL lifecycle because:
- The plan of action, designing the plan, and the development process of the IT services are all executed and analyzed only. This is where the result of the undertaken service can be seen.
- The everyday activities are performed, managed, and controlled with finesse so that the services, when delivered, are customer satisfactory.
Principles of Service Operation
Service operation should strive to maintain a balance between:
- Internal IT perspective and external business perspective: The result or payoff service is what a business is interested in, but the IT service’s main concern is the process, the framework, the execution. A balance has to be brought here.
- Reliability vs open-mindedness: Stability is of utmost importance, but there should also be readiness in need of any change.
- Cost of service and quality of service: It is generally seen that the quality also suffers when the cost is reduced. So a balance of cost efficiency while maintaining the standard of quality has to be brought.
- Proactive vs reactive: Organizations that are reactive are known for crisis management and focus on the existing market scenario, while proactive organizations are intense on acting in advance for a future situation. A balance would be ideal.
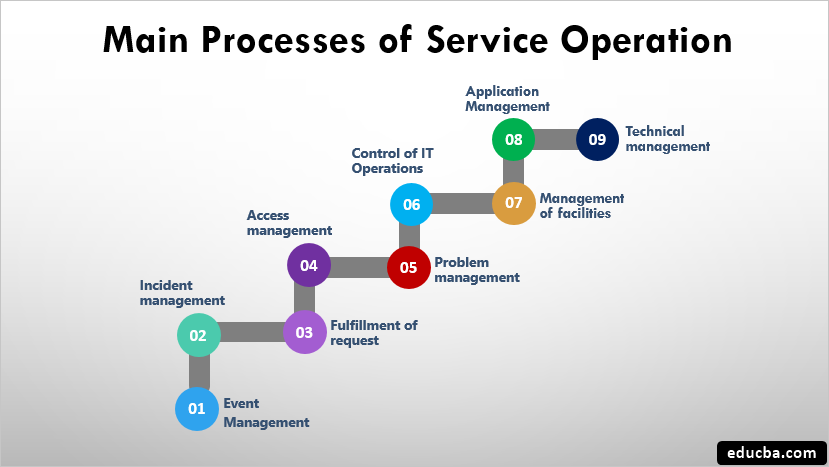
Main Processes
The main processes of Service Operation are :
1. Event management: This process aims to choose, classify, and constantly supervise all the services.
2. Incident management: This process administers all incidents. The main objective here is to deliver IT services to users as early as possible.
3. Fulfillment of request: The purpose is to comply with all requests as small as they might be, as the request to change a password or request for any information.
4. Access management: Approved users only have access to a service, while unapproved users do not have the liberty to use the service. Rights management or identity management is also similar to access management.
5. Problem management: The motive here is to see that the process continues unhindered, and if any problem does occur, the team ensures that minimum damage is done. All the previous data collected is used to foresee any sort of problem that might arise. It is also used to foresee trends. The job here is to solve the problem as soon as possible if it does occur.
6. Control of IT Operations: It is the work of the team to constantly oversee and audit the IT services and their necessary infrastructure. The IT Operations control administers daily tasks connected to infrastructure and application. Tasks such as job planning, backup and reinstating activities, and overall maintenance.
7. Management of facilities: The infrastructure and the facilities available on the physical level are managed here. These facilities include electricity, a cooling system, access to office premises, the workplace’s cooling system, and managing the environment on the whole.
8. Application management: The main objective here is to manage all applications until their entire existence.
9. Technical management: To manage the IT infrastructure, all the technical prowess and support is provided by this team. To understand service operation thoroughly, a few more points are discussed here:
- Service Operation is basically a utility company providing the support that customers need to do their jobs. For, e.g. electricity without which all work would stop and without a process to ensure regular electricity, there would not be reliability. The customer is not interested in the process but just in the timely and cost-effective delivery of the end product.
- Consumers have expectations from technology, so IT organizations must also ensure that the support system for post-delivery issues and the infrastructure to do it is in place, so that continued service to customers can be provided.
- ITIL service operation, just like any other utility company, has to provide different service packages to the user like a service catalogue. These focus on the processes, management, after services, various services offered, warranties, etc.
- The service not only monitors all infrastructure elements but also analyses the experience of the users.
- To prevent users from looking elsewhere to derive business results, service operations must be efficient, easily available, flexible, and cost-effective. Thus IT resources can be used for software as a service (SAAS), platform as a service (PAAS), and infrastructure as a service (IAAS).
- Service Operation is the fourth stage in the ITIL life cycle and is in direct contact with service strategy and continual service improvement and relies on them for any input as well as feedback. There is dependency, and interaction between the stages makes the service more efficient.
In the end, it can be said that to gain success, a business unit or an individual needs the help of IT operations, and the service provided ensures a good experience to the customer. As the expectations of the customer rise every time, the ability of IT organizations to perform also increases. Both benefit from each other by becoming more efficient and effective.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ITIL Service Operation. Here we discuss the principles and the main processes of ITIL Service Operation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –