Updated March 28, 2023
Introduction to Java Array Iterator
- Java Array Iterator defined as iterating all the array elements by applying different looping logic on the array.
- Arrays are used to store homogeneous elements means the same type of elements can be stored at a time. Example: We can store integer numbers, float numbers, double numbers, strings, characters, Objects, etc., but at a time any specific type only.
- Arrays size is not dynamic, so it is always fixed. At the time of array definition, only we specified array size.
- An array can be declared in 3 ways:
- A[]
Example:
int A[]={1,2,4};-
- [] A
Example:
int[] A={1,2,4};-
- []A
Example:
int[]A={1,2,4};Why are Array Elements Iterated?
Perform any specific operation on array elements, then iterate the elements and apply the operation. The Operations are Addition, multiplication, division, subtraction, etc., on the array elements.
In how many ways Array Elements can be Iterated?
- for Loop
- for Each Loop
- while Loop
How Does Array Iterator Works?
As we discussed above, array elements can be iterated in 3 ways, so based on the looping functionality array can iterate its elements.
- For Loop
Syntax:
int a[]=new int[size of an array];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
//array logic
}- For Each Loop
Syntax:
int a[]=new int[size of an array];
for(int i=0:a)
{
//array logic
}- For Each Loop
Syntax:
int a[]=new int[size of an array];
int i=0;
for(i<a.length)
{
//array logic
i++;
}Examples to Implement Java Array Iterator
Below are the examples of Java Array Iterator:
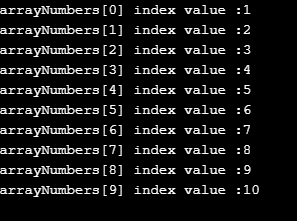
Example #1 – Static Array with For Loop
Code:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//defining static array with 10 elements
int arrayNumbers[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
//for loop
for(int i=0;i<arrayNumbers.length;i++)
{
//displaying array index and its corresponding values
System.out.println("arrayNumbers["+i+"]"+" index value :"+arrayNumbers[i]);
}
}
}Output:
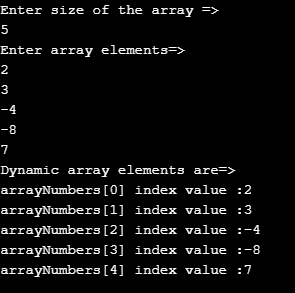
Example #2 – Dynamic Array with For Loop
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Scanner for taking input from user
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter size of the array =>");
// for integer input user nextInt()
int input = scanner.nextInt();
// defining dynamic array with any required size elements
int arrayNumbers[] = new int[input];
System.out.println("Enter array elements=>");
//for loop for adding elements to the array dynamically
for(int i=0;i<arrayNumbers.length;i++)
{
arrayNumbers[i]=scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Dynamic array elements are=>");
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < arrayNumbers.length; i++) {
// displaying array index and its corresponding values
System.out.println("arrayNumbers[" + i + "]" + " index value :" + arrayNumbers[i]);
}
//closing scanner object
scanner.close();
}
}Output:
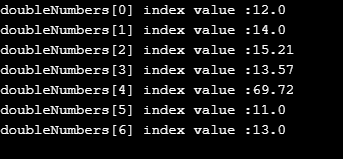
Example #3 – Static Array with For Each Loop
Code:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//defining static array with 7 elements
double doubleNumbers[] = {12.0,14.0,15.21,13.57,69.72,11,13};
int temp=0;
//for each loop
for(double i:doubleNumbers)
{
//displaying array index and its corresponding values
System.out.println("doubleNumbers["+temp+"]"+" index value :"+i);
temp++;//temp is for storing index values as int type because array index never exist in double form
}
}
}Output:
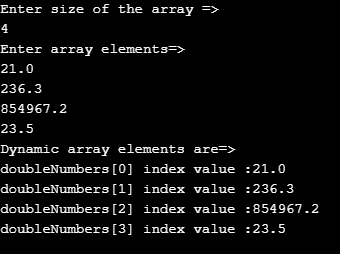
Example #4 – Dynamic Array with For Each Loop
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ForEachDynamicArrayIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Scanner for taking input from user
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter size of the array =>");
// for integer input user nextInt()
int input = scanner.nextInt();
// defining dynamic array with any required size elements
double doubleNumbers[] = new double[input];
System.out.println("Enter array elements=>");
//for loop for adding elements to the array dynamically
for(int i=0;i<doubleNumbers.length;i++)
{
doubleNumbers[i]=scanner.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println("Dynamic array elements are=>");
int temp=0;
// foreach loop
for (double d:doubleNumbers) {
// displaying array index and its corresponding values
System.out.println("doubleNumbers[" + temp + "]" + " index value :" +d);
temp++;//temp is for storing index values as int type because array index never exist in double form
}
//closing scanner object
scanner.close();
}
}Output:
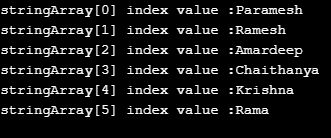
Example #5 – Static Array with While
Code:
public class WhileStaticArrayIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//defining static array with 6 elements
String[] stringArray = {"Paramesh","Ramesh","Amardeep","Chaithanya","Krishna","Rama"};
int temp=0;
//for each loop
while(temp<stringArray.length)
{
//displaying array index and its corresponding values
System.out.println("stringArray["+temp+"]"+" index value :"+stringArray[temp]);
temp++;//temp is for storing index values
}
}
}Output:
Example #6 – Dynamic Array with While Loop
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class WhileDynamicArrayIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Scanner for taking input from user
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter size of the array =>");
// for integer input user nextInt()
int input = scanner.nextInt();
// defining string dynamic array with any required size elements
String stringArray[] = new String[input];
System.out.println("Enter array string elements=>");
// for loop for adding elements to the array dynamically
for (int i = 0; i < stringArray.length; i++) {
stringArray[i] = scanner.next();
}
System.out.println("Dynamic array elements are=>");
int temp = 0;
// foreach loop
while (temp<stringArray.length) {
// displaying array index and its corresponding values
System.out.println("stringArray[" + temp + "]" + " index value :" + stringArray[temp]);
temp++;// temp is for storing index values
}
// closing scanner object
scanner.close();
}
}Output:
Conclusion
An array can be iterated by using for loop, for each loop and while loop with static and dynamic values. Array iteration used to perform any operation on array elements.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Java Array Iterator. Here we discuss how Does Array Iterator Works in Java and its Examples along with its Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –