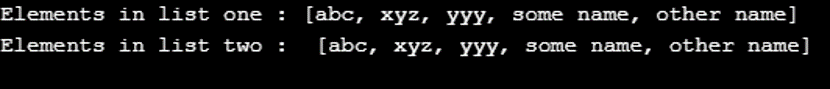Updated March 2, 2023

Definition of Java ArrayList Class
ArrayList is the implementation of the List interface, which comes under the collection framework in java which allows us to grow the size of an array dynamically, i.e., on runtime. This class is available in the java.util.package internally, it uses the array data structure. ArrayList allows only wrapper classes in java, and the user defines classes.
Syntax:
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();We can directly use an instance of ArrayList or assign it to a List reference.
Constructors:
In the array list, we have three constructors available, which are as follows:
- ArrayList(int initialCapacity): In this, we can specify the initial length of the array list. But ArrayList class takes care of it if the size exceeds the initialCapacity mentioned.
- ArrayList(): By this, we can create an empty list without initial capacity, so in this case, the default initialCapacity would be 10.
- ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c): List of a collection.
Methods of Java ArrayList Class
Following are the methods of the java ArrayList class:
- void trimToSize(): This method will trim the list to the current list size.
- Object[] toArray(): Return the array of object.
- boolean remove(Object o): This method is used to remove the object, but it will remove the first occurrence as the list contain duplicate.
- boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c): This method is used to remove all the elements of the list.
- Boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter): This method is used to remove the predicate passed. Used as a filter.
- Add (E e): This method s used to add elements to the list.
- Void add(int index, E element): It takes two-parameter and adds elements t the specific index we mentioned.
- Boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c): This takes a list as an argument and adds all the elements to the end of the current list.
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c): This method adds all the elements to the current list at the specified index we pass.
- Get (int index): This method is used to get the element. It will return the element present at the specified position in the list.
- Int indexOf(Object o): This method is used to get the element’s index passed. It will always return the first occurrence of the element into the list because the list can contain duplicate elements.
- ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index): This method returns an iterator with the specific index.
- Remove (int index): This method removes the element. It will remove the element with the corresponding index passed.
- Protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex): This removes the elements from a specified range.
- Boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c): This method will retain all elements contained in the specified collection.
- Set (int index, E element): This method will set the element to the specified index.
- Void sort(Comparator<? super E> c): This method is used to sort the collection element.
- List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex): This method will be used to return the sublist from the specified index.
- Void clear(): This mentioned is used to clear the elements in the list.
- Object clone(): These methods create a copy of the list.
- Boolean contains(Object o): This method is used to check whether the passing object is present in the list or not.
- Void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity): This method is used to increase the capacity of the array list.
- Boolean isEmpty(): This method is used to check whether the array list is empty or not.
- Iterator<E> iterator(): This method returns iterator.
- int lastIndexOf(Object o): This method returns the last index of the object passed. If the object does not present in the list, it will return -1.
- ListIterator<E> listIterator(): This methods return iterator.
Examples of Java ArrayList Class
Examples of Java ArrayList Class are given below:
1. add an element in ArrayList
The below example will show how to add an element to an array list.
Code:
package com.cont.article;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArratListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
System.out.println("list is :: " + list);
}
}Output:
2. Copying elements of list one to another list
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.addAll(list);
System.out.println("Elements in list one : " + list);
System.out.println("Elements in list two : " + list2);
}
}Output:
3. Remove element from ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
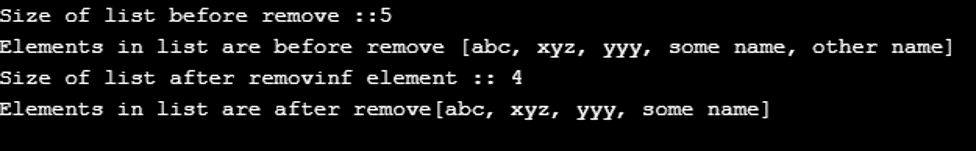
System.out.println("Size of list before remove ::" + list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are before remove " + list);
list.remove(4);
System.out.println("Size of list after removinf element :: " +list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are after remove" + list);
}
}Output:
4. Clear all the elements from ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
list.clear();
System.out.println("Clering all elements of list " +list.size());
}
}Output:
5. Iterate all the elements of ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
System.out.println("Priniting out element.");
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println("Elemnt in the list is");
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}Output:
The array list in java does not contain duplicate elements. Also, the insertion order is maintained in a list, which means we put over elements that will generate the output in the same sequence. Some detailed points which need to be remembered for the array list in java are as follows:
It implements various interfaces:
- Serializable,
- Iterable<E>,
- Cloneable,
- Collection<E>,
- List<E>,
- RandomAccess
The class hierarchy is as follows:
java.lang.Object >> java.util.AbstractCollection<E> >> java.util.AbstractList<E> >> java.util.ArrayList<E>By default, the array list is not synchronized in nature and is not thread-safe, But we can make them synchronized using the collections class synchronized method. The syntax is described below for reference :
List arrList = Collections.synchronizedList (new ArrayList(...));Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java ArrayList Class. Here we also discuss the introduction and methods of Java ArrayList Class, along with different examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –