Updated June 15, 2023

Introduction to Java Authenticator
The Java authenticator class is used to authenticate network connections. This class is a standard Java class. The authenticator class is used in applications that require user authentication to access certain URLs. An authenticator class performs authentication by prompting the user for credential information like username and password.
To perform authentication in an application, the application needs to perform some steps; first, an application class extends the java.net.Authenticator class and overrides the getPasswordAuthentication() function of java.net.Authenticator class in the subclass. Usually, this function contains getXXX() functions to get user information for authentication, like usernames and passwords. The getPasswordAuthentication() function returns the PasswordAuthentication value containing credentials information.
The syntax of the Authenticator class in Java is –
public abstract class Authenticator extends Object
{
// code of the authenticator class
}Authenticator Class Member Functions
Let’s go over the entire list of Authenticator class member functions that can be used for authentication.
1. getPasswordAuthentication() – When a password is required, this function is used. All subclasses should override getPasswordAuthentication (), which returns null by default.
Syntax –
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication();2. getRequestingHost() – This function retrieves the hostname of the site requesting authentication and returns null if no hostname is found.
Syntax –
protected final String getRequestingHost();3. getRequestingPort() – This function is used to get the port number of requesting connection.
Syntax –
protected final int getRequestingPort();4. getRequestingPrompt() – This function is used to prompt the requestor’s string message.
Syntax –
protected final String getRequestingPrompt();5. getRequestingProtocol() – This function is used to get the protocol that is requesting the connection.
Syntax –
protected final int getRequestingProtocol();6. getRequestingScheme() – This function is used to remove the requestor site’s scheme.
Syntax –
protected final String getRequestingScheme();7. getRequestingSite() – This function is used to get InetAddress of the requesting site, and return null if no InetAddress is present.
Syntax –
protected final InetAddress getRequestingSite();8. getRequestingURL() – This function is used to get the URL of the requester.
Syntax –
protected URL getRequestingURL();9. setDefault(Authenticator a) – It is used to set the authenticator to be used by networking when the HTTP server requires authentication.
Syntax –
public static void setDefault(Authenticator a);10. getRequestorType() – This function is used to get whether the requestor is a server or a Proxy.
Syntax –
protected Authenticator.RequestorType getRequestorType();Examples of the Authenticator Class in Java
Next, we write the Java code to understand the Authenticator class more clearly with the following example where we create a subclass of Authenticator class and override the getPasswordAuthentication() function to perform authentication for some URL, as below –
Example #1
Code:
package p1;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Authenticator;
import java.net.PasswordAuthentication;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
class MyAuthenticatorclass extends Authenticator
{
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication()
{
String username = "John", password = "pass123";
this.print();
return new PasswordAuthentication(username, password.toCharArray());
}
void print()
{
int hostname = getRequestingPort();
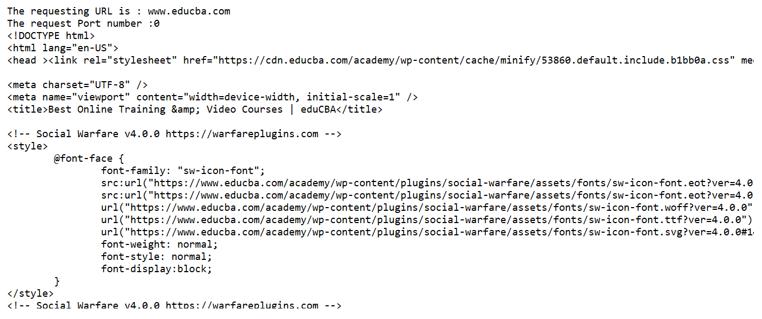
System.out.println("The request Port number :" + hostname);
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] arg)
{ String data;
try {
//create object of authenticator class
MyAuthenticatorclass obj =new MyAuthenticatorclass();
Authenticator.setDefault(new MyAuthenticatorclass());
URL url = new URL("https://www.educba.com/");
// reads data from the url in html form
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream()));
System.out.println("The requesting URL is : "+url.getHost());
obj.getPasswordAuthentication() ;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(data);
}
br.close();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
System.out.println("Malformed URL Exception : " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO Exception: " + e);
}
}
}Output:
Next, we write the java code to understand the Authenticator class where we try to get all information in the overridden getPasswordAuthentication() function, as below –
Example #2
Code:
package p1;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Authenticator;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.PasswordAuthentication;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
class MyAuthenticatorclass extends Authenticator
{
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication()
{
String username = "John", password = "pass123";
this.print();
return new PasswordAuthentication(username, password.toCharArray());
}
void print()
{
// get all information
String prom = getRequestingPrompt();
URL url = getRequestingURL();
int prt = getRequestingPort();
String hostname = getRequestingHost();
InetAddress ipaddress = getRequestingSite();
String sh = getRequestingScheme();
RequestorType rt = getRequestorType();
String protocol = getRequestingProtocol();
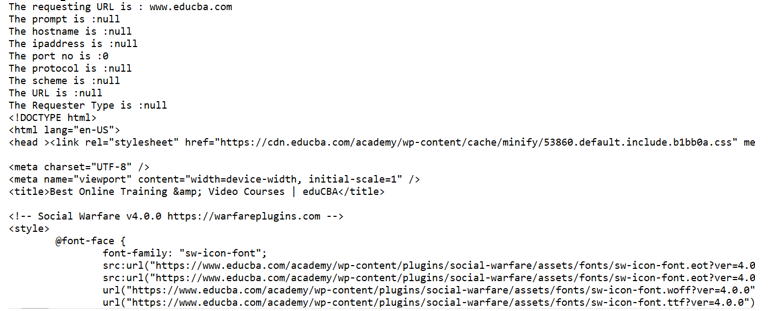
System.out.println("The prompt is :" + prom+"\nThe hostname is :" + hostname+"\nThe ipaddress is :" + ipaddress+"\nThe port no is :" + prt);
System.out.println("The protocol is :" + protocol+"\nThe scheme is :" + sh+"\nThe URL is :" + url+"\nThe Requester Type is :" + rt);
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] arg)
{ String data;
try {
//create object of authenticator class
MyAuthenticatorclass obj =new MyAuthenticatorclass();
Authenticator.setDefault(new MyAuthenticatorclass());
URL url = new URL("https://www.educba.com/");
// reads data from the url in html form
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream()));
System.out.println("The requesting URL is : "+url.getHost());
obj.getPasswordAuthentication() ;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(data);
}
br.close();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
System.out.println("Malformed URL Exception : " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO Exception: " + e);
}
}
}Output:
The above code is trying to get all information related to authentication.
Conclusion
The java authenticator class is a built-in java class that is used to handle URL or network connection authentication. As we’ve seen, this built-in class has ten functions that can each be utilized for a specific purpose.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Authenticator” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.