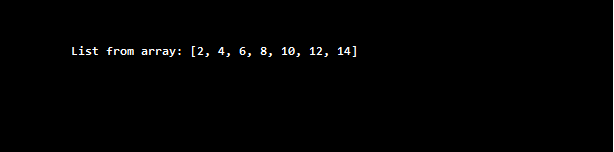Updated April 7, 2023

Introduction to Java Collection to List
Java Collection to List means conversion of Collection to List. Converting Java Collections from one type to another type is a common task in programming. Collection is a data structure that contains, and processes a set of data. Collection framework consists of many interfaces such as Set, Queue, Dequeue, List, and classes such as ArrayList, Vector, Linked List, Priority Queue, Tree Set, Hash Set, Linked Hash Set. Data that is stored in Collection is encapsulated and accessing this data is only accessible via some predefined methods. In this tutorial, we will see the conversion of Collection to an Array List.
Syntax:
Here is the syntax used for converting Java Collection to List.
List<Integer> intVal = values.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());Java Collection must get parameterized with the type declaration. It enables the Java compiler to check if the user tries to use collection with the correct type of objects.
Examples of Java Collection to List
Let us look at few examples which will give an insight into the conversion of Collections.
Example #1
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionToArrayList{
public static void main(String[] args){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("eduCBA ");
list.add("is ");
list.add("best ");
list.add("platform ");
list.add("for ");
list.add("Web ");
list.add("Development ");
list.add("course. ");
String[] s = list.toArray(new String[0]);
for(int i = 0; i< s.length; ++i) {
String data = s[i];
System.out.print(data);
}
}
}Output:
So here we are using one of the Collection frameworks to convert data to a list.
As the Collection framework includes List, Queue, Set, etc. we shall convert the array to a list similar to how we convert a list to an array.
Example #2: Using asList
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Integer[] evenArray = { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
List<Integer> evemList = Arrays.asList(evenArray);
System.out.println("List from array: " + evemList);
}
}Output:
So basically, we have our traditional way of converting array collection to list. But here we are using another method of conversion by using the asList method of the Array class.
Here we are using an array of even numbers, list of integers is created and assigned to output using the asList method of the Array class.
Example #3: Using Collections.addAll() method
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
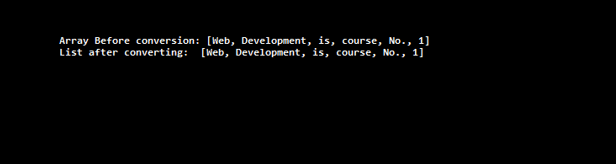
String stringArr[] = { "Web", "Development", "is", "course", "No.", "1" };
System.out.println("Array Before conversion: " + Arrays.toString(stringArr));
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(strList, stringArr);
System.out.println("List after converting: " + strList);
}
}Output:
So, here we are using addAll() method of Collection class as the array and the list are both parts of the collection framework. We initialized an empty array and created an empty list. Collections.addAll() method is used to pass lists and array as arguments. Similar to the way in which Array, one of the Collections was converted to List, we shall see How a Set, a Collection will be converted to List.
Example #4: Using Plain Java
Code:
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> HashSet = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet.add("Mango");
HashSet.add("Apple");
HashSet.add("Orange");
HashSet.add("Jamun");
HashSet.add("Pine");
HashSet.add("Kiwi");
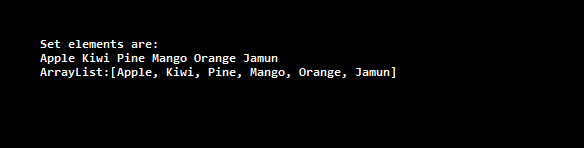
System.out.println("Set elements are: ");
for (String i : HashSet)
System.out.print(i + " ");
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>(HashSet.size());
for (String i : HashSet)
stringList.add(i);
System.out.println("\nArrayList:" + stringList);
}
}Output:
Here we declare and initialize a set, then create list and get set elements added to list.
Example #5: Using Constructor
Code:
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> HashSet = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet.add("Mango");
HashSet.add("Apple");
HashSet.add("Orange");
HashSet.add("Jamun");
HashSet.add("Pine");
HashSet.add("Kiwi");
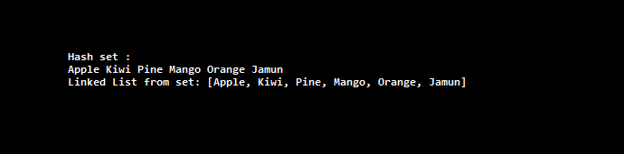
System.out.println("Hash set :");
for(String string: HashSet)
System.out.print(string + " ");
List<String> lList = new LinkedList<String>(HashSet);
System.out.println ("\nLinked List from set: " + lList);
}
}Output:
So the above example is another way of Converting Hash set, Collection to list using constructor. We have used the same Hash set above too, and using list constructor with the set object as an argument. It copies all set elements to list objects.
Example #6: Using Java 8 stream
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> HashSet = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet.add("Mango");
HashSet.add("Apple");
HashSet.add("Orange");
HashSet.add("Jamun");
HashSet.add("Pine");
HashSet.add("Kiwi");
System.out.println("The Hash set:");
for(String string : HashSet)
System.out.print(string + " ");
List<String> stringList = HashSet.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("\nList converted: " + stringList);
}
}Output:
Here, we are using Java 8 stream and collect method to convert Hash Set into the list.
With this, we shall conclude the topic ‘Java Collection to List’. We have seen a general syntax for converting Collection to list. We have seen How Conversion of collections, including Array, Set, etc. are converted to List. Implemented few examples of Conversion of Array and Set to List by various methods, such as using addAll() method, Java 8 stream, general Java class, asList() methods. There are many other Collections in Java that can be converted to List. Thanks! Happy Learning!!
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Collection to List. Here we discuss the Introduction, syntax, conversion of Collection to an Array List, examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –