Introduction to Java Parse String
Parsing String in java is known as converting data in the String format from a file, user input, or a certain network. Parsing String is the process of getting information that is needed in the String format. String parsing in java can be done by using a wrapper class. Using the Split method, a String can be converted to an array by passing the delimiter to the split method. The split method is one of the methods of the wrapper class.
String parsing can also be done through StringTokenizer. StringTokenizer class allows its constructor to break the String into tokens. StringTokenizer is much simpler than other classes. StringTokenizer is a legacy class, so everyone must avoid the use of this class.
Syntax:
String strMsg = "An Example of String";
String delims = "[delimiters]+";
String tokenString = strMsg.split(delims);In the above syntax, multiple delimiter can be used inside the square brackets. “+” sign after bracket treats multiple delimiter as a single delimiter.
Initialization of Parse String
In java, a String can be converted into char, Object, int, date, time, etc. String parsing is initialized by a certain java class method as per the data type is required.
Example #1
In this example, we can see how String is parsing into different types of formats like date & integer. Similarly, we can use other methods to convert a string into other formats.
Code:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class StringParsingInDiffTypeExample {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
System.out.println("String parsing into Date Oject : \n");
String strDate1 = "12/01/2020";
String strDate2 = "12-Jan-2020";
String strDate3 = "Sun, Jan 12 2020";
//converting date format into the date object here
SimpleDateFormat strFormat1 = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
SimpleDateFormat strFormat2 = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MMM-yyyy");
SimpleDateFormat strFormat3 = new SimpleDateFormat("E, MMM dd yyyy");
//date retrieving here after parsing through parse method
Date dateObj1 = strFormat1.parse(strDate1);
Date dateObj2 = strFormat2.parse(strDate2);
Date dateObj3 = strFormat3.parse(strDate3);
//printing here the date as a char
System.out.println("Date String 1 = " + strDate1 + "\t Date Object 1 = " + dateObj1);
System.out.println("Date String 2 = " + strDate2 + "\t Date Object 2 = " + dateObj2);
System.out.println("Date String 3 = " + strDate3 + "\t Date String 3 = " + dateObj3);
System.out.println("\n\nString parsing into integer : \n");
String strVal1 = "50";
String strVal2 = "1000";
String strVal3 = "20000";
//Converting String into int using parseInt()
int intValue1 = Integer.parseInt(strVal1);
int intValue2 = Integer.parseInt(strVal2);
int intValue3 = Integer.parseInt(strVal3);
//Printing integer value
System.out.println(intValue1);
System.out.println(intValue2);
System.out.println(intValue3);
}
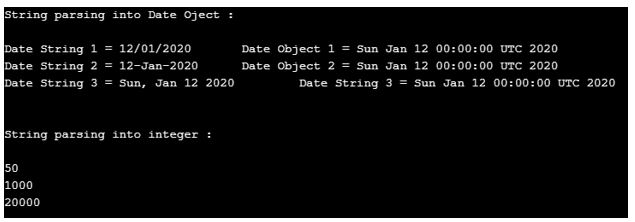
}Output:
Output for the above-given program is given below; we can see how String is converted into different data type by using different methods.
Example #2
In this example, using the split method for parsing of the string to array format.
Code:
public class SplitMethodExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("String Parsing Example #1 :\n");
//In this example one space character is used as a delimiter
String str1 = new String("Nothing is impossible in the world!");
String delimSpace = " ";
String[] arr1 = str1.split(delimSpace);
for (String uniqVal1 : arr1) {
System.out.println(uniqVal1);
}
System.out.println("\n\nString Parsing Example #2 :\n");
//In this example a comma is used as a delimiter
String str2 = new String("Alabama,California,texas,30,78");
String delimsComma = "[,]+";
String[] arr2 = str2.split(delimsComma);
for (String uniqVal2 : arr2) {
System.out.println(uniqVal2);
}
System.out.println("\n\nString Parsing Example #3 :\n");
//In this example multiple delimiter is used used as a delimiter
String str3 = new String("Many of the people always say without thinking ,do you know ?Possibly Not!");
String delims = "[.,?!]+";
String[] arr3 = str3.split(delims);
for (String uniqVal3 : arr3) {
System.out.println(uniqVal3);
}
}
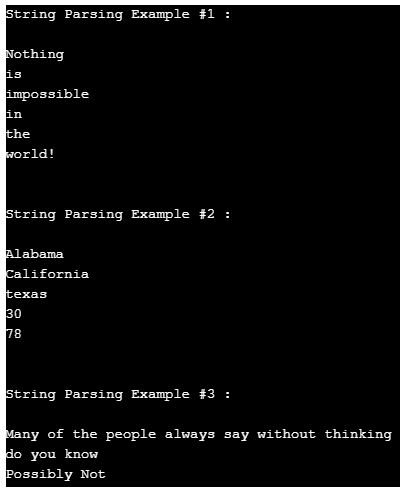
}Output:
The above given an example contains three sections, all the three-section using the different delimiter for parsing the String. In the below-given screenshot, we can see the output of the above-given program.
Example #3
In this example, the StringTokenizer class is used for parsing. The StringTokenizer class’s constructor takes two parameters: the first one is the string & the second one is the delimiter. This class contains some methods, i.e. hasMoreElements() to check whether the next index holding any value or not while nextElement() returns the value at the next index.
Code:
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class StringTokenizerParsingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("StringTokenizer Parsing Example: \n");
String strText = "Kansas,Louisiana,Maryland,Massachusetts,Mississippi,New Jersey";
String delims = ",";
StringTokenizer stObj = new StringTokenizer(strText, delims);
//Iterating here for the next element
while (stObj.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println("StringTokenizer Output: " + stObj.nextElement());
}
}
}Output:
The above parsing output is given below; we can see how comma-separated values are listed in the next column.
Example #4
This example shows how the indexOf method can be used effectively to parse any String in java. In this program, a String in the middle of the sentence is being converted to uppercase.
Code:
public class StringParsingExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
String strPara = "The Paragraph needs additional citations for [verification]";
int openIndex = strPara.indexOf("[");
int closedIndex = strPara.indexOf("]");
// extracting here the String inside of the square bracket
String subString = strPara.substring(openIndex+1, closedIndex);
//converting substring in the uppercase which is inside of
subString= subString.toUpperCase();
// concating here all the substrings
String modifiedPara = strPara.substring(0, openIndex + 1) + subString + strPara.substring(closedIndex);
System.out.println(modifiedPara);
}
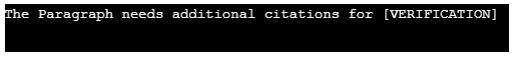
}Output: Output of the above-given program is given below.
Example #5
In this example, we can see how a string is converted into an array of chars.
Code:
public class StringParsingCharExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String strText = "Australia";
char[] charArr = strText.toCharArray();
System.out.println(charArr.length);
char secondPosChar = strText.charAt(2);
System.out.println(secondPosChar);
char[] charSet = new char[9];
strText.getChars(0, 9, charSet, 0);
for (char uniqChar : charSet) {
System.out.println(uniqChar);
}
}
}Output:
The Output for the above-given program is given below.
In the attached output screenshot, we can see how a String is converted into an array of characters by using methods toCharArray().
Trouble understanding the code? You can take Java programming assistance from Java experts online and excel in your coding journey.
Conclusion – Java Parse String
In the above-given article, we have gone through the parsing, String parsing in Java, etc. How the split method plays a role in parsing the data type. Some other ways are also available which can be used for parsing, such as StringTokenizer. If you’re looking to deepen your understanding or need assistance, platforms offering Java Assignment Help can provide valuable support for mastering these concepts.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Java Parse String. Here we discuss the syntax and initialization of the Java Parse String. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –