Updated March 30, 2023
Introduction to Java Pop
In Java, the pop is a method that removes elements in the stack, array, LinkedList, etc. An element can be removed from the stack using the Stack.pop() method, and it will be removed from the top. In the case of LinkedList, LinkedListObject.pop() method is used to remove from the top of the stack denoted by LinkedList. LinkedBlockingDeque.pop()method in ArrayDequere moves the element from the top of the Deque. More details on each of them will be discussed in the following sections.
Syntax
Let us see the syntax of the pop method in a stack, LinkedList, and Deque.
1. Stack
Syntax:
STACK.pop()Parameters: No parameters for this method.
Return Value: Returns the element and removes it from the top of the stack.
2. LinkedListObject
Syntax:
LinkedListObject.pop()Parameters: No parameters for this method.
Return Type: Returns the element and removes it from the top of the stack.
3. LinkedBlockingDeque
Syntax:
LinkedBlockingDeque.pop()Parameters: No parameters for this method.
Return Value: Returns the element and removes it from the top of the stack.
How does the pop method work in Java?
The pop method works similarly in Stack, LinkedList, and Deque. The following steps can be performed for that.
1. Create a stack, LinkedList, or Deque based on the requirement.
Stack<String>s = new Stack<String>( );
LinkedList<Integer>li = newLinkedList<>( );
LinkedBlockingDeque<String> li = new LinkedBlockingDeque<String>(capacity);2. Remove elements from it using the pop method.
s.pop()
li.pop()
dq.pop()Examples of Java Pop
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Java program to pop elements of string type from a stack.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class PopMethodExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create a stack
Stack<String> st = new Stack<String>();
st.push("Happy");
st.push("Sad");
st.push("Confused");
st.push("Tensed");
st.push("Mixed Emotions");
// Print elements in stack
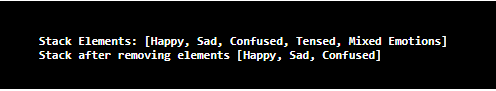
System.out.println("Stack Elements: " + st );
// Pop elements
st.pop();
st.pop();
// Stack after removing new elements
System.out.println("Stack after removing elements " + st);
}
}Output:
First, create a stack s and add elements using the push() method. Then, print the stack and remove the elements using the pop() method. As there is two pop() methods are called, two elements from the top of the stack will be removed on executing the code. At last, the stack after removing elements gets printed.
Example #2
Java program to pop elements of integer type from LinkedList.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class PopMethodExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create a LinkedList
LinkedList<Integer> lis = new LinkedList<>();
lis.push(45);
lis.push(90);
lis.push(67);
lis.push(33);
lis.push(56);
// Print elements in LinkedList
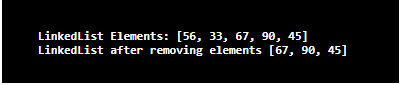
System.out.println("LinkedList Elements: " + lis);
// Pop elements
lis.pop();
lis.pop();
// LinkedList after removing elements
System.out.println("LinkedList after removing elements " + lis);
}
}Output:
Create a LinkedListlisand add elements of integer type using the push() method. Then, print the LinkedListand remove the elements using the pop() method. On executing the code, LinkedList before removing elements and after removing elements can be displayed.
Example #3
Java program to remove integer elements from the stack.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class PopMethodExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create a stack
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
st.push(45);
st.push(90);
st.push(67);
st.push(33);
st.push(56);
// Print elements in stack
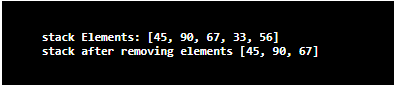
System.out.println("stack Elements: " + st);
// Pop elements
st.pop();
st.pop();
// stack after removing elements
System.out.println("stack after removing elements " + st);
}
}Output:
A stack to accept integer elements is created first. Once it is created, elements are added to the stack using the push() method. After printing the current elements in the stack, two elements are removed from it. For checking whether those elements are from the stack, elements are printed one more time. On executing the code, it can be seen that two elements are removed from the stack.
Example #4
Java program to remove string elements from the LinkedList.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class PopMethodExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create a LinkedList
LinkedList<String> lis = new LinkedList<>();
lis.push("Happy");
lis.push("Sad");
lis.push("Confused");
lis.push("Tensed");
lis.push("Mixed Emotions");
// Print elements in LinkedList
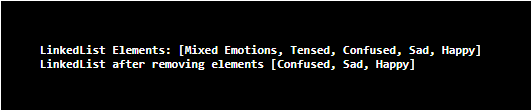
System.out.println("LinkedList Elements: " + lis );
// Pop elements
lis.pop() ;
lis.pop() ;
// LinkedList after removing elements
System.out.println("LinkedList after removing elements " + lis ) ;
}
}Output:
Create a LinkedList li and add elements of string type using the push() method. Then, print the LinkedListand remove the elements using the pop() method. On executing the code, LinkedList before removing elements and after removing elements can be displayed.
Example #5
Java program to remove string elements fromLinkedBlockigDeque.
Code:
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class PopMethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<String> dq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<String>(100);
dq.add("Hia");
dq.add("Ahi");
dq.add("Liba");
dq.add("Geru");
//Removes element from the top of the stack
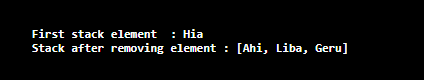
String s = dq.pop();
System.out.println("First stack element : "+ s);
System.out.println("Stack after removing element : "+ dq);
}
}Output:
Create a deque for adding the elements. For that, use the method add() and add the elements of string type. Then, print the Deque and identify the current elements present in it. After printing the current elements in the stack, remove the first element from the stack. For checking whether those elements are removed from the Deque, elements are printed one more time. On executing the code, it can be seen that one element is removed from the Deque.
Example #6
Java program to remove integer elements from LinkedBlockigDeque.
Code:
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class PopMethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer> dq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>(100);
dq.add(34);
dq.add(45);
dq.add(56);
//Removes element from the top of the stack
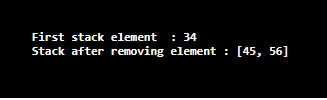
Integer i = dq.pop();
System.out.println("First stack element : "+ i );
System.out.println("Stack after removing element : "+ dq);
}
}Output:
Unlike the above program, elements of integer type are added using add() method. On executing the code, it can be seen that one element is removed from the Deque.
Conclusion
Pop is a method that is used to remove elements from the stack, LinkedList, array with the help of Stack.pop(), LinkedList.pop() and LinkedBlockingDeque.pop() respectively. In this article, details such as syntax, working, and example of the pop method is explained in detail.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Pop. Here we discuss how the pop method works in Java and Examples along with the codes and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –