Introduction to Java String getBytes
getBytes() method in Java is defined as “converting the string into a byte of array”. getBytes() method returns byte[] array. getBytes() method in Java is applied with Strings only. Every string value in a byte array is converted into its equivalent ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) values. We can say it is an encoded form of the data to protect from unknown actions on the data.
Real-time Application: When we want to convert the string into a byte array, then the getBytes() method comes into the picture.
How does getBytes() work in Java?
Java getBytes() method works are based on string values in 3 ways:
- public byte[] getBytes()
Syntax:
String str="Some String";
Byte[] byteArray=Str.getBytes();- public byte[] getBytes(String string) throws UnsupportedEncodingException. The standard supporting Charset in the java application are mentioned below:
- US-ASCII: It is 7-bit ASCII characters.
- ISO-8859-1: It is ISO (Indian Standard Organization) Latin-alphabet.
- UTF-8: It is an 8-bit Universal Coded Character Set format.
- UTF-16BE: This is a 16-bit Universal Coded Character Set format by big-endian order.
- UTF-16LE: This is 16-bit Universal Coded Character Set by little-endian order.
- UTF-16: 16-bit Universal Coded Character Set format.
Syntax:
String str=”UTF-16”;
Byte[] byteArray=Str.getBytes();- public byte[] getBytes(Charset characterSet)
Syntax:
Byte[] byteArray=Str.getBytes(“ASCII”);Examples of Java String getBytes
Given below are the examples of Java String getBytes:
Example #1
public byte[] getBytes()
Code:
package com.getbytes;
public class GetBytesOfNames {
public static void main(String args[]) {
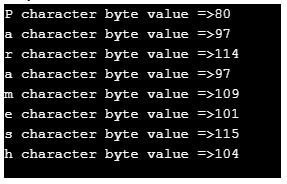
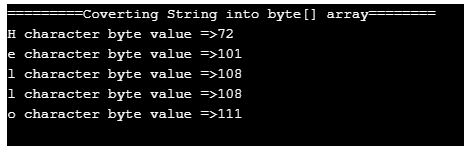
String name = "Paramesh"; /// defining a string
byte[] nameByteArray = name.getBytes(); // converting string into byte array
for (int i = 0; i < nameByteArray.length; i++) {// iterating byte array values
System.out.println(name.charAt(i) + " character byte value =>" + nameByteArray[i]);// displaying values
}
}
}Output:
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output corresponding character gives its equivalent ASCII code by applying the getBytes() method.
Example #2
public byte[] getBytes()
Code:
package com.getbytes;
public class GetBytesOfSpaceValues{
public static void main(String args[]) {
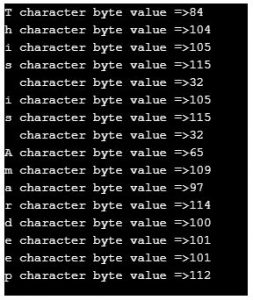
String name = "This is Amardeep"; /// defining a string
byte[] nameByteArray = name.getBytes(); // converting string into byte array
for (int i = 0; i < nameByteArray.length; i++) {// iterating byte array values
System.out.println(name.charAt(i) + " character byte value =>" + nameByteArray[i]);// displaying values
}
}
}Output:
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output corresponding character gives its equivalent ASCII code by applying the getBytes() method.
- Even space also has an ASCII value.
Example #3
public byte[] getBytes(String string)
Code:
package com.getbytes;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class GetBytesString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
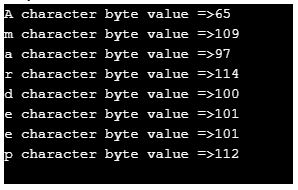
String name = "Amardeep"; // defining a string
byte[] nameByteArray;
try {
nameByteArray = name.getBytes("UTF-8");
for (int i = 0; i < nameByteArray.length; i++) {// iterating byte array values
System.out.println(name.charAt(i) + " character byte value =>" + nameByteArray[i]);// displaying values
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} // converting string into byte array
}
}Output:
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output corresponding character gives its equivalent UTF-8 code by applying the getBytes() method.
Example #4
public byte[] getBytes(String string)
Code:
package com.getbytes;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class GetBytesOfNames {
public static void main(String args[]) {
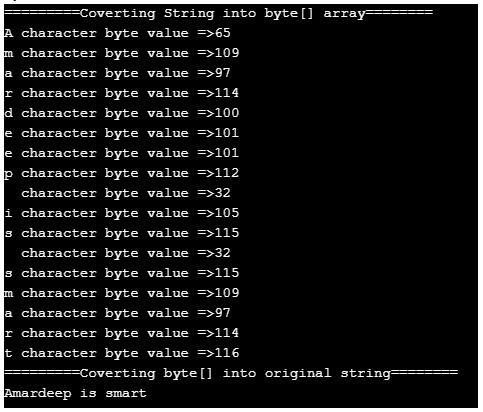
String name = "Amardeep is smart"; // defining a string
byte[] nameByteArray;
try {
nameByteArray = name.getBytes("UTF-8");
System.out.println("=========Coverting String into byte[] array========");
for (int i = 0; i < nameByteArray.length; i++) {// iterating byte array values
System.out.println(name.charAt(i) + " character byte value =>" + nameByteArray[i]);// displaying values
}
String string=new String(nameByteArray);//converting byte array into string
System.out.println("=========Coverting byte[] into original string========");
System.out.println(string);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} // converting string into byte arrayOutput:
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output corresponding character gives its equivalent UTF-8 code by applying the getBytes() method.
- UTF-8-byte array again converted into the original string. It concludes original information can’t be lost.
Example #5
public byte[] getBytes(Charset characterSet)
Code:
package com.getbytes;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class GetBytesCharSet {
public static void main(String args[]) {
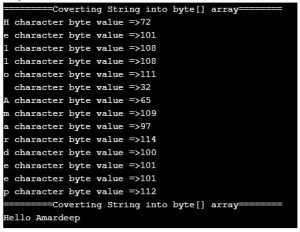
String name = "Hello"; // defining a string
byte[] nameByteArray = name.getBytes(Charset.forName("ASCII"));
System.out.println("=========Coverting String into byte[] array========");
for (int i = 0; i < nameByteArray.length; i++) {// iterating byte array values
System.out.println(name.charAt(i) + " character byte value =>" + nameByteArray[i]);// displaying values
}
}
}Output:
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output corresponding character gives its equivalent ASCII code by applying the getBytes() method.
Example #6
public byte[] getBytes(Charset characterSet)
Code:
package com.getbytes;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class GetBytesOfCharSetAndString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String name = "Hello Amardeep"; // defining a string
byte[] nameByteArray = name.getBytes(Charset.forName("ASCII"));
System.out.println("=========Coverting String into byte[] array========");
for (int i = 0; i < nameByteArray.length; i++) {// iterating byte array values
System.out.println(name.charAt(i) + " character byte value =>" + nameByteArray[i]);// displaying values
}
String string=new String(nameByteArray);
System.out.println("=========Coverting String into byte[] array========");
System.out.println(string);
}
}Output:
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output corresponding character gives its equivalent ASCII code by applying the getBytes() method.
- ASCII code byte array again converted into the original string. It concludes original information can’t be lost.
Conclusion
String can be converted into its equivalent ASCII code, UTF code, ISO code based on getBytes(), getBytes(String string) and getBytes(Charset characterSet).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java String getBytes. Here we discuss the basic concept, examples, and how does getBytes() work in Java along with different examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –