Updated July 10, 2023

Introduction to Java Swing Button
Whenever the user clicks the button, it triggers the click event and invokes the corresponding method in Java Swing Button. The Java Swing application commonly uses the component to trigger events or actions and submit forms. In Java, the button class uses JButton abstract class. This abstract class AbstractButton extends the JComponent class. We can instantiate many button types by using classes that descend from AbstractButton.
Different types of buttons, which are subclasses of AbstractButton, are as follows:
- Common Button: It is created using the class JButton, and the type of event triggered by this button is ActionEvent.
- ToggleButton: It is used to toggle between true or false values.
- CheckBox: It is used to generate an event called ItemEvent.
- RadioButton: It is also used to generate an event called ItemEvent.
How class is declared for javax.swing.JButton :
class JButton extends AbstractButton implements Accessible{}Constructors and Methods of Java Swing Button
Here we will discuss the constructors and methods of the Java swing button:
Constructors
We use constructors to instantiate objects for the JButton class.
- JButton(): Creates and instantiates a button having no set text or icon.
- JButton(Event e): Create and instantiate a button with the supplied event and properties from the provided action.
- JButton(String s): Creates and instantiates a button with text with string s as provided.
- JButton(Icon i): Creates and instantiates a button with an icon i as provided.
- JButton(String s, Icon i): Creates and instantiates a button with initial text as a string and an icon provided, respectively.
Methods
Common methods used for JButton:
- void setText(String s): Sets the provided text to a button created.
- String getText(): Gets the text on the button.
- void setAction(Action a): Sets the button properties according to the action provided.
- Action getAction(): Gets the button properties concerning the action presented in it.
- void setIcon(Icon i): Sets the icon or image the button displays when not pressed. To set an icon on a pressed button, use void setPressedIcon(Icon i)
- Icon getIcon(): The button displays the icon when it is not pressed or selected. To get an icon from a pressed or selected button, use Icon getPressedIcon().
- void addActionListener(ActionListener a): Adds the objects that listen to the action events generated by the button.
- ActionListener removeActionListener(): Removes the objects that listen to the action events generated by the button.
- void addActionListener(ActionListener a): Adds the objects that listen to the action events generated by the button.
- ActionListener removeActionListener(): Removes the objects that listen to the action events generated by the button. Sets the objects that listen to the actions generated by the button. Fine Tuning the JButton appearance:
- void addItemListener(ItemListener a): Adds the objects that listen to the item events generated by the button.
- ItemListener removeItemListener(): Removes the objects that listen to the item events generated by the button.
- void setSelected(boolean): Set the button to selected or pressed mode.
- boolean isSelected(): We obtain the button’s value, whether selected or not. AbstractButton provides methods to align an icon’s and text’s positions on the button.
- void setHorizontalAlignment(int alignment): Sets the horizontal alignment of icon and text. AbstractButton’s default is SwingConstants.CENTER.
Some of the other alignments that can be provided:
-
- SwingConstants.RIGHT
- SwingConstants.LEFT
- SwingConstants.LEADING
- SwingConstants.TRAILING
void setVerticalAlignment(int alignment):
-
- Sets the vertical alignment of icons and text.
- Some of the other alignments that can be provided:
- SwingConstants.TOP
- SwingConstants.BOTTOM
- SwingConstants.CENTER(default)
- int getHorizontalAlignment(): It returns the horizontal alignment of the icon and text.
- int getVerticalAlignment() returns the vertical alignment of the icon and text.
Void setHorizontalTextPosition(int) and void setVerticalTextPosition(int): Used to set the horizontal and vertical position of the button. For horizontal, the positions are: RIGHT, LEFT, LEADING, TRAILING(default), CENTER. For vertical, the positions are TOP, CENTER (the default), and BOTTOM.
- int getHorizontalTextPosition() and int getVerticalTextPosition(): We obtained the horizontal and vertical position of the button.
Examples of Java Swing Button
Given below are the examples:
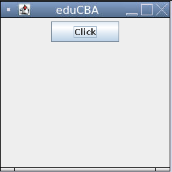
Example #1 – Simple JButton Code
Code:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main {
Main(){
JFrame newFrame=new JFrame("eduCBA");
// Creating Button
JButton b=new JButton("Click");
b.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(100,30));
newFrame.add(b);
newFrame.setSize(250,250);
newFrame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
newFrame.setVisible(true);
newFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main();
}
}Output:
Example #2 – Adding an image to the button
Code:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class JButtonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame=new JFrame("Button Example");
JButton b=new JButton(new ImageIcon("C:\\custom.png"));
frame.add(b);
frame.setSize(500,500);
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Swing Button” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.