Updated July 5, 2023

Definition of JavaFX Animation
In JavaFX, by altering the property by time, animation can be done to a particular node. For this, a package javafx.animation is provided by JavaFX. It consists of classes that help in animating the nodes. For all these classes, the animation is considered the base class. There are different animations like Fill Transition, Scale Transition, Fade Transition, Stroke Transition, Rotate Transition, Sequential Transition, etc in this. In this article, we will see more in animation.
Constructors
Below are the two constructors of animation in JavaFX.
- Animation()
- Animation(double targetFramerate)
Methods
Following are the methods of animation in JavaFX.
- autoReverseProperty(): This property defines whether, on alternating cycles, animation reverses the direction or not.
- currentRateProperty(): This is a read-only variable that denotes the current direction or current speed at which the animation has to be played.
- currentTimeProperty(): This property defines the play head position of the animation.
- cycleCountProperty(): This property defines the count of cycles of animation.
- cycleDurationProperty(): This is a read-only variable that denotes the cycle duration of the animation that has to be played.
- delayProperty(): This property delays the animation.
- getCuePoints(): Retrieves the cue points that mark important positions within the animation.
- getCurrentRate(): Retrieves the value of the currentRate property, indicating the current playback rate of the animation.
- getCurrentTime(): Retrieves the value of the currentTime property, representing the current position within the animation timeline.
- getCycleCount(): Retrieves the value of the cycleCount property, indicating the number of cycles the animation will perform.
- getCycleDuration(): Retrieves the value of the cycleDuration property, representing the duration of each cycle in the animation.
- getDelay(): Retrieves the value of the delay property, indicating the delay before the animation starts.
- getRate(): Retrieves the value of the rate property, indicating the playback rate of the animation.
- getStatus(): Retrieves the value of the status property, indicating the current status of the animation.
- getTotalDuration(): Retrieves the value of the totalDuration property, representing the total duration of the animation, including all cycles.
- isAutoReverse(): Retrieves the value of the autoReverse property, indicating whether the animation will play in reverse after each cycle.
- jumpTo(Durationtime): This method helps in jumping to the animation’s specific position.
- jumpTo(StringcuePoint): This method helps in jumping to the animation’s predefined position.
- pause(): This method pauses the animation.
- play(): This method plays the animation from the present position in a direction denoted by rate.
- playFromStart(): This method plays the animation from the position which is initial and moves in a forward direction.
- setOnFinished(EventHandler<ActionEvent> v): OnFinished property’s value will be set as v.
- statusProperty(): Animation starts.
- onFinishedProperty(): This property explains the action that has to be executed at the animation conclusion.
- rateProperty(): This property defines the direction or speed of playing the animation.
- totalDurationProperty(): This is a read-only variable that denotes the cycle duration of animation that has to be played, including the repeats.
How to Create Animation in JavaFX?
- First, a node that is required is created using a corresponding class.
- Once this is done, configure the properties.
Rectangle rt = new Rectangle(136,112,112,112);
r.setFill(Color.YELLOW);- Instantiate the corresponding transition class or animation class, which has to be applied
RotateTransition r = new RotateTransition();- Set the transition properties such as cycle count and duration.
r.setDuration(Duration.millis(2000));
r.setAxis(Rotate.Y_Axis);
r.setCycleCount(600);- Fix the target node where the transition has to be applied.
r.setnode(rt);- Play the transition with the help of play() method
r.play();Examples of JavaFX Animation
Now, we will see a sample program on JavaFX animation.
Example #1
Code:
JavaFX program to demonstrate animation.
Code:
import javafx.animation.RotateTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Polygon;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
//main class
public class AnimationSamplePorogram extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage st) {
//create a hexagon
Polygon hx = new Polygon();
//Add coordinates to the created hexagon
hx.getPoints().addAll(new Double[]{
220.0, 60.0,
420.0, 60.0,
430.0, 160.0,
430.0, 260.0,
230.0, 260.0,
180.0, 160.0,
});
//fill color for the created hexagon
hx.setFill(Color.YELLOW);
//rotate transitioncreation
RotateTransition rt = new RotateTransition();
//Set the duration for the rotate transition created
rt.setDuration(Duration.millis(2000));
//Set the node for the rotate transition created
rt.setNode(hx);
//Set the angle of the rotate transition created
rt.setByAngle(360);
//Set the cycle count for rotate transition created
rt.setCycleCount(60);
//Set false as the auto reverse value
rt.setAutoReverse(false);
//start playing the animation
rt.play();
//Create a Group object
Group g = new Group(hx);
//Create a scene object
Scene sc = new Scene(g, 600, 300);
//Set title of the Stage st
st.setTitle("Animation example ");
//Add scene to the stage st
st.setScene(sc);
//Display the contents of the stage st
st.show();
}
//main method
public static void main(String args[]){
//launches the application
launch(args);
}
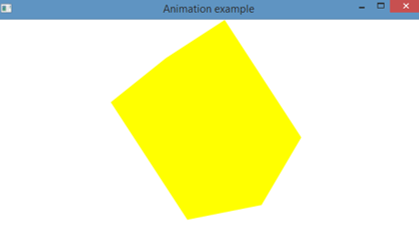
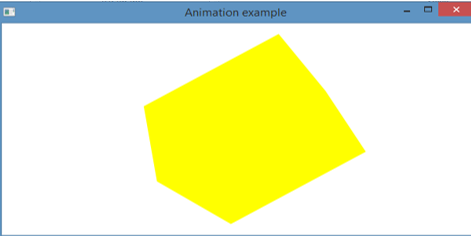
}Output:
First, import all the necessary packages. Then, create a hexagon and add coordinates to the created hexagon. After this, fill color for the created hexagon. Moreover, set the node, angle, and cycle count also for the rotate transition created. Then, set false as the auto-reverse value and start playing the animation using the play() method. Next is to create a Group object and a scene object. Also, set the title for the created stage and add a scene to it. After this, display the contents of the stage st using the method show().
On executing the code, it can be seen that a hexagon of yellow color is rotating 360 degrees. This rotation will be for around 2000 seconds. The screenshots provided are taken two times for showing that the hexagon is rotating.
Conclusion
In JavaFX, the package “javafx.animation” is utilized to incorporate animation functionality. This package includes classes that assist in animating nodes within a JavaFX application. It offers various types of animations, such as Fill Transition and Scale Transition, which can be utilized to create dynamic visual effects.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JavaFX Animation. Here we discuss Definitions, methods, How to create animation in JavaFX? and examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –