Updated April 12, 2023
Definition of JavaFX dialog
In JavaFX, a dialog wraps down a DialogPane and offers the required API to give it to end-users. This class has one generic type, R, that denotes the result property type. A dialog can be organized for adding content, adding buttons, setting modality, and state the blocking as well as non-blocking behavior of the dialog. Several properties can be gain access to and set by the API of the dialog– header text, title, content text, width/height, location, resizable, and the content graphic or header graphic.
Let us see more on the JavaFX dialog in the below sections:
Syntax:
Below is the syntax used for JavaFX dialog.
Dialog<String> dg = new Dialog<String>();Constructors
Following is the constructor of JavaFX dialog.
- Dialog(): A dialog will be created without an identified owner.
Methods of JavaFX dialog
Below are the common methods used in JavaFX dialog.
- buildEventDispatchChain(EventDispatchChaintail): An Event Dispatch Chain will be constructed for the target.
- close(): Dialog will be hidden.
- contentTextProperty(): For the dialog, this property denotes a content text.
- getDialogPane(): dialogPane property’s value will be retrieved.
- dialogPaneProperty(): Dialog’s root node, the pane consists of all visual items depicted in the dialog.
- getGraphic(): graphic property’s value will be retrieved.
- getContentText(): currently-set text content will be returned for the dialog pane.
- getHeaderText(): currently-set header content will be returned for the dialog pane.
- getHeight(): Dialog’s height will be returned.
- getModality(): Dialog’s modality attribute will be returned.
- getOnCloseRequest(): onCloseRequest property’s value will be retrieved.
- getOnHidden(): onHidden property’s value will be retrieved.
- getOnHiding(): onHiding property’s value will be retrieved.
- getOnShowing(): onShowing property’s value will be retrieved.
- getOnShown(): onShown property’s value will be retrieved.
- getResult(): result property’s value will be retrieved.
- getResultConverter(): resultConverter property’s value will be retrieved.
- getX(): x property’s value will be retrieved.
- getY(): y property’s value will be retrieved.
- getOwner(): Dialog’s owner window will be retrieved or if unowned, null will be retrieved.
- getTitle(): Dialog’s title will be retrieved.
- getWidth(): Dialog’s width will be retrieved.
- hide(): Dialog will be closed.
- headerTextProperty(): Dialog pane’s header text will be represented by this property.
- heightProperty(): Dialog pane’s height will be represented by this property.
- initModality(Modalitymodality): Dialog’s modality will be specified.
- initOwner(Windowwindow): Dialog’s owner Window will be specified or if top-level unowned, null will be retrieved.
- initStyle(StageStylestyle): Dialog’s style will be specified.
- isResizable(): Dialog’s resize ability will be returned. That is, checks whether it is resizable or not.
- isShowing(): Dialog’s display ability will be returned. That is, checks whether it is shown or not.
- onCloseRequestProperty(): If there is an external request for closing the dialog is present, this property will be called.
- onHiddenProperty(): After dialog is hidden, this property will be called.
- onHidingProperty(): Before dialog is hidden, this property will be called.
- onShowingProperty(): Before dialog is shown, this property will be called.
- onShownProperty(): After dialog is shown, this property will be called.
- resizableProperty(): Dialog’s resize ability will be returned.
- resultProperty(): Dialog’s return value will be checked when this property is called.
- setContentText(StringcontentText): String that has to be displayed in the content area of the dialog will be set.
- setDialogPane(DialogPanevalue): Dialog pane’s value will be set by this property.
- setHeaderText(StringheaderText): String that has to be displayed in the header area of the dialog will be set.
- setHeight(double height): Dialog’s height will be set.
- setOnCloseRequest(EventHandler<DialogEvent> value): onCloseRequest property’s value will be set.
- setOnHidden(EventHandler<DialogEvent> value): onHidden property’s value will be set.
- setOnHiding(EventHandler<DialogEvent> value): onHiding property’s value will be set.
- setOnShowing(EventHandler<DialogEvent> value): onShowing property’s value will be set.
- setOnShown(EventHandler<DialogEvent> value): onShown property’s value will be set.
- setResizable(boolean resizable): dialog’s resize ability by the user will be set.
- setResult(Rvalue): result property’s value will be set.
- setResultConverter(Callback<ButtonType,R> value): resultConverter property’s value will be set.
- setX(double x): x property’s value will be set.
- setY(double y): y property’s value will be set.
- setTitle(Stringtitle): Dialog’s title will be set.
- setWidth(double width): Dialog’s width will be set.
- setGraphic(Nodegraphic): Dialog graphic will be set that will be shown in header if that is displaying or to the content left side.
- show(): Dialog will be shown but won’t wait for response of the user.
- showAndWait(): Dialog will be shown and wait for response of the user.
- showingProperty(): This property denotes whether the dialog is currently displaying.
- titleProperty(): Dialog’s title property will be returned.
- widthProperty(): Dialog’s width property will be returned.
- xProperty(): Dialog’s horizontal location.
- yProperty(): Dialog’s vertical location.
Example of JavaFX dialog
Let us see a sample program for creating a JavaFX dialog.
Code:
//JavaFX prorgram that demonstrates the dg
//import all necessary classes
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.ButtonBar.ButtonData;
import javafx.scene.control.ButtonType;
import javafx.scene.control.Dialog;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
//main class
public class DialogProgram extends Application {
//starts here...
@Override
public void start(Stage st)
{
//dialog creation
Dialog<String> dg = new Dialog<String>();
//set title
dg.setTitle("Sample dialog");
ButtonType bt = new ButtonType("Click", ButtonData.OK_DONE);
//Set dialog content
dg.setContentText("dialog sample for demo");
//To the dialog pane, add the buttons
dg.getDialogPane().getButtonTypes().add(bt);
//Set the label
Text tt = new Text("Please click on the button for displaying the dialog");
//set the font
Font fn = Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.ITALIC, 14);
tt.setFont(fn);
//Create a button
Button btn = new Button("Dialog display");
//Dialog display on button clicking
btn.setOnAction(e -> {
dg.showAndWait();
});
//create a hbox for holding button as well as label
HBox pn = new HBox(14);
//Set the space seperating the nodes of a pane
pn.setPadding(new Insets(60, 160, 60, 70));
//add children
pn.getChildren().addAll(tt, btn);
//Create a scene object
Scene sc = new Scene(new Group(pn), 596, 252, Color.RED);
//set the title
st.setTitle("Dialogg");
//set the scene
st.setScene(sc);
st.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}Output:
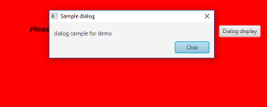
In this program, all the necessary classes are imported first. Then, a dialog is created and set the title. Once this is completed, buttons and events related to button clicking are also created. On executing the code, a button will be displayed as shown above. On clicking the button, a dialog appears as displayed below.
Conclusion
A dialog wraps down a DialogPane and offers the required API to give it to end-users. In this article, different aspects of dialog in JavaFX is explained in detail.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JavaFX dialog. Here we discuss the Definition, syntax, Constructor, Methods, and Example with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –