Updated July 10, 2023
Introduction of Job Costing
Job costing is a method of costing which relates to a small kind of work or task to be accomplished by the job worker, wherein all the direct costs associated with the completion of the specific job are accumulated to find out the applicable cost for that particular job & which the same is charged to the customer with a margin.
Explanation
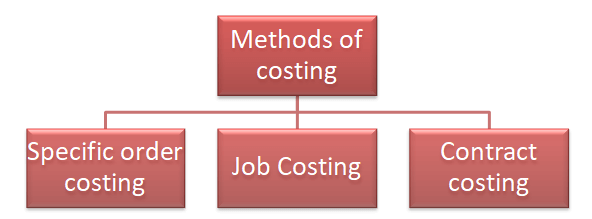
Job costing is a method of costing enumerated as follows:
- The basic difference between job costing & contract costing is that small tasks are performed in job costing & long-term contracts are performed in contract costing.
- Regarding our main topic, only directly attributable costs are relevant for job costing.
- As per CIMA (Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, London), job costing refers to customer-centric specific costing wherein costs are attributed to each job. Therefore, each job is treated as a distinct unit.
- It can also be made as a part of specific order costing, which has a component manufactured by a job worker.
- Examples of job costing include repairs of computers, machinery, plant, vehicles, mobile phones, furniture, etc.
Objectives of Job Costing
- The foremost objective behind job Costing is ascertaining the costs involved in the job.
- Each job’s costing helps identify the cost of the entire production chain. So, job costing can be studied in isolation or as part of the production chain.
- Another basic objective is to identify which jobs are profit-making & which are loss-making. This objective also identifies the time allocated by the job worker on the jobs.
- The moment the manager recognizes a loss-making job, he can decide to control the costs involved in the job.
- Controlling costs means comparing the actual cost with the estimated or budgeted cost for the job. This comparison is an in-built objective of job costing.
- This comparison further helps the manager rethink the process of estimating the costs.
- The error in estimating the costs can help decide the estimated cost for similar types of jobs to be undertaken in the future.
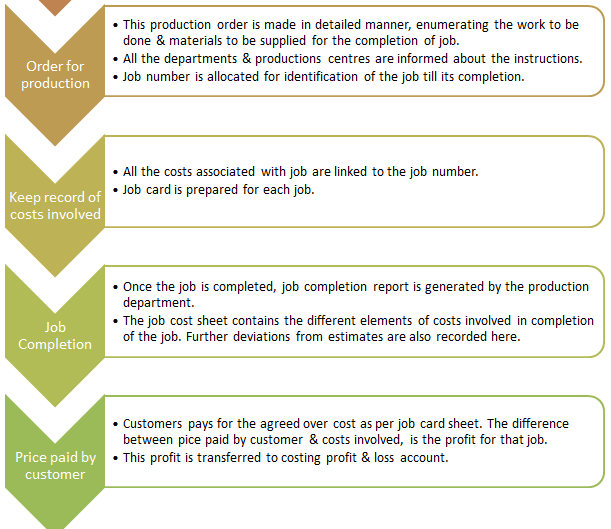
The Procedure of Job Costing
The starting point is an inquiry from the customer & the ending point is the realization of the amount from the customer. Thus, It is normally a customized work. The bill of materials varies according to the requirement of each customer.
The step-wise procedure of job costing is explained as follows:
Example of Job Costing
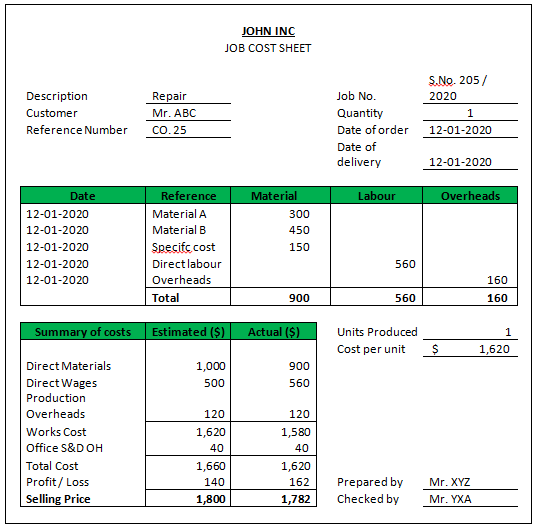
John Inc is involved in the job work process wherein they repair the machines. Material A required in the job is 20 units costing $ 15 each. Material B required is 15 units @ $ 30 each. The customers want specific work to be executed for which materials cost is $ 150 (fully consumed in this job) & service cost $ 30. The labor hours required are 8 hours. The direct labor rate is $ 70 per hour. Production overheads are $ 15 per hour. Selling, distribution &administrative overheads are applied at $ 15 per hour.
Calculation of Job Sheet:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Direct Materials | |
| Material A (20 units * $ 15) | 300 |
| Material B (15 units * $ 30) | 450 |
| Specific Material | 150 |
| Direct Labour | |
| (8 hours * $ 70 per hour) | 560 |
| Production Overheads | |
| (8 hours * $ 15 per hour) | 120 |
| Works Cost | 1,580 |
| SD&A Overheads | |
| (8 hours * $ 5 per hour) | 40 |
| Total Cost | 1,620 |
| Margin @ 10% | 162 |
| Price to be charged | 1,782 |
Explanation:
- The customer is charged $ 1782 for the execution of the above job.
- The production department later identifies whether any abnormal cost was incurred but not charged to the customer.
- The job cost sheet is prepared as follows for reference purposes:
Components of Job Costing
The five basic components of job costing are enlisted as follows:
- Direct Material: Some job orders require installation or repairing of components. Thus, direct material may be consumed in the job process.
- Direct labor: This is the direct cost involved in the job process. This is the real task for any job worker.
- Direct expenses: Few expenses may be required for any specific job. Such expenses are clubbed here.
- Prime Cost: The above three expenses are called the prime cost of the job.
- Cost of production: To the prime cost, we add selling, distribution & administration overheads to arrive at the cost of production.
Advantages
Some of the advantages are given below:
- Every job is undertaken as per the requirement of the customer. Thus, no second thought is required for specifications.
- Job workers need to keep stock of the finished goods. The item is produced only after specific order is received. Thus, inventory cost is saved to that extent.
- Using a separate job cost sheet, we can identify the profits involved in each job.
- It has a major role in the production planning phase.
- Since the cost is segregated for each job, we can easily identify the costs involved.
- Ascertainment of profit is easy as compared to other methods of cost.
- An entity can also identify the abnormal loss involved in the process. Then, an entity can reconcile the normal profit for the job after adjusting for the abnormal loss.
- Managers can easily relate to spoilage issues of each job. He can then determine the reason for spoilage.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are given below:
- Humans are bound to errors. Since job costing involves a lot of clerical work, there are chances of mistakes. Thus, extra costs must be incurred for hiring a supervisor for the entire production chain.
- Job workers are normally semi-skilled, having no or minimal knowledge of computers & systems. Thus, automatic the process of job costing is difficult in this scenario.
- Keeping track of each job in a multi-sized organization is difficult unless an automatic system is in place.
- Job cost sheets do not consider the effects of inflation.
- Each job differs from one others. Thus, different skill sets are required for each job work type. Thus, there cannot be a standardized process of job work. Each job will have a different bill of material.
- The job costs sheet does not consider the prevailing market conditions such as a strike of laborers, inappropriate raw materials, issues in quality of production, stock out situation of emergency supplies, etc.
- For multi-sized organizations, experts are required to take control over different simultaneous jobs.
Conclusion
It helps in identifying the costs associated with each job. Loss-making jobs can easily be traced through the system of control mechanisms. Once determined, the company can take reasonable actions to avoid such losses in future jobs. However, every efficient mechanism demands some costs to be incurred by the company. Efficiency can also be managed through the involvement of experts or managers. This hiring is possibly in large-sized organizations & not small-scale organizations. A small-scale organization can think about efficiency at the job workers’ level.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Job Costing. Here we also discuss the introduction and objectives of job costing along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –