Updated March 17, 2023
Overview of JTextArea in Java
When we talk about Java and swing package, the JTextArea is something that comes into the picture. It represents a multi-line display of area that contains text and can also be used for text editing. It is used to inherit Java’s component class. The text font can be set to different sizes and colors and can even be appended along with the new set of text. Basically, all these text area can be customized as per the requirements and user’s needs. It is a lightweight component that is used to provide source compatibility along with the java.awt.TextArea class where the compatibility can be easily mapped.
Constructors of JTextArea in Java
Let us study more about the different types of constructors:
- JTextArea(): This is used to construct a new blank text-based area.
- JTextArea(int row, int column): This JTextArea is similar to that of the unparameterized JTextArea, with the difference is that it uses the rows and column parameters. It is used to construct a new text field-based area and a fixed number of rows and columns.
- JTextArea(String s): It is used to construct a new text-based area along with a given initial text.
- JTextArea(String s, int row, int column): This one is much more similar to those like the string values or the ones containing row and column parameterized values, so, therefore, this constructs a given initial text and a fixed number of rows and column values.
Methods of JTextArea in Java
After reading about the various constructors related to JTextArea, let us also read some of the major methods which form the basis of the JTextArea in Java.
- Append(String s): As the name suggests, this method is used for appending one given string with the text of the text area.
- setFont(Font f): This method is used to fix the font size and font type of text area to the given font.
- getLineCount(): This function is used to get the number of lines in the text area text field.
- setColumns(int c): This is used to set the column number of the text area along with the given integer.
- setRows(int r): This function is used to set the rows of the text area along with the given integer.
- getColumns(): This function is used to fetch the number of columns along with the text area field.
- getRows(): This function is used to get the number of rows of a particular text area.
Examples of JTextArea
Let us study JTextArea with the help of a basic example that explains how a JTextArea field is created.
Example #1
Program in Java to create a sample JTextArea field.
Code:
//importing basic packages and relevant classes
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
class txt extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
// creating JFrame with frame f
static JFrame F1;
// creating JButton with button b
static JButton B1, B2, B4, B3;
// creating label to display text label l
static JLabel L1, L2;
// creating a public text area to create a text area jjt
static JTextArea jjt;
// creating a default constructor
txt()
{
}
// creating main class for compiler entry
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
// creation of a frame for storing text field option and a Jbutton field
F1 = new JFrame("Entered Text Field");
// creation of a new label for storing display text field option
L1 = new JLabel("Not entered anything");
// creation of a new button for submit
B1 = new JButton("submit button");
// creation of an object for text class
txt te = new txt();
// adding an addActionListener event to button
B1.addActionListener(te);
// creation of a new text area. Also specify rows and column numbers
jjt = new JTextArea(100, 100);
//creation of a new JPanel
JPanel P1 = new JPanel();
// addition of the text area and the button to the new panel added
P1.add(jjt);
F1.add(P1);
P1.add(L1);
P1.add(B1);
// setting the frame size in squared form
F1.setSize(100, 100);
//to display
F1.show();
}
// Whenever the button is pressed for actionPerformed
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
//implementation of getActionCommand
String s1 = e.getActionCommand();
if (s1.equalsIgnoreCase("submit button")) {
// setting of label text to field text
L1.setText(jjt.getText());
}
}
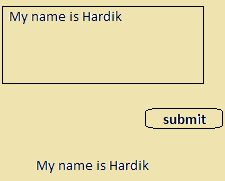
}Output:
Example #2
In this example, we are going to see a public text getting displayed by using JTextArea.
Code:
//importing basic packages and relevant classes
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;//defining a class TxtEG
class TxtEG
{
//calling a default constructor after creation
TxtEG(){
//creation of frames with the object f
JFrame f= new JFrame();
// creation of a JTextArea
JTextArea area=new JTextArea("Welcome");
//setting boundary
area.setBounds(10,30, 200,200);
//adding properties to the frame
f.setVisible(true);
f.setSize(300,300);
f.add(area);
f.setLayout(null);
}
//declaring method main
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
new TxtEG();
}}Output:
Example #3
In this example, we will be reading about the Java JTextArea along with the Action Listener fields and events.
Code:
//importing basic packages and relevant classes
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.*;
//defining the class which is implementing the interface ActionListener
class TarEG implements ActionListener{
//Defining labels, button and Jtext area
JLabel l1,l2;
JTextArea area;
JButton b;
//defining the default contructor
TarEG() {
//Defining JFrames, Labels and set other important properties
JFrame f= new JFrame()
l1=new JLabel();
//Setting bounds
l1.setBounds(50,25,100,30);
//Setting labels
l2=new JLabel();
l2.setBounds(160,25,100,30);
//Defining new
area=new JTextArea();
//Setting different bounds
area.setBounds(20,75,250,200);
b=new JButton("Word Count");
b.setBounds(100,300,120,30);
//Adding action listeners and putting the value to this to point to current object value
b.addActionListener(this);
//adding properties
f.setVisible(true);
f.setLayout(null);
f.add(l1);f.add(area);f.add(b);f.add(l2);
f.setSize(450,450);
}
//declaring the actionPerformed event
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
//declaring string text area
String text=area.getText();
//splitting words based on the string value
String words[]=text.split("\\s");
//calculating the length of words
l1.setText("Words: "+words.length);
//setting the character length
l2.setText("Characters: "+text.length());
}
//declaring the main function
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TarEG();
}
}Output:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we studied the most crucial component of the Java Swings, i.e. JTextArea, which is very essential in forming the windows and text areas. I hope you liked this article. To extend your support by following our blog for more articles like these.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JTextArea in Java. Here we discuss different types of constructors, methods of JTextArea in java, along with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –