What Are Learning Styles?
Learning styles are the different ways people like to learn. It involves how one thinks, feels, and even reacts to learning. Some people might like listening to explanations, while others prefer reading or doing things hands-on.
People have different learning styles, and knowing them can improve learning for everyone. Though some argue about how much they really matter, it’s still helpful to understand and respect everyone’s unique way of learning.
How Do Learning Styles Enhance Education Through Personalized Approaches?
In education, creating learning environments where everyone feels included and can learn well is extremely important. Understanding learning styles is a big part of that. Teachers work hard to meet all students’ needs, considering how they like to learn best.
For instance, some learners love pictures and diagrams, while others prefer getting their hands with hands-on activities. Whether you are a student trying to do your best or a teacher looking to improve your teaching, knowing about different learning styles is key. It’s like how students might look for personalized help, like searching for “do my online class,” to find the right support. In this article, we will explore learning styles in detail, examine different ideas about them, and discuss what they mean for education.
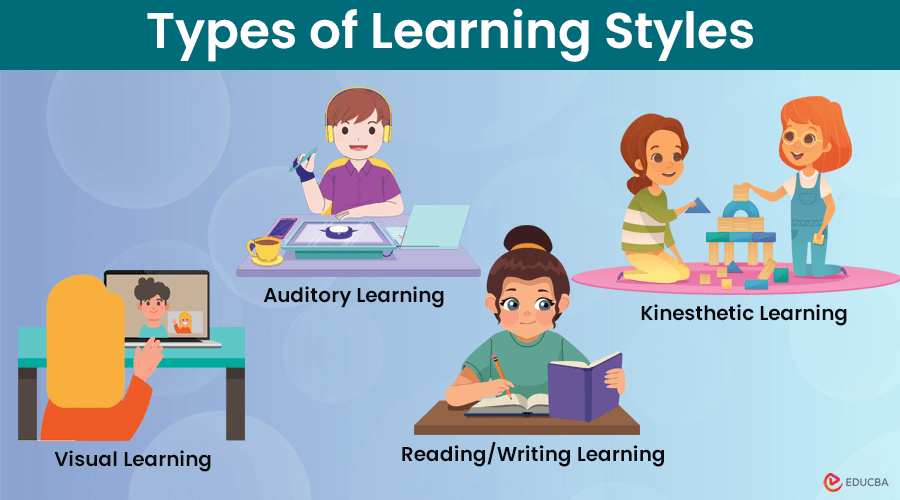
Types of Learning Styles
The different types of learning styles are as follows:
1. Visual Learning
Visual learners prefer to see information presented visually. They learn through visual aids such as diagrams, charts, maps, videos, and demonstrations.
2. Auditory Learning
Auditory learners prefer to learn through listening. They grasp information best through lectures, discussions, audio recordings, and verbal instructions.
3. Reading/Writing Learning
Similar to the verbal learning style, individuals with this preference learn best through reading and writing. They excel in activities such as reading textbooks, writing notes, and engaging in written exercises.
4. Kinesthetic Learning
Kinesthetic learners learn from hands-on experiences and physical activities. They prefer interacting with materials, manipulating objects, and engaging in real-life simulations.
5. Social Learning
In this style, learners prefer to learn in groups or with others. They enjoy group discussions, teamwork, and cooperative learning environments.
6. Logical Learning
Learners are often analytical and enjoy reasoning and problem-solving. They tend to excel in mathematics, science, and logic-based disciplines. They prefer structured, logical presentations of information.
7. Solitary Learning
People with this style prefer to learn alone. They enjoy self-study and prefer independently working through problems and material.
8. Verbal Learning
Individuals with this style learn best through words. They enjoy reading, writing, and speaking. They often excel in languages, literature, and other verbal-based activities. They may also benefit from techniques such as listening to lectures and participating in discussions.
Learning Style Models
Learning style models are frameworks that categorize different learning styles into one. These models are used in educational settings to understand individual learning preferences and customize teaching methods to accommodate diverse learning styles. However, while these models offer valuable insights, educators and researchers continue to debate the validity and effectiveness of categorizing learners into specific styles.
Some well-known learning style models include:
1. VARK Model
This model categorizes learners into four main styles: Visual, Auditory, Reading/Writing, and Kinesthetic. It suggests that individuals may have preferences for learning through visual aids, listening to lectures or discussions, reading and writing, or hands-on activities.
2. Felder-Silverman Learning Style Model
This model, developed by Richard M. Felder and Barbara A. Soloman, suggests that understanding the below preferences can help educators design instructional strategies accommodating diverse learning styles. It categorizes learners along four dimensions:
- Sensory/Intuitive: Individuals may lean towards sensory or intuitive processing.
- Active/Reflective: They may prefer active engagement or reflection.
- Visual/Verbal: Some individuals have preferences for visual or verbal information.
- Sequential/Global: They may approach learning sequentially or holistically.
3. Kolb’s Experiential Learning Theory
Developed by David Kolb, this model proposes that learning is a continuous process that involves four stages:
- Concrete Experience
- Reflective Observation
- Abstract Conceptualization
- Active Experimentation
Individuals may prefer certain stages over others, resulting in different learning styles.
Strategies to Implement Diverse Learning Styles in Education
To help all students learn better, teachers can use different teaching methods and materials, and here are some strategies to address different learning styles.
#1. Using Multimodal Resources
Offering materials in various formats is essential to teach a diverse group of learners effectively. This means providing visuals, audio recordings, written texts, and hands-on activities. Doing so allows you to adapt to different learning styles and helps strengthen understanding through different sensory modalities.
#2. Creating Customized Lessons
It’s important to adjust teaching methods in a classroom to suit each student’s unique learning style. This could mean organizing students into groups based on how they learn best or providing different assignments to meet individual needs. By doing this, every student gets the support they need to succeed.
#3. Promote Active Learning
Make learning more engaging by including activities where students actively participate. This could mean doing hands-on experiments, having group discussions, or solving problems together. These activities appeal to different ways of learning and help students remember what they have learned.
#4. Offer Flexible Assessments
Assess students in ways that match how they learn best. For example, some students might do well in written exams, while others shine in presentations or hands-on projects. By offering different assessment methods, you ensure everyone has a chance to show what they know in a way that suits them.
#5. Guide Students to Self-Reflect
Help students become aware of how they learn and think about their learning process. Encourage them to think about what works best for them and how to improve their study habits. This way, they can take control of their learning and use strategies that work well for them.
Challenges of Learning Styles
Learning styles are very common, but there are the following challenges:
- Some critics say they lack solid evidence, and there are no studies proving that teaching a specific style works.
- Also, sorting learners into fixed styles might ignore how people’s preferences can change.
- Moreover, using personalized learning can be challenging for teachers as adjusting teaching methods for different styles requires careful planning and training.
Final Thoughts
The debate about learning styles among educators and researchers is ongoing, but its importance is clear: it encourages education focusing on the learner. When we acknowledge and respect the different ways people learn, we create a better learning environment for everyone. Teachers can use personalized learning methods to help students discover their strengths and achieve their best.
Recommended Articles
We hope you found this EDUCBA article on Learning Styles helpful. For similar articles, refer to the following:
