Updated October 31, 2023
Difference Between Lease vs Rent
In Lease vs. Rent, a lease is when you borrow something for a long time (over 11 months), such as property or a car. However, renting means you pay to use something for a shorter period,less than 11 months, like a camera, camping gear, etc.
Let us study much more about lease and rent in detail:
We often need something desired or needed, such as a bigger house or a car, to make our daily commute easy. Business entities may require big machinery and large pieces of land to set up their factories. However, sometimes, individuals and companies may not have an adequate supply of capital to fund the purchase of these assets. When direct purchasing of a particular asset is impossible, many individuals and companies opt for leasing or renting.
What Does it Mean to “lease out” Something?
A lease is a legal contract between two parties with terms and conditions. The contract addresses the opposite parties as “lessor” and “lessee”. The asset’s owner is known as the lessor, while the user of the asset is known as the lessee.
Let’s take a simple example to make this concrete.
Suppose a student has moved to a new town for college graduation and is looking for a house. Due to financial constraints, the student can’t buy an entire house and hence decides to look for a place available for monthly usage in return for payments made. The owner of the house (lessor) and the student (lessee) will get into a legal contract called a lease agreement. The agreement will entail all the details and guidelines about the maintenance of the property by the lessee.
Characteristics of a Lease Agreement
- One of the defining characteristics of a lease agreement is that the onus of maintenance lies with the lessee. The contract specifies clear guidelines regarding the allowed use of the asset, and those guidelines bind the lessee.
- Typically, the duration of the lease agreement starts from 1 year and can last as long as 20 years, though there is no clear upper bound on the duration.
There are two main categories of a lease agreement, namely:
- Operating Leases
- Capital Leases
The classification of a lease into an operating or capital lease is based on the accounting treatment. The following conditions determine when a lease agreement is treated as a capital lease:
- If the value of payments made on the lease agreement makes up for most of the fair market value of an asset.
- The duration of the lease agreement and the effective useful life of the asset being leased out are almost the same.
- At the agreement’s expiration, there is an option to purchase the asset.
Additionally, capital lease constraints the recording of the asset as a “fixed asset” on the financial statements. The obligation is listed as a liability on the financial statements.
There are no such requirements or constraints for operating leases. For accounting purposes, you can record lease payments as expenses.
What Does it Mean to “rent” Something?
Like a lease, renting is a contract binding two parties obligatory to each other per the terms mentioned. Let us continue with the above example of a student and try to understand it.
After getting into a lease agreement for the house, let’s assume he needed a powerful desktop with specific requirements to do assignments. Instead of having the desktop for a long duration, he needs it only for 3 weeks. He will rent it from someone for a smaller duration to meet this requirement. This is the process of “renting”. He will get into a “rent agreement” with the supplier of the desktop for the required duration.
Characteristics of a Rent Agreement
- The defining characteristic of a rental agreement is that the asset user is not responsible for the maintenance of it. The person who rents it is responsible for ensuring it is usable.
- Rental agreements are better suited for assets to be used only temporarily. In our case, the student needs the desktop only for a few weeks. So, he would prefer renting it out rather than going to a lease agreement for a longer duration.
- Renting typically covers a shorter period, usually a maximum of 1 year. Like a lease agreement, a rent agreement can extend the contract after the term ends.
In general, rent agreements are usually far more relaxed concerning terms and conditions.
For accounting purposes, rental costs are always recorded as an expense on the income statement of the companies.
Head To Head Comparison Between Lease vs Rent (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 Difference between Lease vs Rent
Key Differences Between Lease vs Rent
Let us discuss some of the major Differences Between Lease vs Rent:
- Businesses opt for a lease agreement when they face a shortfall of the required capital to purchase a crucial asset necessary for their operations. On the other hand, renting is chosen when a specific task requires an asset but is not critical for the business’s operations.
- The duration of a lease agreement has usually lasted many years, while rent agreements are generally made for less than a year.
- There are two types of lease agreements, namely operating lease and capital lease, depending on the accounting treatment.
- Businesses generally lease assets/equipment that are crucial to their operations. Renting is done for land, properties, or other assets on a need-of-use basis.
- In a lease agreement, the lessee is responsible for maintaining the asset. In renting an asset, maintaining it does not lie with its user.
- Lease agreements bind the lessor and lessee to clear and defined terms and conditions of use. Regarding usage terms and conditions, rent agreements have a comparatively relaxed approach.
- The lease agreement comes with the option of owning the asset at the end of the tenure of the contract. A rental agreement does not provide the option of purchase.
Lease vs Rent Comparison Table
Below is the comparison Table Between Lease vs Rent
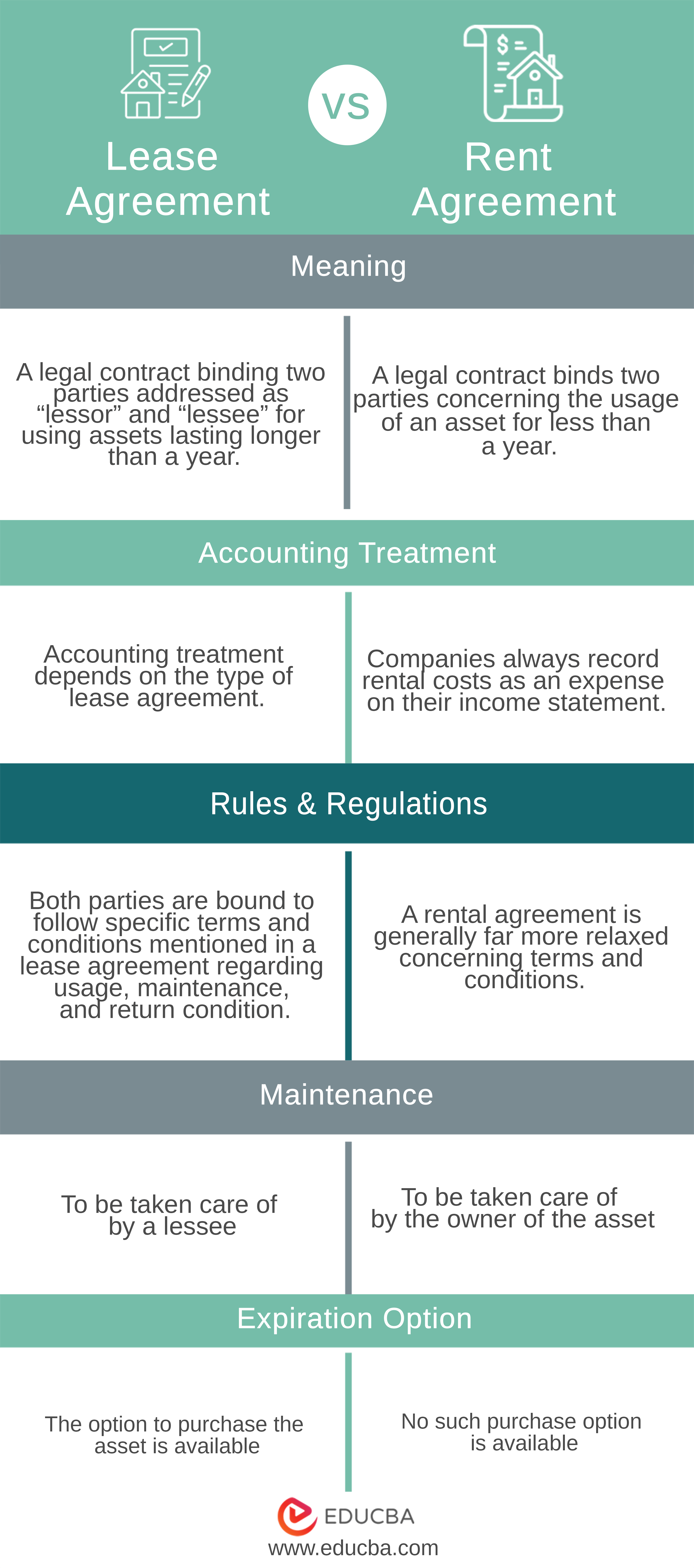
| The Basis of Comparison | Lease Agreement | Rent Agreement |
| Related to | Leasing | Renting |
| Meaning | A legal contract binding two parties addressed as “lessor” and “lessee” for using assets lasting longer than a year. | A legal contract binds two parties concerning the usage of an asset for less than a year. |
| Accounting treatment | Accounting treatment depends on the type of lease agreement. | Companies always record rental costs as an expense on their income statement. |
| Rules & Regulations | Both parties must adhere to specific terms and conditions stated in a lease agreement concerning the usage, maintenance, and return conditions. | A rental agreement is generally far more relaxed concerning terms and conditions. |
| Maintenance | The lessee must take care of it. | The owner of the asset is responsible for taking care of it. |
| Expiration Option | The option to purchase the asset is available | No such purchase option is available |
Conclusion
While the above example explains the difference between lease vs rents out an asset, in real life, the decision to rent or lease includes careful consideration of many factors and constraints
If an asset is a crucial part of your business, entering a lease agreement is always better. For instance, a company manufacturing hardware should lease out its machinery rather than take it on rent. The other subtle factor is the lease agreement’s guarantee and other specified conditions, which may prove crucial for business operations later.
Choosing to rent an asset is better when you need it for a short period or when your business is uncertain about the future use of that particular asset. Although renting costs may come out to be more in the short run, the overall expenses might be less in the long run, where there is a risk of technological change, thus making the asset obsolete.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Lease vs Rent. We also discuss the Lease vs Rent key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.