Updated May 10, 2023
Introduction to Left Outer Join in MySQL
In this article, we will see about the Left Outer Join in MySQL. Left Outer Join gets all the rows from the left table and the common rows of both tables.
Let us take an example of the right join.
Example:
Below represents the Venn diagram of the left outer join.
In the below diagram, Table A is left joined to Table B. Here are all the rows from the table. A gets considered, and common rows from both tables.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM TABLE_A A
LEFT OUTER JOIN TABLE_B B
ON A.Common_COLUMN=B.Common_COLUMN
WHERE <Condition>Key Differences between Left Join vs Right Join
Given below are the key differences between left join vs right join:
| Left Outer Join | Right Outer Join |
| Consider all the rows from the table and common rows from both tables. | Consider all rows from the right table and common from both tables. |
| INNER Join + all rows from the left table. | INNER Join + all rows from the right table. |
| Joins based on a condition. | Joins based on a condition. |
| ON keyword is used to specify the condition and join the tables. | ON keyword is used to specify the condition and join the tables. |
| The result set contains NULL set values. The below syntax can be used to neglect the NULL values:
SELECT * FROM TABLE_A A |
The result set contains NULL set values. The below syntax can be used to neglect the NULL values:
SELECT * FROM TABLE_A A |
| SELECT * FROM TABLE_A LEFT OUTER JOIN TABLE B ON A. Common_COLUMN =B. Common_COLUMN |
SELECT * FROM TABLE_A RIGHT OUTER JOIN TABLE B ON A. Common_COLUMN =B. Common_COLUMN |
How to use LEFT Outer Join in MYSQL?
- LEFT Outer Join = All rows from LEFT table + INNER Join.
- Consider all rows from the left table and common from both tables.
- Joins based on a condition.
- You can use the ON keyword to specify the condition and join the tables.
Examples to Implement Left Outer Join
Below is an example of implementing Left Outer Join in MySQL:
Example #1
Let us consider two tables and apply LEFT Outer join on the tables:
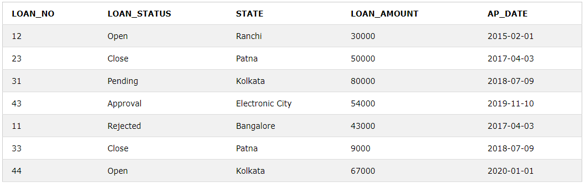
Loan Table:
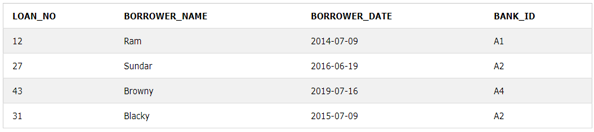
Borrower:
Query to get the loan_no, status, and borrower date from two tables:
Code:
SELECT L.LOAN_NO, L.LOAN_STATUS, B.BORROWER_DATE
FROM LOAN L LEFT OUTER JOIN BORROWER B
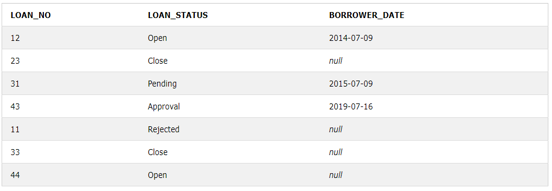
ON L.LOAN_NO=B.LOAN_NOLet’s check the output of the above table after applying the left outer join on them.
Output:
The result set contains NULL set values. The below syntax can be used to neglect the NULL values:
Code:
SELECT * FROM TABLE_A A
LEFT OUTER JOIN TABLE B B
ON A. Common_COLUMN =B. Common_COLUMN
WHERE A.Common_COLUMN IS NULLExample #2
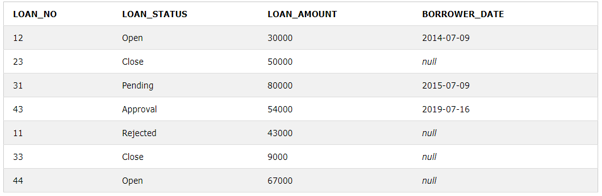
Let us consider two tables and apply LEFT outer join on the tables: Query to get the loan_no, status, loan_aount, and borrower date from two tables.
Code:
SELECT L.LOAN_NO, L.LOAN_STATUS,L.LOAN_AMOUNT, B.BORROWER_DATE
FROM LOAN L LEFT OUTER JOIN BORROWER B
ON L.LOAN_NO=B.LOAN_NOLet’s check the output of the above table after applying the left outer join on them.
Output:
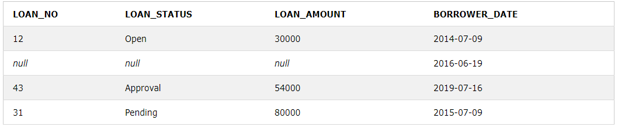
Example #3
Let us consider two tables and apply the Left outer join on the tables: Query to get the loan_no, status, loan_amount, and borrower date from two tables.
Code:
SELECT L.LOAN_NO, L.LOAN_STATUS,L.LOAN_AMOUNT, B.BORROWER_DATE
FROM BORROWER B LEFT OUTER JOIN LOAN L
ON L.LOAN_NO=B.LOAN_NOLet’s check the output of the above table after applying the left outer join on them.
Output:
In the above table, LOAN is on the right table, and the borrower is on the left. As in left OUTER join, we get inner join+ all rows from the left table. We left join the Borrower table with the Loan table to get all the rows from the Borrower table and inner join the rows. Values not present will be NULL.
Conclusion
To fetch data relevant to the customer requirement, we might need to join tables that will fulfill. As mentioned earlier, joins are used to get data from multiple tables. To join more than one table, we need at least one column common in both tables. Tables get joined based on the condition specified.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Left Outer Join in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.