Introduction to Levels of Six Sigma
Six Sigma levels are professionals that exist in every hierarchy in an organization, each executive having a distinct role to play in improving the efficiency of a product or a service. The different levels of sig sigma tell us who can perform what role and when it has to be dealt with a project. At each level, there is an underlying difference that a professional maybe having in terms of skills, knowledge and technical vocabulary to undertake a project.
Six Sigma has various levels of certification which are to be spoken in detail in this article. Employees who have completed their certification of six sigma, naturally become inherent and indispensable in chalking out methods of improvement and processes in their respective organizations. They become a chunk of key stakeholders and assess the quality control with consistent monitoring of projects, process, and services. They work towards eliminating the variation in discrepancies, redundancy, and anomalies in the manufacturing operations through introduction and adherence to standard protocols of processes. These key stakeholders are also responsible for establishing metrics which helps to reduce the variation in defects.
Some of the leading organizations in the world establish standard practices of Six Sigma along with adaptive measures of lean manufacturing. Collaborated together, they cut down on waste to elevate their organizations as effective as it could be. To name a few companies which have successfully implanted Six Sigma in its’ roots are Xerox, 3M, and BAE Systems. In order for a business in achieving optimal results by putting into practice the principles of Six Sigma and Lean manufacturing, there are experts who are trained in the application tools and right techniques, taking charge of the changes to be made enterprise-wide.
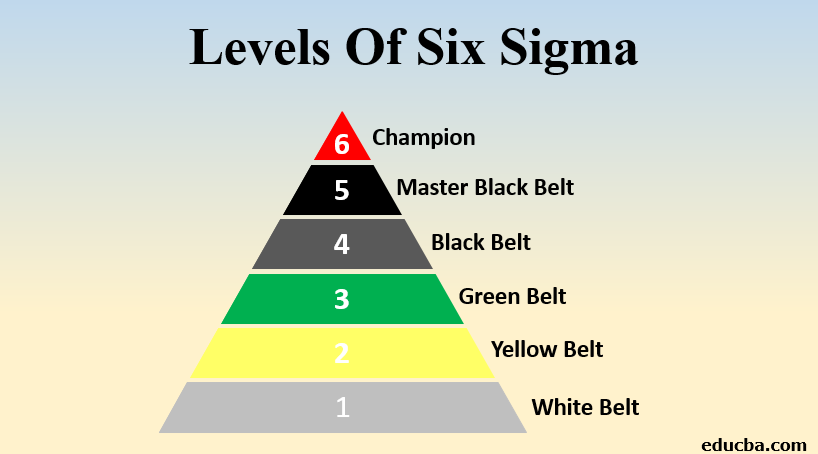
Levels of Six Sigma
Let us now take a look at different levels of Six Sigma. Each level of certification implies the role that a stakeholder is qualified to enact with respect to implementing projects and enhancing quality work in management practices. This helps in equipping trained personnel to be full of active participants when it comes to upscaling their company’s culture and pushing off downtime.
Let us now begin exploring the different levels in the certification ladder and how each one can prove to add to the skillset of the professional, helping him to move ahead in his career.
1. White Belt
This is the first level of certification in the Six Sigma certification training. Professionals who have not undergone prior formal certification training or any other extended training are called six sigma white belt holders. This session will give them an overview of effective methods needed and the vocabulary to study for LSS workers throughout the entire hierarchy of the organization. It shows them how they are the ones who contribute towards efficiency and most reliable outcomes. With this basic platform, to begin with, white belt holders participate in those projects that are driven towards problem-solving. It strictly revolves around quality management and reducing waste.
2. Yellow Belt
Holding this designation means that it indicates exposure to concepts of Six Sigma that moves ahead of the fundamentals that a white belt holder seeks. Yellow Belts practitioners have training sessions attended over a period of two days, enhancing the knowledge that they need to work on the project and dealing with team members who are all inter-dependent closely. They may uplift the projects that had a limited scope and help managers who are at belts in the higher level.
3. Green Belt
For getting a green belt six sigma certification, required professionals are expected to attend the full course that exposes them to methods of Six Sigma, how to develop, improve and reduce variation in services and processes. They know how to apply frameworks which are for problem-solving, one example is DMAIC. This cycle of improvement chalks out a series of steps to analyze the problems that prevail in a business process. They carve out important metrics to measure changes, infer relevant data and execute solutions post which sustains the results over a period of time. The green belt is extremely valuable for professionals who are into the project management field, medical and healthcare and also financial management. It serves as a base for performance metrics and control charts tools like (FMEA) failure modes and effect analysis. Once the certification is completed, executives are prepared to take charge of projects, joining connections of LSS concepts with the organization goals. They have the knowledge to apply leadership tools for implementing action, finding ways to reduce waste and infer sights that are crucial from the data.
4. Black Belt
This is an advanced training level that leaders undergo to upgrade their skills, after the completion of green belt certification. It is pre-requisite to have previous LSS knowledge so that leaders and stakeholders become the master of their skills and knowledge which to apply when planning. This helps to take care of the fact that they have to lead many complex projects which are expansive, disruptive and may need organizational changes. Professionals who are black belt certified could be considered to demonstrate their learning and real account experiences by carrying out a live project for their higher-ups. It could also be for a non-profit organization. By making a project charter, gathering data and infusing six sigma tools for a real project context, students harbor and grow the potential they need for making their business more efficient, productive and increasing the customer satisfaction at the same time. Together with the application of lean efforts, they run high-quality improvement with scope for making a huge impact on the productivity of the company.
5. Master Black Belt
A professional with thorough leadership skills and problem-solving approaches can elevate to hold a master black belt in LSS. The designation of a Master black belt holder is about an expert who has a wide spectrum of strategy all throughout the business and thereby coordinating all cross-functional teams.
6. Champion
A professional is called champion when he is a manager in the upper level leading LSS deployment and strategy. Now, based on the number of objectives that are set by professional leaders, champions are the ones who ensure that most initiatives to lower waste and to eliminate variation actually help in removing faults as per the alignment with the needs of the company. Guided by their leaders who are master black belts, such managers help a lot by mentoring high-end professionals who are involved in the implementation of LSS, and also tracking how much progress has been made.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Levels of Six Sigma. Here we have discussed the different Levels of Six Sigma in the certification ladder which will help you move ahead in your career. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
