Updated July 29, 2023
Leverage Ratio Formula (Table of Contents)
- Leverage Ratio Formula
- Examples of Leverage Ratio Formula(With Excel Template)
- Leverage Ratio Formula Calculator
Leverage Ratio Formula
Leverage ratio can be defined as the ratio of total debt to total equity of any firm to understand the level of debt being incurred by any firm or entity.
The Formula of Leverage Ratio is as below:
Examples of Leverage Ratio Formula (With Excel Template)
Now, let us see an example to understand the Leverage Ratio Formula in a better manner.
Example #1
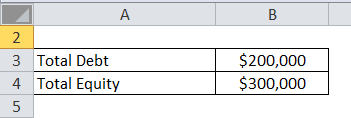
Let’s take an example of company X, whose Total Debt is $200000 and Total Equity is $300000. Calculate the Leverage Ratio of a company.
Solution:
We can calculate the Leverage Ratio by using the below formula
Leverage Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
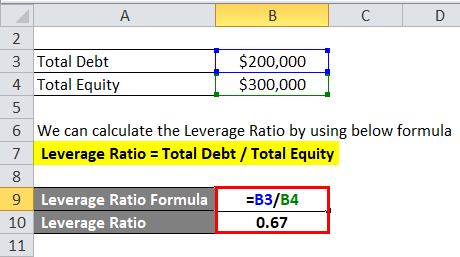
- Leverage Ratio = $2,00,000 / $3,00,000
- Leverage Ratio = 0.67
Example #2
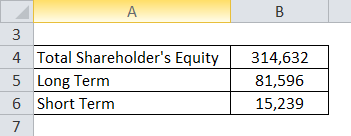
Let us take the example of Reliance, whose Total Shareholder equity is Rs 3,14,632 Cr, long-term debt is Rs 81,596 Cr, and short-term debt is Rs 15,239 Cr. Calculate the Leverage Ratio of a Reliance company.
Solution:
Hence we don’t have Total Debt, so first, we will find out the Total Debt
We can calculate the Total Debt by using the below formula
Total Debt = Long-Term + Short Term
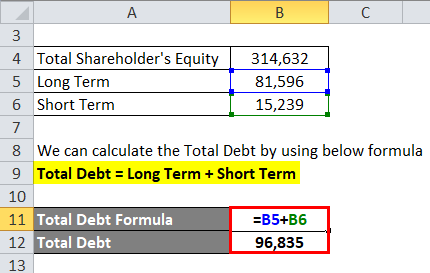
- Total Debt = Rs 81,596 Cr + Rs 15,239 Cr
- Total Debt = Rs 96,835 Cr
Hence now will find out the Leverage Ratio
We can calculate the Leverage Ratio by using the below formula
Leverage Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
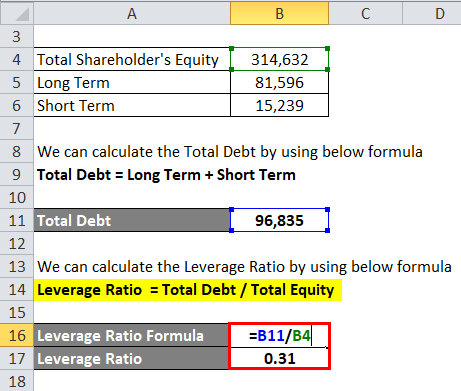
- Leverage Ratio = Rs 96,835 Cr / Rs 3,14,632 Cr
- Leverage Ratio = 0.31
Example #3
Let us take the example of the company Tata Steel whose Total Shareholder equity is Rs 61,514 Cr, long-term debt is Rs 24,568 Cr and short-term debt are Rs 670 Cr. Calculate the Leverage Ratio of a Tata Steel company.
Solution:
Hence we don’t have Total Debt, so first, we will find the Total Debt.
We can calculate the Total Debt by using the below formula
Total Debt = Long-Term + Short Term
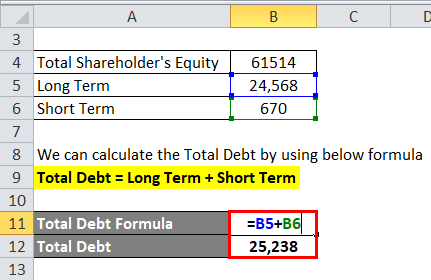
- Total Debt = Rs 24,568 Cr + Rs 670 Cr
- Total Debt = Rs 25,238 Cr
Hence now will find out the Leverage Ratio.
We can calculate the Leverage Ratio by using the below formula
Leverage Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
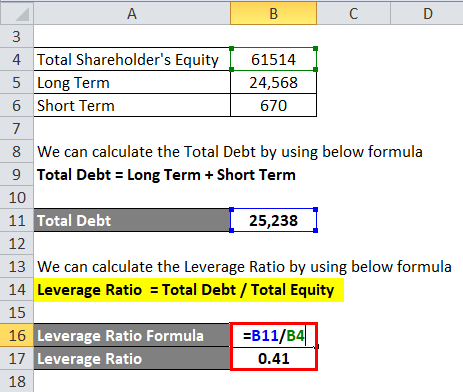
- Leverage Ratio = Rs 25,238 Cr / Rs 61,514 Cr
- Leverage Ratio = 0.41
Hence the Leverage Ratio is 0.41
Explanation of Leverage Ratio Formula
Leverage ratio can be defined as the ratio of total debt to total equity of any firm to understand the level of debt being incurred by any firm or entity. Debt is an essential component for any firm as it is significantly cheaper than other forms of money and amplifies profits. On the other hand, a higher-leveraged company can face issues if there is a decline in the business of the company. So leverage can reap benefits if used well or create risk for a company if not properly utilized.
There are various kinds of leverage ratios. Some are debt/equity, debt/EBITDA, debt/assets, or debt to total capital. Debt/Equity is a common measure used by investors. There are various ways in which leverage is created for a company: –
- A company might take debt to purchase assets such as property, plant, or equipment.
- A company borrows debt for short-term requirements, such as inventory, liquidity, etc.
- A company might borrow to finance an acquisition of another company.
- A private equity firm does Leveraged Buyouts.
- An individual may borrow to finance his/her purchase of a house.
- Investors in equity markets may borrow to add stocks to their portfolios.
Increasing leverage can multiply earnings for an individual or a company. But it also comes with the warning of additional risk. If the cash flows do not support it, then there is a chance of the company or individual defaulting on their payments. Hence the level of leverage should be defined wisely.
Relevance and Uses
The leverage ratio is an indicator of the inherent risk of a company. When the debt ratio is very high compared to its peers, the firm is carrying a significant burden since the principal and interest payments would be blocking the company’s cash flows. These cash flows could have been used for capital expenditure or other important ways to grow the company. Also, there are possible circumstances where the cash flows are not large enough to support the debt payments. Then the company might have to default.
Conversely, if any company’s debt level is low, the debt payments do not amount to a large portion of the company’s cash flows; hence, they are not sensitive to external circumstances such as business changes. But it also indicates the company can increase its debt level because debt is cheaper than other forms of money. Each company has to find its optimum level of debt to support.
But there is no optimum level of debt for any particular company. Leverage ratios should be compared with companies operating in a similar industry. For example, steel companies generally have a higher level of debt than other industries. Hence when looking at the debt level of any steel company, it should only be compared with its peers. If the debt level exceeds its peer companies, there may be a cause for concern. Both investors and lenders to any particular firm prefer lower leverage levels since it guarantees that their interests are protected in case of a decline in the company’s business or even during default or liquidation. This is one of the reasons why higher leverage ratios may prevent any firm or company from attracting additional capital.
Leverage Ratio Formula Calculator
You can use the following Leverage Ratio Formula Calculator
| Total Debt | |
| Total Equity | |
| Leverage Ratio Formula | |
| Leverage Ratio Formula | = |
|
|
Conclusion
The leverage ratio is the total debt-to-equity ratio for any firm or company. Leverage has the benefit of multiplying earnings but also means the company is taking additional risks. The company might default on its payments if the cash flows do not support them. Any company’s leverage must be compared to its peers’ leverage levels to determine whether the level is higher or lower. It cannot be compared with companies operating in other industries.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Leverage Ratio Formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate the Leverage Ratio along with practical examples. We also provide you Leverage Ratio Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


