Updated July 11, 2023

What is Leveraged Finance?
The term “leveraged finance” refers to the funds raised by companies from outside the organization through debt instruments instead of using the equity route.
Generally, it carries a fixed periodic repayment schedule. It carries a slightly higher interest rate than other forms of debt financing due to its heightened vulnerability to the risk of default. Companies can utilize the funds raised through leveraged finance for various purposes, including asset acquisition or liability repayment.
In the case of leveraged finance, the proportion of debt is much higher than the standard type of debt financing. Higher debt means higher interest payout and repayment obligations that the companies must fulfill, irrespective of their ability to generate profit, to retain solvency.
Key Takeaways
Some of the key takeaways of the article are:
- It refers to using borrowed funds to boost the return on investment from a project or business.
- Investors use it to enhance their purchasing power in the market.
- It can be a double-edged sword. It can be highly fruitful if the business grows as expected, but it can be fatal if it fails to achieve the target performance.
Example of Leveraged Finance
Let us look at an example to understand the concept of leveraged finance. Let us assume that ASD Inc. decided to acquire QWE Inc. for a purchase consideration of $50 million. The acquisition will be funded through $45 million of debt and $5 million of cash, meaning 90% of the funding is through debt instruments leading to leveraged finance. In this way, ASD Inc. utilized its $5 million of cash and leveraged finance of $45 million to invest in a $50 million business and generate more opportunities to increase shareholder value.
However, the acquirer may be in trouble if it fails to generate adequate cash flow to service the high debt obligations due to leveraged finance. It serves as a double-edged sword, offering high benefits when businesses align with expectations but turning excruciatingly painful if business growth deteriorates.
Effects of Leveraged Finance (Excel Template)
Let us now look at the illustration below to understand the effect of leveraged finance on a business transaction.
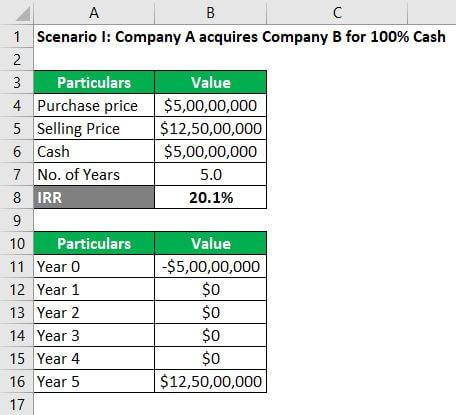
Scenario I: Company A acquires Company B for 100% cash
Let us assume that there is an investment opportunity wherein Company A acquires Company B for $50 million in cash. Company A’s analysis indicates that it can sell Company B after five years for $125 million with no other cash flow in the interim period (for the sake of simplicity).
So, the IRR for the scenario I come out to be 20.1% (refer to the Excel file for calculation).
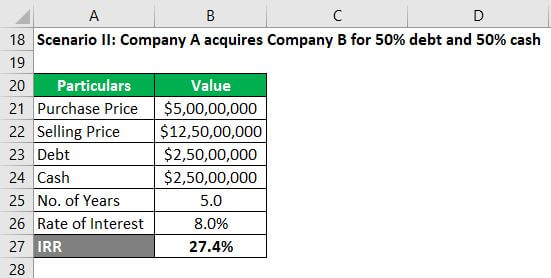
Scenario II: Company A acquires Company B for 50% debt and 50% cash
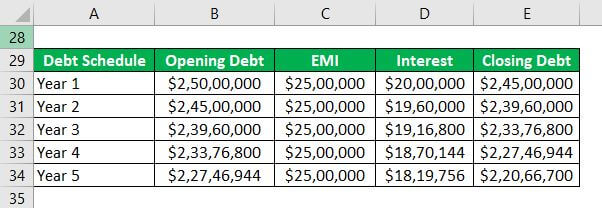
Let us assume that in the case mentioned above, Company A decides to fund the purchase with $25 million of debt and $25 million of money and then sell for $125 million after five years. It also assumed that the total payment for the debt and interest would be $2.5 million a year.
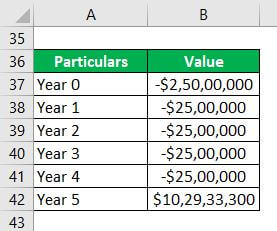
So, at the end of 5 years, the total outstanding debt will be $22 million. Consequently, the net (of debt) amount to be received at the time of selling = $125 million – $22 million = $103 million.
So, the IRR for scenario II is 27.4% (refer to the Excel file for calculation).
Hence, the difference in return of 7.3% (= 27.4% – 20.1%) captures the effect of leveraged finance on a business transaction.
Advantages of Leveraged Finance
The following are some of the significant advantages:
- It multiplies the power of every dollar invested in a project. A successful leverage-financed project can generate a much higher return than a typical debt-financed project.
- Loan syndication suits projects with a relatively short holding period, where the subject business aims for specific growth objectives like management buyouts or acquisitions.
Disadvantages of Leveraged Finance
The following are some of the significant disadvantages:
- In general, debt funding helps a business grow at a faster rate. But debt beyond a certain level can put a business into a state of leverage that is too hot to handle. As a result, leveraged finance magnifies risk exposure.
- Given the high associated with leveraged finance products, companies need to pay a much higher cost of funding to compensate the investors for assuming the risk.
- Its products are usually complex, which consumes additional management time.
Conclusion
It is essential to use leveraged finance in a well-planned manner to be effective. Otherwise, too much leverage can prove dangerous for a business. The extent of financial leverage is either a deliberate choice of the management or is governed by the policies set by the lenders. In most cases, the level of financial leverage or capital structure is determined based on risk management strategies. However, a company’s financial leverage should be maintained so that leverage doesn’t push it to the brink of default.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Leveraged Finance. Here we discuss the introduction, examples, effects, advantages, and disadvantages, along with a detailed explanation and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –