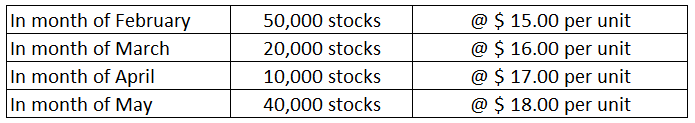Updated July 19, 2023

Definition of LIFO Liquidation
LIFO Liquidation is an event occurring with entities who are in the practice of using the LIFO (Last in, first out method) method for the cost of the inventories where the entity has to use older stocks acquired except the latest stock acquired due to a sudden increase in the market demand of the products and to fill full the demand the entity has to use up its older stocks.
Explanation
The LIFO Liquidation is based on the consumption of the older stocks that the company has stocked up or left for the completion of the demand and supply of their product in the current market. This results in a reduction in the COGS of the current month with the matching concept of sales during the same period. Due to the same, the profit of the period increased, and the company had to pay taxes on the same gain, which is more than the profit that would have been made if all the materials had been purchased in the same month.
How Does it Work?
Generally, the companies who follow the LIFO method for the cost of their inventories in the business acquire enough stock per the market demand of their products to fulfill the customers’ demand in the same month. However, sometimes due to abnormal reasons, there is a sudden spike in demand for the product in the market, and for fulfilling the demand in the market, the company has to use up its older stock, which was purchased at a relatively lower cost compared to the current monthly rate. With the passing months, usually, the cost of the materials gets increases. Due to the LIFO Liquidation event, the cost of goods sold (COGS) of the finished accounts less, resulting in more profit. The increase in profit may result in more taxes to be paid by the company, which may take the larger appropriation of profit.
Example of LIFO Liquidation
Let’s understand the concept through an example.
ABC Inc. manufacturing company deals in a product named “P Product.” As per history, they recorded good demand in the market for their products. For recording the inventory costing used in making their final product, the company used the LIFO method for the valuation. In the past months, the company has left some of the stocks, and the detail of the same is as follows:-
The company provided that the company needs 2 units of Inventories to produce 1 unit of the finished goods. As per the trend of the demand for the product, the company decided that they need materials for the production of the 35,000 units of the final goods. The company is getting the products @ 20.00 per unit. However, the actual demand for the product results in 60,000 units @ $ 50.00, and for fulfilling the demand, the company has to use the inventories acquired during the previous periods.
Solution:
As per the situation provided, the company has acquired 70,000 units of raw material @ $ 20.00 per unit costing $ 14, 00,000.00 and as per the information of the raw materials has been provided following can be summarized:
| Months | Units | Rate ($) | Amount |
| February | 50000 | 15.00 | 7,50,000.00 |
| March | 20000 | 16.00 | 3,20,000.00 |
| April | 10000 | 17.00 | 1,70,000.00 |
| May | 40000 | 18.00 | 7,20,000.00 |
| June | 70000 | 20.00 | 1,40,000.00 |
As per the situation, the company has acquired 70000 units of raw materials for fulfilling the demand, but the actual demand came up to 60,000 units of final goods for which the materials of 1,20,000 units, and for fulfilling the stock the company has to use the stock of the previous months.
As the company is following the LIFO method, for fulfilling the demand, the company will use 70,000 units of raw material from the month of June, 40,000 units from the month of May, and 10,000 units from the month of April, and the costing will lead to the following:
| Months | Units | Rate ($) | Amount |
| April | 10000 | 17.00 | 1,70,000.00 |
| May | 40000 | 18.00 | 7,20,000.00 |
| June | 70000 | 20.00 | 14,00,000.00 |
Total = $ 22, 90,000.00
However, if the total material has been acquired in the month of June @ 20.00, the COGS would have been $ 24, 00,000.00 that is greater by $ 1, 10,000.00 comparing to the actual COGS of $ 22, 90,000.00.
The actual profit earned by the company in the month of June would be
Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price
- Profit = (60000 * 50) – 2290000
- Profit = $ 7, 10,000.00
Therefore, the company has to pay the tax on the same profit, but if all of the materials had been purchased in June, the profit would have been lessened by $ 1, 10,000.00, so the tax amount has to be paid on the profit amount.
Why it Occurs?
The primary reason for the occurrence of LIFO Liquidation is due to the unexpected increase in demand or supply of the products needs to be, which is unexpectedly more than the estimated quantity, and the second effect of the same is due to continuous increase in the price of the direct materials needed for the manufacturing of the final products. Due to a sudden increase in supply and demand of the products, the company has to use up their reserve or left stocks of the previous periods due to the unavailability of the raw materials and due to continuous increases in the prices of the raw materials, the use of the previous stocks results in less amount of cost of goods sold and which finally results into more profit to the company.
Effects of LIFO Liquidation
The primary effect that LIFO Liquidation does is increasing the profit of the company for the affected period. This reading may seem a good thing, but due to this, without any reason, the company has to pay more taxes, which they could have avoided if they had the necessary raw material stock at the current price of the market. The increase in profitability results in more taxes to be paid on the income, and that might take a reasonable appropriation of the profit that the company has made.
Advantages of LIFO Liquidation
Some of the advantages are given below:
- The increase in the demand for the product is a good sign for the company’s business. As the market demand for the product increases, the company is doing good and increasing its market share.
- The increase in profit of the company is good for the company’s financials to attract investors.
- LIFO Liquidation inspires the theory of stocking up raw materials when their prices are dynamic and relatively low, which might increase in the future.
Disadvantages of LIFO Liquidation
Some of the disadvantages are given below:
- The more taxes paid by the company in that period takes up some part of their profits that they could have made and used up for growing up the business.
- This does not provide the actual matching accounting concept and provides false financial data.
- The use of old stocks puts questionability on the products of the business.
Conclusion
The LIFO Liquidation highlights the incompetency of the organization to predict the demands of their products in the market successfully, and it shows the company to better study their standings in the market. The LIFO Liquidation provides a profit for the short term, and the review of the same is to be done to plan better and not fail the expectation of the consumers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “LIFO Liquidation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.