Updated April 5, 2023

Introduction to LINQ SelectMany
LINQ SelectMany is a Category of Query Operator which comes under Projection Operators. SelectMany operator used to select the elements from collection of collection called Nested Collection. SelectMany returns a single result from a nested collection; the result contains the concatenation elements for each source value. SelectMany operator works with combination of records and returns with single result. Here SelectMany operator combines the records from chain of results and then it converts as a resultant set of single result.
Syntax
Let’s identify with the following syntax for LINQ SelectMany operator,
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, int, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TCollection, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TCollection>> collectionSelector, Func<TSource, TCollection, TResult> resultSelector);In this syntax we are using SelectMany to select from combination of records and returns with single result.
How SelectMany works in LINQ?
In LINQ query operator Select and SelectMany come under the Projection Operator. The Select Operator is used to select the values from a collection whereas the SelectMany Operator is used to select the values from the nested collection which is called a collection of the collection The SelectMany operator projects the elements from sequence to IEnumerable<T> and then it finally returns the flat result as one single sequence. To understand clearly the operator works when we having the collection of properties from that we need to specify each and every item to collection one at a time.
Examples
SelectMany operators used to select the elements from a collection of a collection called Nested Collection. SelectMany returns a single result from a nested collection; the result contains the concatenation elements for each source value.
Example #1
Code:
In this program, it describes the first syntax as shown above in the syntax heading as follows; let’s see the following program,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Console_LinQSelectMany
{
//Program_Sample - 1
class Program_LINQ_SelectMany
{
// Getting Employee details in EmployeeClass
public class EmployeeClass
{
public int EmployeeID { get; set; }
public string EmployeeName { get; set; }
public List<DepartmentClass> DepartmentList { get; set; }
}
public class DepartmentClass
{
public string Dept_Name { get; set; }
}
class LinqProgram
{
static public void Main()
{
List<EmployeeClass> employeesList = new List<EmployeeClass>();
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 1,
EmployeeName = "Smith",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Development" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Human-Resources"}
} });
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 2,
EmployeeName = "Gorge",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Designing" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Business-Analyst"}
}
});
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 3,
EmployeeName = "Peter",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Business-Analyst" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Human-Resources"}
}
});
Console.WriteLine("\nLINQ - SelectMany Method");
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------\n");
Console.WriteLine("Department - Names");
Console.WriteLine("------------------\n");
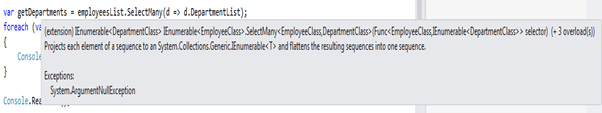
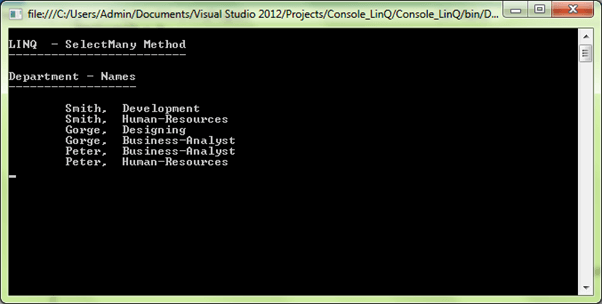
var getDepartments = employeesList.SelectMany(d => d.DepartmentList);
foreach (var dept in getDepartments)
{
Console.WriteLine(dept.Dept_Name);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
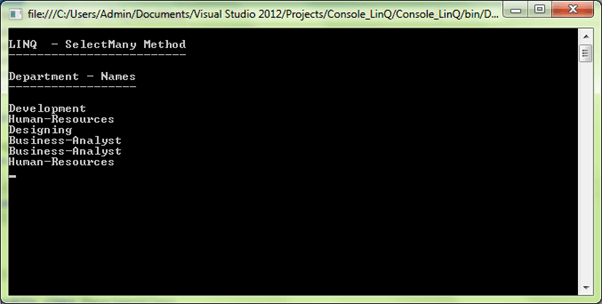
}It is a SelectMany first overloaded method; here it displays the department names linked with each Employee List.
var getDepartments = employeesList.SelectMany(d => d.DepartmentList);Output:
Example #2
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Console_LinQSelectMany
{
//Program_Sample - 2
class Program_LINQ_SelectMany
{
// Getting Employee details in EmployeeClass
public class EmployeeClass
{
public int EmployeeID { get; set; }
public string EmployeeName { get; set; }
public List<DepartmentClass> DepartmentList { get; set; }
}
public class DepartmentClass
{
public string Dept_Name { get; set; }
}
class LinqProgram
{
static public void Main()
{
List<EmployeeClass> employeesList = new List<EmployeeClass>();
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 1,
EmployeeName = "Smith",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Development" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Human-Resources"}
}
});
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 2,
EmployeeName = "Gorge",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Designing" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Business-Analyst"}
}
});
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 3,
EmployeeName = "Peter",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Business-Analyst" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Human-Resources"}
}
});
Console.WriteLine("\nLINQ - SelectMany Method");
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------\n");
Console.WriteLine("Department - Names");
Console.WriteLine("------------------\n");
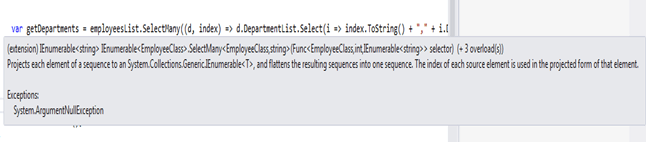
var getDepartments = employeesList.SelectMany((d, index) => d.DepartmentList.Select(i => index.ToString() + "," + i.Dept_Name));
foreach (var dept in getDepartments)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t"+dept);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
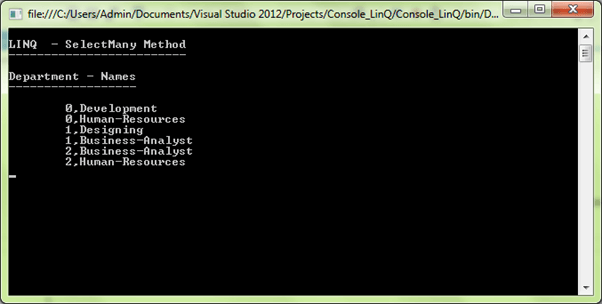
}It is a SelectMany second overloaded method as shown in syntax; here it displays each department name with including the corresponding index value of every object sequence.
Output:
Example #3
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Console_LinQSelectMany
{
//Program_Sample - 3
class Program_LINQ_SelectMany
{
// Getting Employee details in EmployeeClass
public class EmployeeClass
{
public int EmployeeID { get; set; }
public string EmployeeName { get; set; }
public List<DepartmentClass> DepartmentList { get; set; }
}
public class DepartmentClass
{
public string Dept_Name { get; set; }
}
class LinqProgram
{
static public void Main()
{
List<EmployeeClass> employeesList = new List<EmployeeClass>();
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 1,
EmployeeName = "Smith",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Development" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Human-Resources"}
}
});
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 2,
EmployeeName = "Gorge",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Designing" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Business-Analyst"}
}
});
employeesList.Add(new EmployeeClass
{
EmployeeID = 3,
EmployeeName = "Peter",
DepartmentList = new List<DepartmentClass>()
{
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Business-Analyst" },
new DepartmentClass { Dept_Name = "Human-Resources"}
}
});
Console.WriteLine("\nLINQ - SelectMany Method");
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------\n");
Console.WriteLine("Department - Names");
Console.WriteLine("------------------\n");
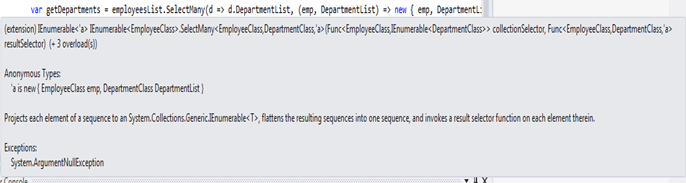
var getDepartments = employeesList.SelectMany(d => d.DepartmentList, (emp, DepartmentList) => new { emp, DepartmentList });
foreach (var item in getDepartments)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t"+item.emp.EmployeeName + ",\t" + item.DepartmentList.Dept_Name);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}In this program it follows the third overloaded method as shown in the above syntax, it displays with the reference type it returns the object type which has reference to both department and employee object of each employee.
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, I hope you have learned the SelectMany Operator easily with several examples. By using the SelectMany method we can return a single result from a nested collection. Hope the article helps to understand by seeing the examples programmatically.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to LINQ SelectMany. Here we discuss the SelectMany Operator easily with several examples along with the programs and outputs. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –