Updated March 20, 2023

Difference Between Linux vs BSD
Linux vs BSD is free and open-source operating systems that are greatly inspired by the Unix operating system. BSD stands for Berkeley Software Distributions. And Linux was developed by a Finnish student Linus Torvalds. Both Linux shares a lot of similarities than differences. But Linux is more popular and widely used as compared to BSD. BSD is a collection of modifications and updates to Bell Unix, which was developed at Berkeley at the University of California. Later it was evolved into a properly operating system. Linux sometimes is also called GNU/Linux because its distributions are built up of multiple software.
Head to Head Comparison Between Linux vs BSD(Infographics)
Below are the top 9 differences between Linux vs BSD:
Key Differences Between Linux vs BSD
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between Linux vs BSD:
Even though there are so many similarities between Linux and BSD, there are so many technical differences between them. Technically speaking, Linux is not an operating system; instead, it is more like a kernel. The core of an operating system is known as Kernel. The kernel is neither considered as software nor hardware. It somewhere lies between hardware and software. An operating system is developed on top of a kernel. A kernel gives the user the advantage of available resources in a system.
Below are mentioned the major key differences between Linux and BSD:
1. Operating system and Kernel
- Technically, Linux is a kernel. Linux Distributions bring together all the software required for creating a whole Linux operating system. There are various Linux Distributions available in the market like Ubuntu, Red Hat, Debian, Mint, Arch, etc. On the other hand, BSD can act as an operating system and a kernel simultaneously. For example, BSD operating systems like NetBSD, FreeBSD, etc., has both Operating System and Kernel. And it is available as a single package.
- The installation of FreeBSD is direct and provides both the Operating System and Kernel. But for installing Linux, a Linux distribution must be chosen first. The Linux Distribution is developed with the use of the Linux Kernel.
- By default, BSD provides a ports system that helps in the installation of various software packages. All the software packages in the ports system are available in the form of source code, which systems should compile before running. They are also available as a binary form that is pre-installed.
2. Licensing difference
- Even though most people do not care much about licensing, licensing differences between both Linux and BSD are very significant.
- Licensing used by Linux is the GNU General Public License, which is commonly known as GPL. In this type of licensing, anybody can add different features or modify Linux Kernel source code according to them, but the source code of the modified Linux Kernel should be released for public use.
- On the other hand, BSD has its own license. BSD license grants developers permission to modify or add new features and components to BSD distributions or Kernel. In BSD licensing, developers need not release their modified source as in Linux. Even though BSD is open-source, a developer who modifies it can declare it as a closed-source if he wants. They also can release source code to anyone.
3. Compatibility and availability of Software
- The public decides the adaptability and popularity of an operating system based on its compatibility and availability of it. The more compatible is an operating system with the latest applications available in the market, and the more it is available, then the more it will become popular among the public. Linux developers can easily modify or add new features to the Linux operating system and can easily release it to the public in the form of binary packages that are pre-compiled and ready for installation.
- These packages can be installed with the help of yum, apt, or any other package managers. This possibility is much easier for the Linux operating system as it is open-source.
- On the other hand, this is difficult in the case of BSD as there are thousands of ports system available to the users for downloading the source code for various programs. These source code should also be compiled in the developer’s system once they are successfully downloaded. This creates a lot of headaches for BSD developers and users, which further leads to the unpopularity of it.
- Even though BSD provides binary packages that are pre-complied to solve this issue, the application programs are still hardly available.
4. The choice between Linux and BSD
- Among Unix-based open-source operating systems, Linux is the most popular one. Because of this reason, Linux has more hardware support than BSD. In the case of FreeBSD, the development team has many tools that allow them to create their own tools for their systems. On the other hand, the GNU suite provides tools for Linux systems that are not customizable.
- The number of applications in BSD is likely to be very less. Developers have built Linux compatibility packages for BSD, which allows the use of Linux applications on the BSD platform. On the other hand, Linux does not have this issue with applications because many public Linux platforms are available.
- There numerous distributions available for Linux platform users. Some of the famous Linux distributions include Red Hat, Debian, Slackware, Gentoo, Puppy Linux, Solus, etc. Major BSD operating systems are OpenBSD, FreeBSD, and NetBSD. macOS, the operating system of Apple PCs, is a closed source operating system of the BSD platform.
Linux vs BSD Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the topmost comparison between Linux vs BSD:
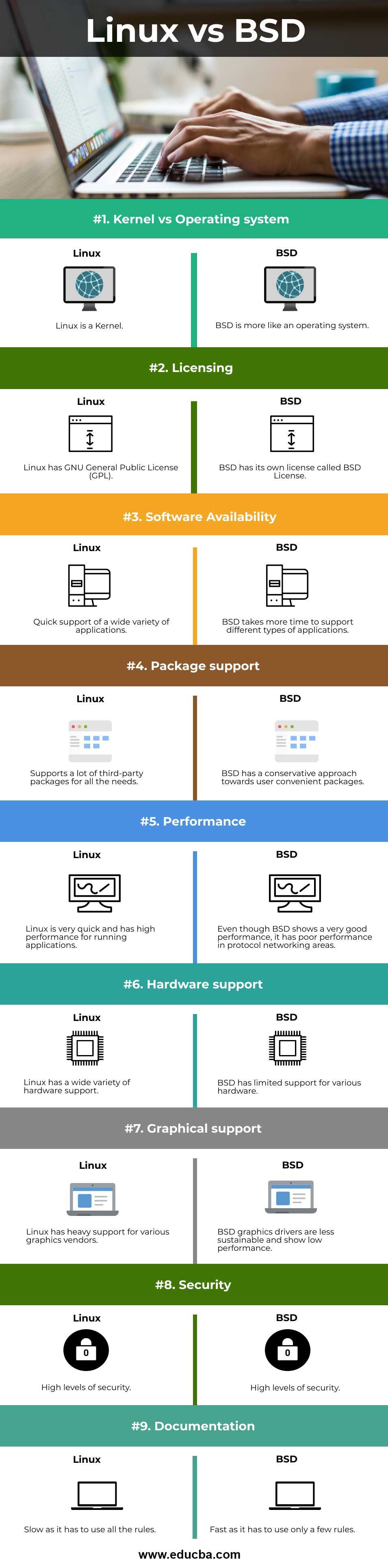
| Comparison | Linux | BSD |
| Kernel vs Operating system | Linux is a Kernel. | BSD is more like an operating system. |
| Licensing | Linux has the GNU General Public License (GPL). | BSD has its own license called BSD License. |
| Software Availability | Quick support of a wide variety of applications. | BSD takes more time to support different types of applications. |
| Package Support | Supports a lot of third-party packages for all the needs. | BSD has a conservative approach to user convenient packages. |
| Performance | Linux is very quick and has high performance for running applications. | Even though BSD shows a very good performance, it has poor performance in protocol networking areas. |
| Hardware support | Linux has a wide variety of hardware support. | BSD has limited support for various hardware. |
| Graphical support | Linux has heavy support for various graphics vendors. | BSD graphics drivers are less sustainable and show low performance. |
| Security | High levels of security. | High levels of security. |
| Documentation | High-quality documentation is available. | High-quality documentation is available. |
Conclusion
Both BSD and Linux are free, an open-source operating system based on Unix. Even though Linux and BSD have many similarities, they have a considerable number of differences too. It is the developer’s choice to choose between Linux and BSD according to their requirements and convenience.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Linux vs BSD. Here we discuss major key differences between Linux vs BSD along with infographics and respective comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –