Difference Between Linux vs FreeBSD
FreeBSD, like Linux, is a free, open-source and secure Berkeley Software Distributions or BSD operating system that is built on top of Unix operating systems. FreeBSD is one of the most popular operating system distributions of BSD. Even though FreeBSD shares many similarities with Linux distributions, they have major differences between them in many important aspects. Comparing to FreeBSD, Linux is widely popular in the market. University of California, Berkeley developed Bell Unix and was later updated and modified in multiple ways and later evolved as the current BSD. FreeBSD is one of the complete open-source BSD operating systems. In this topic, we are going to learn about Linux vs FreeBSD.
Head to Head Comparison Between Linux vs FreeBSD (Infographics)
Below are the top 11 differences between Linux and FreeBSD.
Key Differences Between Linux vs FreeBSD
Below are the major key differences between Linux and FreeBSD.
Both FreeBSD and Linux are open-source, which differs in their licensing and has Unix-like nature. FreeBSD was evolved from Unix operating system over the years after multiple updates and modifications. On the other hand, Linux was developed from scratch as a different alternative for Unix. Both Linux and FreeBSD have divided the file system hierarchy. Also, they both similar kind of shell environments that serves as the primary way of interaction. Apart from these, they also share similar programming API features. Due to various similarities, both Linux and FreeBSD can share many applications and tools with each other.
Some of the differences between Linux and FreeBSD are as follows:
1. Licensing differences
- Differences in licensing of both Linux and FreeBSD is one of the major differences between them.
- All the Linux distributions, Linux Kernel, Linux applications, GNU-based applications are licensed under GNU General Public License or GNU GPL.
- GNU GPL is also called a copyleft
- GNU GPL license gives the freedom to access, share, and modify Linux source code.
- Anyone can access, share and edit Linux without any legal issues due to its GNU GPL license.
- On the other hand, FreeBSD has its own license called a BSD license. All the FreeBSD kernel and all the tools will come under this license.
- In terms of permissibility, BSD License is almost like GNU GPL, but the BSD License derivative work is not required for maintaining the terms of the license.
- Anyone can easily access, share, or modify its source code without contributing the modifications back or releasing the updated source code.
- The original BSD license and copyright certificate should be included, and the updated source code is the only requirement.
- The call of each of the licenses depends completely on the user’s need and their philosophy.
- The GNU GPL license encourages an open and free ecosystem along with sharing.
- Proprietary software should be careful about relying on software that is GNU-based.
- On the other hand, software that is BSD licensed can be incorporated easily and freely into proprietary and closed-source applications.
- This makes BSD software more attractive to most of businesses and developers who hope to commercialize their software as they can directly sell the software retaining their source.
2. Lineage differences
- The history and lineage of the systems is another major difference between Linux and FreeBSD.
- Linus Torvalds developed a Linux kernel to replace MINIX that was very restrictive for education purposes at the University of Helsinki.
- He then combined the developed Linux kernel with multiple GNU components to build a complete Unix-like operating system.
- Linux was completely developed from scratch without using anything from the existed Unix operating system.
- Linux differs from Unix in many ways.
- On the other hand, FreeBSD has close ties with the Unix operating system.
- Berkeley Software Distributions or BSD was developed in Berkeley at the University of California.
- BSD is an extended version of the Unix operating system, and their licensing terms are highly agreeable.
- Later, BSD rewrites all the original licenses with a complete BSD license, and the operating system was later completely replaced with all possible open-source alternatives.
3. The difference in the scope of the system
- In terms of system design and development efforts, differences in the system scope are one of the key differences between Linux and FreeBSD.
- Linux is just a kernel alone and uses various extra components from different sources. But FreeBSD has a kernel along with its own operating system that acts as a single-package unit.
- Even though this difference may look smaller, it affects how you interact and manages the system.
- All the Linux club distributions together to work as a single package, and they together interoperate nicely.
- These components are tracked and managed using package management tools of distribution.
- On the other hand, FreeBSD works as a complete operating system.
- All the FreeBSD software and kernel are developed and well maintained by developers of FreeBSD.
- It is impossible to change the components of this package because it all together works like monolithic software.
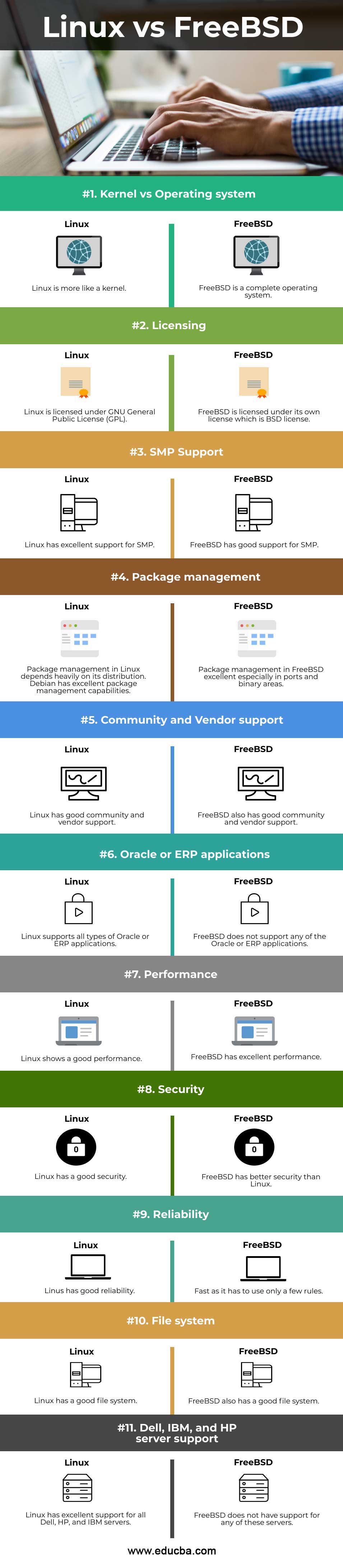
Linux vs FreeBSD Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top 11 difference between Linux and FreeBSD.
| Comparison | Linux | FreeBSD |
| Kernel vs Operating system | Linux is more like a kernel. | FreeBSD is a complete operating system. |
| Licensing | Linux is licensed under GNU General Public License (GPL) | FreeBSD is licensed under its own license, which is the BSD license. |
| SMP Support | Linux has excellent support for SMP. | FreeBSD has good support for SMP. |
| Package management | Package management in Linux depends heavily on its distribution. Debian has excellent package management capabilities. | Package management in FreeBSD excellent, especially in ports and binary areas. |
| Community and Vendor support | Linux has good community and vendor support. | FreeBSD also has good community and vendor support. |
| Oracle or ERP applications | Linux supports all types of Oracle or ERP applications. | FreeBSD does not support any of the Oracle or ERP applications. |
| Performance | Linux shows good performance. | FreeBSD has excellent performance. |
| Security | Linux has good security. | FreeBSD has better security than Linux. |
| Reliability | Linus has good reliability. | FreeBSD has excellent reliability. |
| File system | Linux has a good file system. | FreeBSD also has a good file system. |
| Dell, IBM, and HP server support | Linux has excellent support for all Dell, HP, and IBM servers. | FreeBSD does not have support for any of these servers. |
Conclusion
Both FreeBSD and Linux are Unix-based, free, open-source operating system. Linux and FreeBSD share pretty good similarities, but still, there are many considerable between them. Anyone who wants a full-fledged operating system, they can go for FreeBSD. But if they require just a kernel, Linux is the best option.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Linux vs FreeBSD. Here we discuss the Linux vs FreeBSD key differences with infographics and comparison table, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –