Updated July 11, 2023
What is Liquidation?
The term “liquidation” refers to selling off business assets and distributing the money among the claimants. Such an event usually occurs when a company becomes insolvent, which means it cannot pay its debts and other obligations on time. Hence, the company utilizes the funds generated from Liquidation to repay the shareholders and the creditors.
In short, the company sells off its assets to settle its liabilities, including debts, payables, and other business obligations. In some cases, this process is referred to as dissolution or winding-up.
Key Takeaways
Some of the key takeaways of the article are:
- It is the process of dissolving a company by selling its assets to settle its liabilities. The owners and shareholders retain only the remaining amount.
- It involves selling off inventory and other business assets, usually at steep discounts.
- After liquidating, the entity ceases to exist, and authorities remove it from the company registrar.
- Some of the significant reasons behind Liquidation include inadequate cash flow generation, poor operational performance, the exit of the investors, and indebtedness.
How Does Liquidation Work?
A typical business liquidation process involves the following steps (not exhaustive):
- The directors or management decide to liquidate a business for various reasons, such as inadequate cash flow. Alternatively, a court may initiate a dissolution order in the case of compulsory Liquidation.
- An insolvency professional is appointed as the official liquidator who will take charge of the entire liquidation process.
- The owners are forced to relinquish their powers & authorities, and the insolvency professional takes them over.
- Before commencing the liquidation process, the insolvency professional evaluates the assets to liquidate. In this stage, the liquidator verifies all information regarding the payables and debts of the company.
- Once the liquidation process is over, the authorized liquidator distributes the money among the claimants based on the priority of their orders.
- After the Liquidation, the subject company ceases to exist; hence, its name is taken off the company registrar.
Example of Liquidation
Now, let us look at some examples to understand the concept in the real world.
Example #1
Marka was a UAE-based retail brand confirmed to be bankrupt by a local court, and all of its assets were brought into Liquidation. The company sent legal notices to both its subsidiaries and the parent company. The company’s directors and managers were deprived of all rights.
The court ordered the board of directors to hand over all assets, funds, and documents within five days. They were also instructed to pay 448 million Dirhams. Additionally, the directors faced fines for failing to manage the company and providing appropriate financial information disclosure, thereby attempting to cover up severe cash flow problems.
Example #2
In October 2021, a Singapore-based interior design company, Design Studio Group, decided to wind up the business. The company voluntarily made the decision to wind up, primarily driven by its inability to generate adequate cash flow to repay the outstanding debts. In line with the Liquidation of the parent company, the subsidiary companies have also commenced the voluntary liquidation process. After the winding-up application, the company can no longer resume trading its shares.
What Assets can be Liquidated?
Typically, it takes place as part of a bankruptcy filing process. In general, most businesses liquidate their inventory. However, many other business assets can also be liquidated. Such assets include vehicles, store fixtures, furniture, décor & decorations, art, wall hangings, machinery, tools, equipment, etc.
Liquidation Specialists
Liquidation specialists play a crucial role in addressing one of the most challenging aspects of the liquidation process: the limited time available for asset sales. This situation leads to deep discounts, selling assets well below market value. In such cases, the buying companies can rely on the expertise of liquidation specialists, who facilitate the purchase of all assets at once and sell them in the market at a higher price.
Some especially good companies in liquidation sales include Tuesday Morning, Big Lots, and Ollie’s. These companies usually buy the leftover inventory at much lower than its actual market price. Then they resell them at less than their retail price but still make a massive profit given that the purchase price is significantly lower than the retail price.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Liquidation
Below are some of the significant advantages and disadvantages.
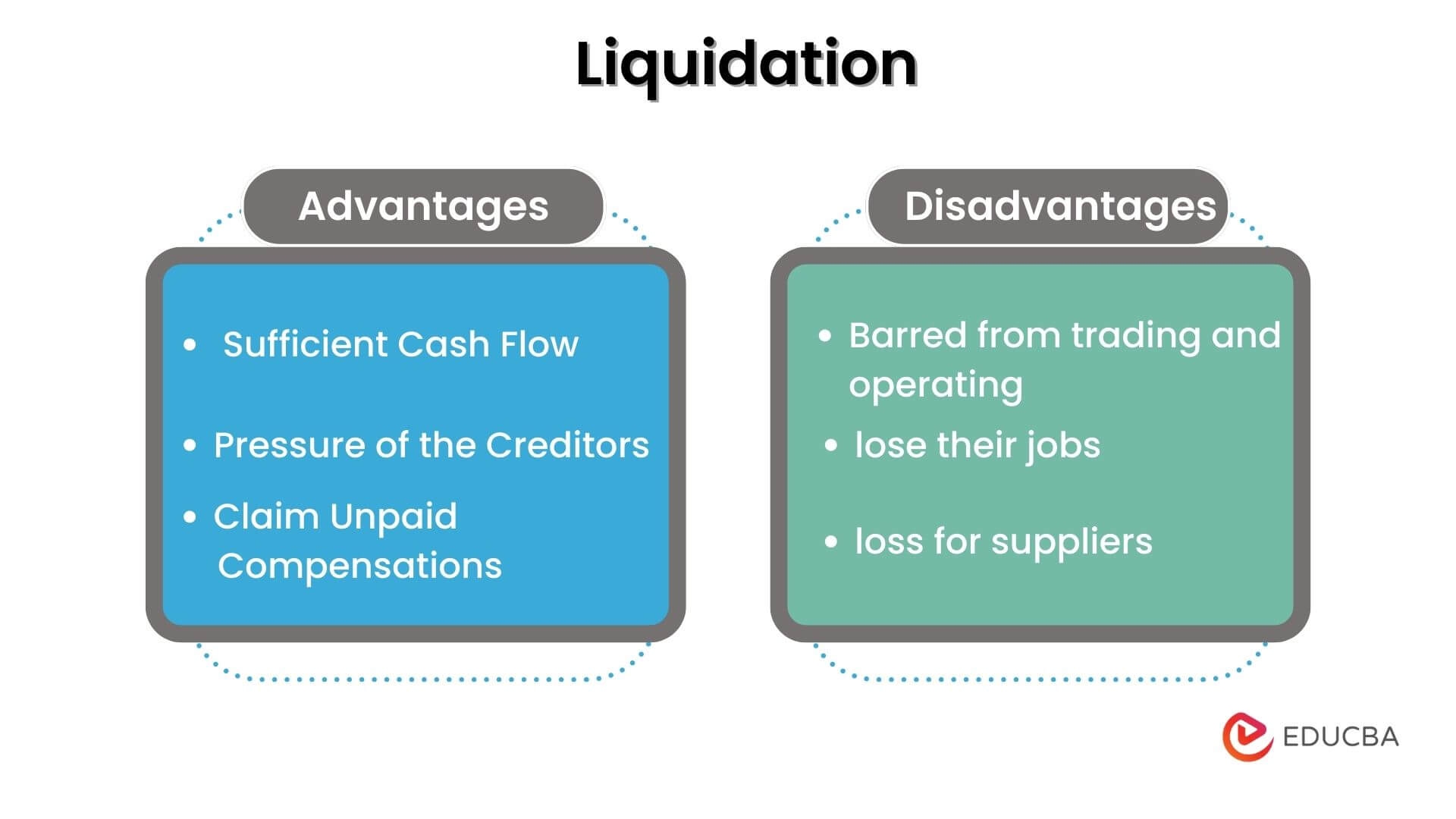
Advantages of Liquidation
- It helps to end the sufferings of an insolvent business struggling to generate sufficient cash flow to cover the business obligations.
- The appointed insolvency professionals eventually handle the creditors, relieving the business owners from the pressure they exert.
- The employees of the liquidated companies may be able to claim unpaid compensation.
Disadvantages of Liquidation
- After liquidation, regulatory authorities will prohibit companies from trading and operating under the same name again.
- The employees of the liquidated companies will probably lose their jobs.
- The business obligations owed to the suppliers beyond the owners’ capacity to pay will be written off, leading to supplier losses.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that Liquidation is a difficult decision for businesses as it involves severe consequences, such as permanent loss of employees, loss of reputation, etc. Most companies see it as a complete termination of future business opportunities. However, they unwillingly opt for it as a last resort to come out of business debts and obligations.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Liquidation. Here we also discuss the definitions, working, examples, specialists, advantages, and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –