Updated November 10, 2023
Difference Between Liquidity vs Solvency
Liquidity refers to the firm’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations or how quickly it can convert its current assets into cash. Assets such as inventory, receivables, equipment, vehicles, and real estate aren’t considered liquid as they can take months to convert to cash. Solvency refers to the firm’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations. One of the primary objectives of any business is to have enough assets to cover its liabilities. This is known as solvency. Along with liquidity, solvency enables businesses to continue operating.
Head To Head Comparison Between Liquidity vs Solvency (Infographics)
Below is the top 8 difference between Liquidity and Solvency
Key Differences Between Liquidity vs Solvency
We may note, before investing, that the relevant factors that need to be looked upon are – liquidity vs solvency, as these are related measures and help the investors to examine the financial health and position of the company carefully. Both Liquidities vs Solvency are popular choices in the market. Let us discuss some of the major differences between Liquidity and Solvency:
- Liquidity refers to the firm’s ability to meet its current liabilities with the help of its current assets. On the other hand, solvency refers to the firm’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations.
- Liquidity can be calculated using current, cash, quick ratio/acid test ratio, etc. However, solvency can be calculated using ratios like debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, debt-to-asset ratio, etc.
- Liquidity is the short-term concept as it relates more to short-term cash flow. On the other hand, solvency is the concept of the long term, which relates more to the long-term financial stability of the firm.
- Better solvency ratios indicate a more creditworthy and financially sound company in the long term. On the other hand, liquidity ratios indicate how easy it will be for the company to raise enough cash or convert assets into cash.
- Liquidity helps to determine the current picture of the firm’s performance, but solvency can determine whether the firm will remain solvent or not.
- A bad Liquidity vs solvency position should be a warning sign to investors. It suggests that the company might be facing trouble meeting its short-term obligations and is struggling to fund its long-term obligations.
- A solvent company owns more than it owes; in other words, it has a positive net worth and a manageable debt load. On the other hand, a company with adequate liquidity may have enough cash available to pay off its current bills.
- Suppose a company finds that it has unexpected expenses but has high liquidity. In that case, it can easily sell some of its cash assets to pay those expenses without facing financial challenges. On the other hand, a company must have lower debts to ensure that they can reinvest in their business to expand operations, as higher debts require to payment of high-interest payments, which will eventually erode all the profits, and the firm will not remain solvent.
Liquidity vs Solvency Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Liquidity vs Solvency
| The basis Of Comparison |
Liquidity |
Solvency |
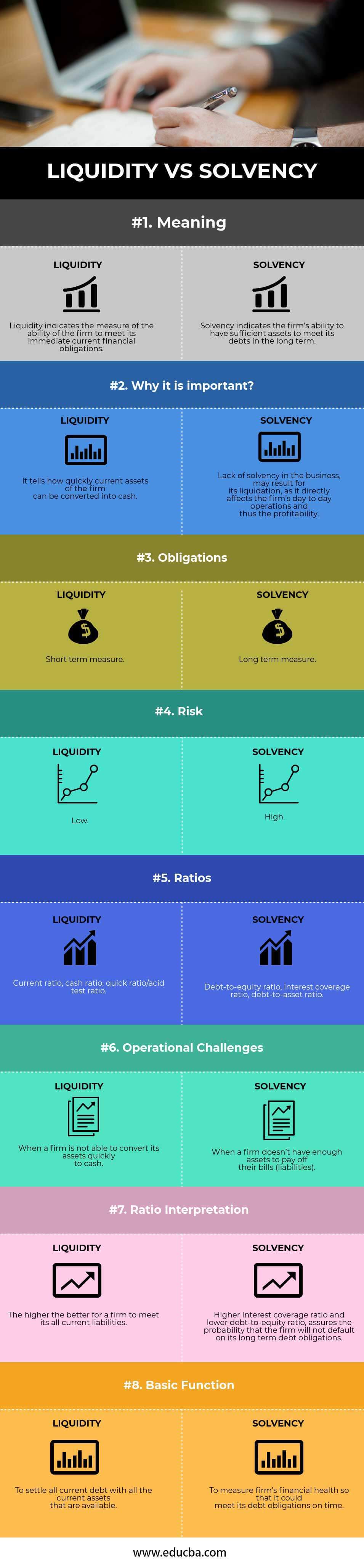
| Meaning | Liquidity indicates the measure of the ability of the firm to meet its immediate current financial obligations. | Solvency indicates the firm’s ability to have sufficient assets to meet its debts in the long term. |
| Why is it important? | It tells how quickly the firm’s assets can be converted into cash. | Lack of solvency in the business may result in its liquidation, as it directly affects the firm’s day-to-day operations and, thus, profitability. |
| Obligations | Short-term measure | Long-term measure |
| Risk | Low | High |
| Ratios | The current ratio, cash ratio, quick ratio/acid test ratio. | Debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, and debt-to-asset ratio. |
| Operational challenges | When a firm is not able to convert its assets quickly to cash. | When a firm doesn’t have enough assets to pay off its bills (liabilities). |
| Ratio interpretation | The higher, the better for a firm to meet all its current liabilities. | A higher Interest coverage ratio and lower debt-to-equity ratio assure the probability that the firm will not default on its long-term debt obligations. |
| Basic function | To settle all current debt with all the available current assets. | To measure a firm’s financial health to meet its debt obligations on time. |
Conclusion
- Moreover, the Liquidity vs Solvency article shows that liquidity and solvency help investors know whether the company can cover its financial obligations. These ratios are used in the credit analysis of the firm by investors, creditors, suppliers, and financial institutions to make a sound/profitable business decision. If the firms can remain liquid or maintain their solvency, they can easily avoid drowning in debt and becoming insolvent.
- In financial stress, such assets can become difficult to convert to cash. Stocks and marketable securities are considered liquid assets because these assets can be converted to cash in a relatively short period of time in the event of a financial emergency.
- The firms own assets, and liabilities are what firms owe on those assets. So, suppose firms have too many liabilities and not enough assets to pay those liabilities. In that case, they will face a financial crisis and eventually be unable to continue the business.
- As mentioned above, a firm’s liquidity and solvency positions can give us a relevant snapshot of its current health and how well it is structured to meet its short and long-term obligations.
- Monitoring liquidity and solvency helps us determine whether a firm is taking on more debt than it can manage; it can also help determine if a firm can realistically pay off those debts in the long term.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Liquidity vs Solvency. Here, we also discuss the Liquidity vs Solvency key differences with infographics and comparison tables. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –