Difference Between Loans vs Advances
The center of these two concepts is Money and Timing. Money is an integral part of any business. Any company must have sufficient money or funds to run the business for investment purposes. There may be situations arising when an individual or a firm may need funds to fulfill their obligations. Loans and advances fulfill different needs, with timing being another distinguishing factor. Every person giving out money or “lends the money” wants his money to grow and return. This growth of money happens over ‘time’.
What is a Loan?
An amount in the form of debt given out by a financial organization to another firm or an individual in exchange for the future repayment of the same amount along with interest over a period.
Before any exchange of funds occurs, each party involved in a transaction mutually agrees upon the loan terms. This contract typically includes the
- The amount lent out,
- The amount to repay,
- The number of payments that shall be made,
- The repayment period,
- And collateral, if any.
A borrower holds collateral, an asset of the same or higher value than the borrowed amount. It is for the security purpose of the Lender in a scenario where a borrower might default on the repayment.
The borrower pays back the loan amount with interest. They can pay as a lump sum or in installments methods. These terms are usually defined in the contract mentioned above.
These funds lent by the lender to the borrower come into use for capital requirements, machine purchases, building construction, etc. The amount is paid back over the years rather than in the short term (within one year).
Credibility is the borrower’s financial position or capacity to repay the loans. Before lending out the money, a lending institution checks for the borrower’s credibility. This analysis is based on his/their firm’s history of financial transactions. Credibility also decides the interest rate the borrower will pay back to the lender.
Focusing on the classification of loans,
- Based on Security
- Secured Loan: The loan is backed by collateral.
- Unsecured Loan: The loan with no asset/ collateral to be pledged. Comes with a greater interest rate as compared to a secured loan.
- Based on Repayment
- Time Loan: The entire loan amount (including interest) paid at a future specified date.
- Installment Loan: A series of small amounts (each payment includes a part of the interest and lent amount) distributed over a period. The amount can be evenly distributed or, as mentioned in the contract.
- Demand Loan: The amount and interest are paid back to the lender upon his request or ‘demand’.
The basis of the purpose of such loans can be
- Car Loan
- Home Loan
- Education Loan
- Commercial Loan
- Personal Loan
What are Advances?
The source of financing provided by the banks to the companies to meet their short-term requirements (less than one year). Contrasting to loans, advances are a credit facility. The central bank (such as the RBI in India) and the lending bank decides the terms of advances rather than a mutual agreement by both parties, like in the case of loans.
Advances are facilitated to the companies under the:
- Primary security: Hypothecation of debtors, promissory notes, etc. In this case, the bank prioritizes repaying the loan before any other private debt holders in the company.
- Collateral Loan: Mortgage of property (land, buildings, etc), other fixed assets like machines, etc
- Guarantees: given by the partners, promoters, directors, etc
Different Types of Bank Advances
- Short-Term Loan: The entire amount is given to the borrower at one time
- Overdraft: a provision by the bank wherein the customer can overdraw money from his/ her account until a specified cap
- Bill Purchase: Advances granted by the bank upon pledging the bills
- Cash credit: A provision by the bank wherein a customer can advance money up to an asset pledged
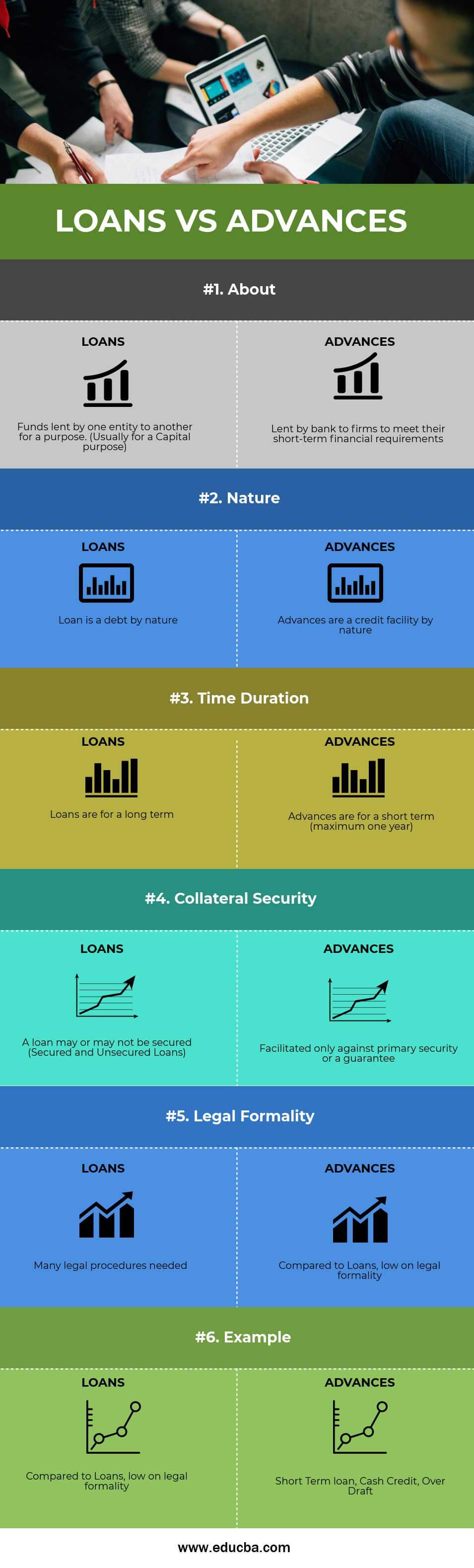
Head To Head Comparison Between Loans vs Advances (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between Loans vs Advances
Key Differences Between Loans vs Advances
Both Loans vs Advances are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences:
- Loans are a source of long-term financing (typically more than a year), whereas advances are a source of short-term funding, that is, to be repaid within less than a year.
- The monetary value of an advance is usually less than that compared to a loan.
- As advances are intended for a short duration, the interest rate charged on them is typically less than that for loans.
- Compared to advances, the legal formalities in obtaining a loan should be lower.
Loans vs Advances Comparison Table
Below are the 6 topmost Comparisons Between Loans vs Advances
|
The Basis Of Comparison |
LOANS |
ADVANCES |
| About | Funds lent by one entity to another for a purpose. (Usually for a Capital purpose) | Lent by a bank to firms to meet their short-term financial requirements |
| Nature | A loan is a debt by nature | Advances are a credit facility by nature |
| Time Duration | Loans are for a long-term | Advances are for a short term (maximum one year) |
| Collateral Security | A loan may or may not be secured (Secured and Unsecured Loans) | Facilitated only against primary security or a guarantee |
| Legal Formality | Many legal procedures needed | Compared to Loans, they are low on legal formality |
| Example | Commercial Loan, Education Loan, Car Loan, Home Loan | Short-Term Loan, Cash Credit, Over Draft |
Conclusion
People often use the terms “advance” and “loan” interchangeably in colloquial language, even though they may have different legal or technical meanings. But technically, both Loans vs Advances are distinct. Based on the requirement, a company that needs financing for a capital purpose shall get a loan. The lender and borrower agree to repay the total sum with interest over a period. A company wanting to bridge its short-term financial requirements shall seek advances from the bank.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top differences between Loans vs Advances. Here we also discuss the Loans vs Advances key differences with infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –