Introduction to Logical Operators in C#
Logical operators in computer programming are operators used to control program flow based on the values of certain conditions. The operands can be considered as a conditional value resulting in a true or false. Although the operators are called logical operators yet their use is not restricted to the Boolean values but they can be used with all the types. The primary function of the logical operators is in the transformation of the relational statements into conditional values. In C# logical operators are used to performing logical operations on two or more operands.
These logical operations include logical AND, logical OR, Logical NOT. The logical operators can be used as logical conditional operators as well as relational conditional operators and the use of operand value in terms of their existence as physical or Boolean value is dependent on the use of the logical operator in the operation. The logical operators are basic translations of the logical GATE operations and follow the exact logic of the logical GATE counterparts.
Logical Operators in C#
Below are explained in detail the top four logical operators in c #:
1. Logical AND Operator
The logical AND operator evaluate to true if the value of both the operands is true i.e. the value of the logical AND operation is only equal to true if and only if the operands used in the operation evaluate to true themselves. The logical operation of AND is denoted by the use of two ampersand &&.
| Name | Description | Syntax | Symbol |
| Logical AND | The logical operation yields true if and only if the value of the operand in non zero | a && b | && |
Truth Table:
| Logical AND | ||
| A | B | OUTPUT |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
2. Logical OR Operator
The logical operator translates to a statement that evaluates to be non zero if any of the values of the operand used in the operation is a non zero entity. The symbols used for logical operation is denoted as ||.
| Name | Description | Syntax | Symbol |
| Logical OR | The logical operation yields true if the value of any of its operand in non zero. | a || b | || |
Truth Table:
| Logical OR | ||
| A | B | OUTPUT |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | TRUE |
| FALSE | TRUE | TRUE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
3. Logical NOT Operator
The physical existence of the logical NOT is based on the negation principle. The logical NOT operator as the name suggests is used in the negation of the primary operand to its logically opposite value.
| Name | Description | Syntax | Symbol |
| Logical NOT | The logical operation yields true if the value of the operand is zero or False. | !a | ! |
4. Logical exclusive OR (Logical XOR)
The logical XOR condition evaluates to true if and only if the value of both the operands in the operation are unequal. This is represented by the symbol ^. This is widely used in conditions where the segregation is required based on the equality of the operands.
| Name | Description | Syntax | Symbol |
| Logical Exclusive OR | The logical operation yields true if the value of both of its operands is unequal. | a^ b | ^ |
Truth Table:
| Logical XOR | ||
| A | B | OUTPUT |
| TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| TRUE | FALSE | TRUE |
| FALSE | TRUE | TRUE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
Examples of Logical Operators in C#
Let us illustrate the above logics using the following examples.
Examples of Logical AND
Following are the examples of logical AND operator in C#.
Example #1
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int X = 11, Y = 10;
bool logicalAND;
// AND operator
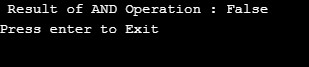
logicalAND = (X <= Y) && (X > 10);
Console.WriteLine(" Result of AND Operation : " + logicalAND);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to Exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
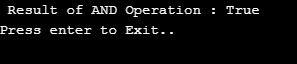
The true value of AND operation comes if we change the value of y.
Example #2
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 11, y = 20;
bool logicalAND;
logicalAND = (x <= y) && (x > 10);
Console.WriteLine(" Result of AND Operation : " + logicalAND);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to Exit..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Examples of Logical OR
Following are the examples of logical OR operator in C#.
Example #1
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int X = 11, Y = 20;
bool logicalOR;
// AND operator
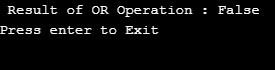
logicalOR = (X >= Y) || (X < 8);
Console.WriteLine(" Result of OR Operation : " + logicalOR);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to Exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
This will evaluate to False as both the logical operands evaluate to a value of false. To demonstrate the true occurrence of the OR operator lets change the value of X to 21 i.e. greater than Y.
Example #2
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int X = 21, Y = 20;
bool logicalOR;
// AND operator
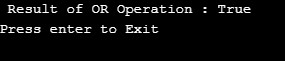
logicalOR = (X >= Y) || (X < 8);
Console.WriteLine(" Result of OR Operation : " + logicalOR);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to Exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Example of Logical NOT
Following are the examples of logical NOT operators in C#.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a = true, logicalNOT;
logicalNOT = !a;
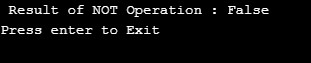
Console.WriteLine(" Result of NOT Operation : " + logicalNOT);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to Exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Example of Logical Exclusive OR
Following are the examples of the logical exclusive OR operator in C#.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int X = 21, Y = 22;
bool logicalXOR;
logicalXOR = (X > Y) ^ (X < 22);
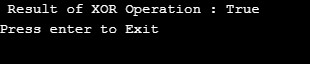
Console.WriteLine(" Result of XOR Operation : " + logicalXOR);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to Exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
This will yield true as the value of X > Y operand is false and X<22 operand is true.
Conclusion
From the above examples, we have become aware of the various logical operators in C#. The primary use of the logical operators is found in decision flow diagrams where they are used in conditional decision making based on the status of the operands.
AND, OR, NOT operators are traditional logical operators used in the condition evaluation whereas XOR is rather a modern operator. The term logical operator comes due to the fact that the output of all the operations involving logical operators is a bool value i.e either true or false.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Logical Operators in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and top 4 logical operators in C# along with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-