Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Logical Operators in PowerShell
We have seen many conditions in if statement, like if($j -lt 10), But if we wanted to check multiple conditions at once, for example, $j -lt 10 and $i -lt 15 .So we have logical operators to tackle this kind of situation. Logical operators in PowerShell combine two or more expressions and statements together. In very simple words if we wanted to convert multiple conditions in a single condition than we can use logical operators in PowerShell. Let us call Logical Operator with the name of LO for syntax.
Syntax:
if(cond1 LO1 cond2 LO2 cond3){
Statement 1
Statement 2
...
}
So in the above syntax (cond1 LO1 cond2 LO2 cond3) combined to make one condition.
In the above syntax (cond1 LO1 cond2 LO2 cond3)=single condition. As it will return a single value combination of multiple conditions.
Examples of Logical Operators in PowerShell
The following are the examples of logical operators in Powershell explained in detail.
Example #1
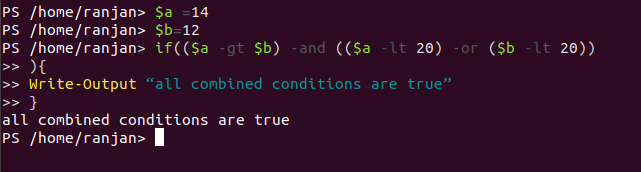
In this example we are combining three conditions all ,($a -gt $b) =one condition,(($a -lt 20) -or ($b -lt 20))=one condition by two combination and ($a -gt $b) -and (($a -lt 20) -or ($b -lt 20)) =one condition, by a combination of all three we are getting one single condition. So if all of these conditions will be true then only output “all combined conditions are true” will be shown.
Code:
$a =14
$b=12
if(($a -gt $b) -and (($a -lt 20) -or ($b -lt 20))
){
Write-Output “all combined conditions are true”
}
Output:
Example #2
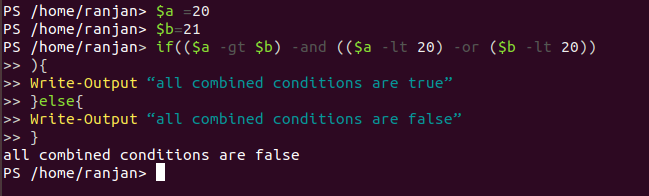
In this example we are combining three conditions all ,($a -gt $b) =one condition,(($a -lt 20) -or ($b -lt 20))=one condition,($a -gt $b) -and (($a -lt 20) -or ($b -lt 20)) =one condition, by a combination of all three we are getting one single condition. Here we can see we are combining all three conditions to form a single condition, their output will be single.
Code:
$a =20
$b=21
if(($a -gt $b) -and (($a -lt 20) -or ($b -lt 20))
){
Write-Output “all combined conditions are true”
}else{
Write-Output “all combined conditions are false”
}
Output:
List of Logical Operators in PowerShell
There are 5 main logical operators in PowerShell, they are “and”, “or”,”xor”,”not=(!)”. let us discuss each with example in brief.
1) -and Operator
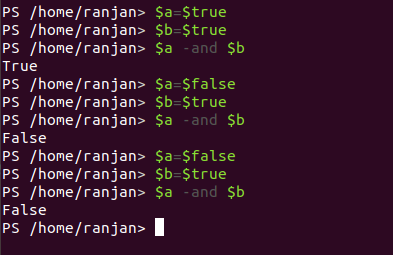
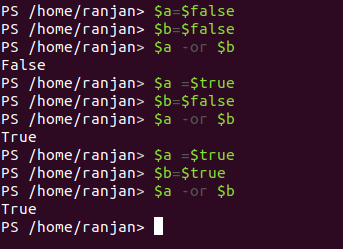
and is called as Logical and, the output of any logical and is True if $a and $b are True otherwise False, below are some examples for logical and operators.
Code:
$a -and $b //false (if both are false)
$a -and $b //false (if any one of them is false)
$a -and $b //true (if both of them are true)
So basically logical and operator true only when both are true. The screen for the execution of the above examples is given below.
Output:
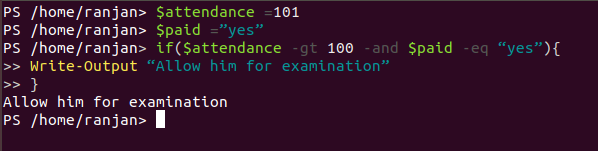
In general and operators used where we want all conditions should be full filled. For example, suppose In a class teacher decided to allow for exams only those students whose attendance is more than 100 and also they paid the class fee. So here both conditions need to full fill.
Code:
$attendance =101
$paid =”yes”
if($attendance -gt 100 -and $paid -eq “yes”){
Write-Output “Allow him for examination”
}
Output:
We can also test this program by passing different inputs value of $attendance and $paid.
2) -or Operator
Logical or, False if $a and $b are False, otherwise some examples are given below:
Code:
$a -or $b //false(if both are false)
$a -or $b //true (if any one of them is true)
$a -or $b //true (if both of them are true)
So basically logical and operator false only when both are false. The screen for the execution of the above examples is given below.
Output:
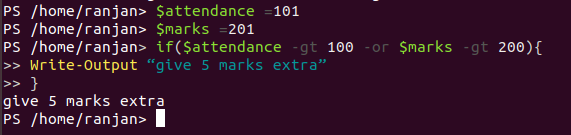
In general or operators are used when we want to consider any condition is true like students having attended more than 100 will get 5 marks extra or the student who scores more than 200 marks.
Code:
$attendance =101
$marks =201
if($attendance -gt 100 -or $marks -gt 200){
Write-Output “give 5 marks extra”
}
Output:
We can also test this program by passing different inputs value of $attendance and $paid.
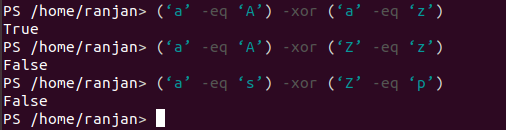
3) -xor Operator
Logical exclusive or ,True if either $a or $b is True,otherwise
Code:
(‘a’ -eq ‘A’) -xor (‘a’ -eq ‘z’) //true as one of them is true
(‘a’ -eq ‘A’) -xor (‘Z’ -eq ‘z’)//false as one of them is false
(‘a’ -eq ‘s’) -xor (‘Z’ -eq ‘p’) //false as both of them are false
Below screen show output of the above example,
Output:
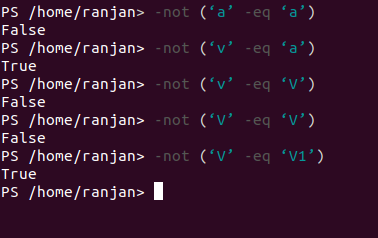
4) -not Operator
Logical not, True if $a is False, otherwise
Code:
-not (‘a’ -eq ‘a’) //false as output of expression is true
-not (‘v’ -eq ‘a’)// true as output expression is false
-not (‘v’ -eq ‘V’) //false as output expression is true
-not (‘V’ -eq ‘V1’) //true as output expression is false
Screen for the above example is given below,
Output:
5) ! Operator
The ! operator is the same as that of the -not operator. Simply! operator converts true to false and false to true.
Code:
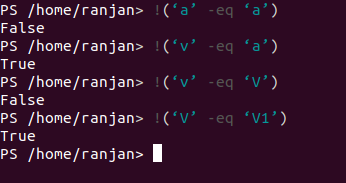
!(‘a’ -eq ‘a’) //false as output of expression is true
!(‘v’ -eq ‘a’)// true as output expression is false
!(‘v’ -eq ‘V’) //false as output expression is true
!(‘V’ -eq ‘V1’) //true as output expression is false
Screen for the above example is given below,
Output:
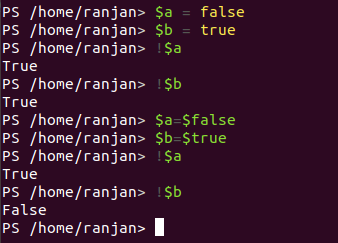
Code:
$a =false
$b=true
!$a //true
!($b) //true
$a=$false
$b=$true
!($a) //true
!($b) //false
Screen for the above example is given below,
Output:
Some real-world examples with mixing all operators together,
Suppose our server and database is running and we want implements certain check were it will check all the time if server and database are running or not.
Code:
if($server -eq “running” -and $database -eq “running”){
Write-Output “server is running and database is running”
}elseif($server -eq “not running” -and $database -eq “running”){
Write-Output “server is not running and database running”
}elseif($server -eq “running” -and $database -eq “not running”){
Write-Output “server is running and database not running”
}else{
Write-Output “server and database both are not running”
}
1st Input:
$server =”not running”;
$database =”running”
2nd Input:
$server =”running”;
$database =”not running”
Conclusion
To conclude, Without a logical operator, our programming will be blank, because of logical operators only we are able to write situational code, we are able to deal with different conditions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Logical Operators in PowerShell. Here we discuss the introduction and top 5 logical operators in Powershell with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –