What is a Loss Leader Pricing Strategy?
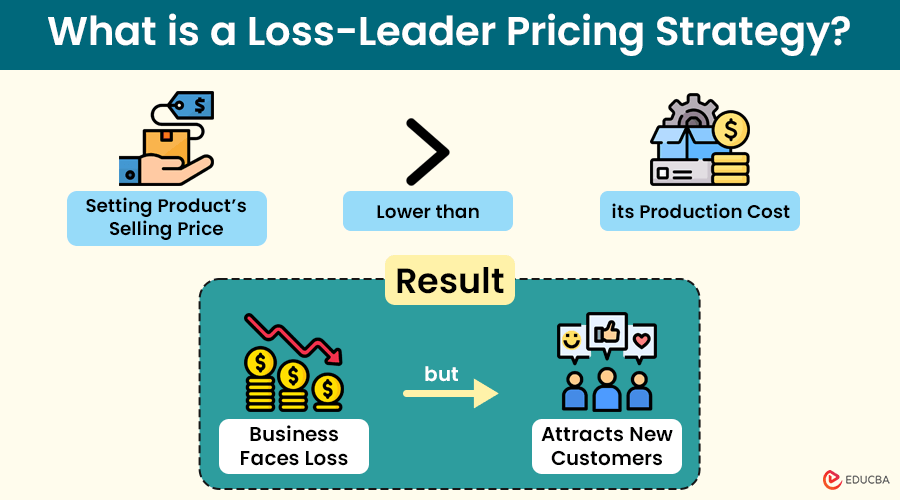
Loss leader pricing is a strategy where businesses sell their products at prices lower than: 1. the cost of production, or 2. the market value of the product. It helps them attract customers, increase sales volume, clear out inventory, and boost market share.
Most companies use this strategy when they are entering a new market and want to be competitive with other competitors in order to sell their products and attract customers.
For example, a clothing store can sell basic t-shirts, which cost $5 to make, at a low price of $4.99. When shoppers come in to buy cheap t-shirts, they often end up buying more expensive items like jeans, jackets, and accessories.
Table of Contents
How Does it Work?
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
#1. The company selects a popular or essential item to sell at a loss.
#2. They set the price of the selected item below market or production cost.
#3. As they advertise the low prices, they attract as many customers as possible.
#4. Once inside the store, customers view a range of other products that retailers strategically sell with a high profit margin.
#5. The customers often select both the loss leader pricing item and other products that don’t have any discounts.
#6. The increased traffic leads to higher overall sales volumes, enhances customer loyalty, and also covers up the business’s loss of selling at lower prices.
Real-World Examples
#1. Costco’s Hot Dogs
Despite inflation, Costco has sold its hot dogs and coke combo for just $1.50 since the 1980s. It is an example of loss leader pricing where their low-cost offering serves as a customer magnet, drawing in shoppers who often make additional purchases throughout the store.
By consistently offering this deal, Costco enhances customer loyalty and leverages the combo to increase foot traffic, boost overall sales volume, clear inventory, and solidify its market share.
#2. ALDI
ALDI is a store popular for its food and beverages section. It often profits from these items, plus other home essentials. Therefore, using loss leader pricing, ALDI sells its non-food products at low rates. This attracts customers, who then buy groceries and other necessities, helping ALDI recover its losses.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of loss leader pricing:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Low prices attract more customers. | Selling products below cost can result in financial losses. |
| Helps quickly sell off excess or outdated stock. | Frequent discounts can make the brand seem cheap. |
| Draws in new customers who might not visit otherwise. | High demand can lead to stock shortages and customer dissatisfaction. |
| Attractive deals can foster loyalty and repeat business. | Pressure to reduce costs can strain supplier relations. |
Final Thoughts
An effective market strategy for surviving in solid markets with a competitive edge should involve selling prices much lower than production. This will shift the old customers of competitive firms to a new base of consumers who are purchasing products much lower than the price they are willing to pay at other companies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What companies use loss leader pricing?
Answer: Many companies across various industries use loss leader pricing. For instance, large retail chains like Walmart and Target frequently use loss leader strategies by offering essential items, like groceries, at below-cost prices to draw customers into their stores. Furthermore, tech companies like Amazon also use loss leader pricing with e-books or devices like the Kindle to encourage customers to purchase more profitable items and services like Amazon Prime memberships and digital content.
Q2. Is loss leader pricing illegal?
Answer: Loss leader pricing is generally legal in many countries, like the US and the UK. However, it can become illegal if it reaches the realm of predatory pricing, where a company sets prices extremely low to eliminate competition and create a monopoly.
Q3. List the various purposes of loss leader pricing.
Answer: The primary purpose of loss leader pricing is to:
- Attract customers
- Increase website or store traffic
- Boost sales
- Increase market share
- Enhance customer loyalty.
Q4. Explain loss leader vs. predatory pricing.
Answer: Loss leader pricing and predatory pricing both involve setting low prices, but they serve different purposes and have different implications.
Loss leader pricing, which is generally legal, aims to attract customers by offering certain products at a loss to encourage the purchase of additional items, thus increasing overall sales and customer loyalty.
Predatory pricing involves setting prices extremely low to drive competitors out of the market. Once they eliminate the competition, they raise prices to monopolistic levels. Predatory pricing is often illegal and is subject to antitrust laws.
Recommended Articles
We hope you found this article on loss leader pricing informative. For similar articles, check these resources.