Updated April 10, 2023
Difference Between LTE vs WIFI
The 4G wireless technology is the third generation partnership that is built on long term evolution. LTE is integrated on the high-speed downlink packet that serves the rapid speed and network protocol to establish a connection through mobile communication components. Wi-Fi enables a few types of computing components that include mobile phones and personal computers and link all the wireless network via a router. The principle of all the wireless technology remains the same, and its major differences and comparison explained in this article.
The Key Differences of LTE vs Wi-Fi The significant difference between LTE vs Wi-Fi are its types, history, considerations, and speed ranges discussed below.
Head to Head Comparison between LTE vs WIFI (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 comparisons between IPS and IDS:
Key Difference Between LTE vs WIFI
Below are some of the key differences between LIT and WIFI:
History of Wireless Networks
The LTE is expanded as Long Term Evolution and released in 2008 based on 3GPP technology. It is developed to work with mobile computing devices like tablets, smartphones, laptops, and personal computers. The availability of LTE technology is limited to several mobile phones that can be accessed only to the 4G network at the implementation time. Wi-Fi technology is implemented in 1999 with the release standard of 802.11b and offers all major functionalities on wireless networking and mobile computing devices. Dissimilar LTE technology, the standards of Wi-Fi needs a router to serve connectivity of the wireless network.
Types of Wireless Network
The LTE technology is available in the varied version of releases, even in the current update of the Release 12 version. The protocol of Wi-Fi involves 802.11b, 802.11n, 802.11g, and 802.11a. The standards of LTE are developed by cumulative efforts of the wireless service provider and electronics manufacturers that include AT&T, Samsung, and T-Mobile. The Wi-Fi standards are designed with suitable specifications by an international enterprise, a Wi-Fi alliance composed of a few related enterprises that work under 3GPP.
1. Speed Range of Wireless Networks
The LTE technology offers a speed rate of data transfer from 100 megabits per second to 1 gigabit per second. Whereas the Wi-Fi standard has the speed rate of data transfer from 11 megabytes per second to 600 megabytes per second. A collection of situations and conditions that cause varying speeds at the time of poor weather, traffic in networks, and every device’s capabilities. The standard of LTE allows the linked components which have widely established network coverage over nationwide. The computing components based on Wi-Fi must remain constant in 300 ft of the wireless router to sustain the wireless network’s functionality.
2. Consideration of Wireless Networks
The user can access the mobile router to gain the benefits of the LTE network. The mobile router enables the communicating devices to associate the wireless service provider of the 4G network with the help of Wi-Fi technology at one end and LTE on the other end. Simultaneously, the Wi-Fi is developed based on 802.16 and maximizes the type of wireless connectivity from 300ft until 30 miles. Wi-Fi is segregated on LTE technology and is relied on a Wi-Fi enabled router for the connection rather than a 4G network of the wireless service provider.
Advantages
LTE is a popular 4G technology, and now it’s at a rapid pace one around, and it is dependent on several factors. It is based on radio waves, unlike Wi-Fi and 3G based on microwaves, so it is developed to operate on the existing hardware components. It also affects the LTE networks to have the best penetration in the remote location to get a maximum coverage span. LTE can be operated on fiber optic cables, gives better codecs for encoding the signals, and improves the transfer of multimedia files and data communications. The wireless signal on Wi-Fi enables other components to link the important transmitter for interactions. It can share files and carries voice messages. The main need for wi-fi is making the component share the wireless signal similar to the phone, computer, or router.
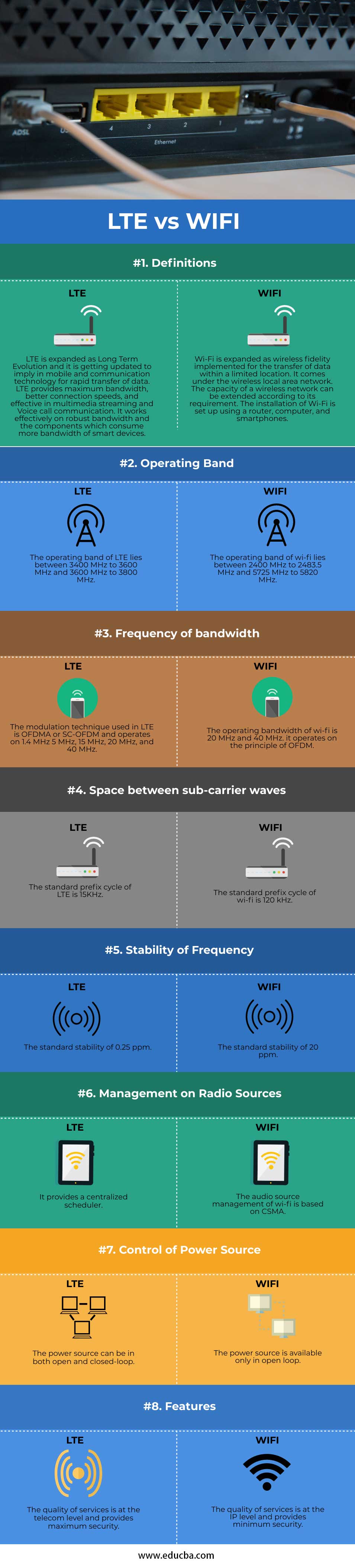
Comparison Table of LTE vs Wi-Fi
Below is the Comparison of LTE vs WIFI:
| Behavioral Elements | LTE | Wi-Fi |
| Definition | LTE is expanded as Long Term Evolution, and it is getting updated to imply in mobile and communication technology for rapid transfer of data. LTE provides maximum bandwidth, better connection speeds and effective in multimedia streaming and Voice call communication. It works effectively on robust bandwidth and the components which consume more bandwidth of smart devices. | Wi-Fi is expanded as wireless fidelity implemented for the transfer of data within a limited location. It comes under the wireless local area network. The capacity of a wireless network can be extended according to its requirement. The installation of Wi-Fi is set up using a router, computer, and smartphones. |
| Operating Band | The operating band of LTE lies between 3400 MHz to 3600 MHz and 3600 MHz to 3800 MHz | The operating band of wi-fi lies between 2400 MHz to 2483.5 MHz and 5725 MHz to 5820 MHz |
| Frequency of bandwidth | The modulation technique used in LTE is OFDMA or SC-OFDM and operates on 1.4 MHz 5 MHz, 15 MHz, 20 MHz, and 40 MHz | The operating bandwidth of wi-fi is 20 MHz and 40 MHz. it operates on the principle of OFDM |
| Space between sub-carrier waves | The standard prefix cycle of LTE is 15KHz. | The standard prefix cycle of wi-fi is 120 kHz |
| Stability of Frequency | The standard stability of 0.25 ppm | The standard stability of 20 ppm |
| Management on Radio Sources | It provides a centralized scheduler. | The audio source management of wi-fi is based on CSMA. |
| Control of Power Source | The power source can be in both open and closed-loop | The power source is available only in an open loop. |
| Features | The quality of services is at the telecom level and provides maximum security. | The quality of services is at the IP level and provides minimum security. |
Conclusion
The use of the internet has been increasing drastically in recent days. LTE or mobile broadband and Wi-Fi are implemented for easy and instant internet access and perform functionalities required for data establishment. The importance of cyberspace and the integration of IoT applications that are implemented via Wi-Fi and LTE to access the internet.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to LTE vs WIFI. Here we discuss the difference between LTE vs WIFI, head to head comparison with infographics, and comparison table. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –