Difference Between Mac and IP Addresses
Mac and IP addresses define the device which is connected to the network. Mac is the physical address of the computer, like our home address. So in a network, various devices can be identified using a Mac address. Whereas IP address defines the connection of network by giving a number. In the article Mac vs IP Addresses, Both addresses are important to connect the device to the network. Mac address is given to the device, and it is unique to the device’s network card. IP address recognizes the connection between computer-to-computer and network-to-network.
MAC Address
- The manufacturer assigns a number to NIC (Network Interface Controller) in the computer hardware component. This number is called the Mac address. Mac address controls the data from the device which is taken by the network. Devices connect to the internet via Ethernet or Wi-Fi, and these use Mac addresses in the network. 12 digits are hexadecimal in Mac address. These 12 digits appear in 6 pairs separated by colons. The first half of the Mac address is manufacturer ID, and the last half is used to identify the device. The first part is also called an Organizational Unique Identifier.
- This number is enrolled in the device during the manufacturing process of the device itself. The manufacturer reuses the second half of the Mac address, i.e. the device identifying the part. However, each Mac address is unique to the network card in the device. The manufacturer has 1.68 million available addresses so that no two devices with the same address appear in the same network. When a device’s network card is burnt, the number starts from 00. Therefore chances are less for the number to be the same. If the two devices with the same Mac address appear in the same network, the network becomes confused to send the data packets to the device. It sends the data to the device that responds first. If it is not the device supposed to receive the data, it becomes a problem for the device, and hence unique address of Mac is preferred. Command prompt gives the Mac address by typing getmac over there.
IP Address
- IP address help to identify the device in the global market. The IP address is written in 4 decimal numbers separated by dots. Some numbers are reserved for special purposes. IPv4 contains 32 bits, whereas IPv6 has 128 bits. Network and device identification are carried out with IPv4 addresses. IPv6 address is written in hexadecimal with 8 sets and 4 digits, and this is separated with colons. IPv6 also has network and device identification. Software configurations help the IP address to bind with the device in the global network.
- Network routing equipment uses the IP addresses for the device. The router is used to hide the IP address. If the device is connected directly, the IP address is visible on the internet. If the device is connected via a router, the internet displays the IP address of the router. A private network is set up by the router so that the device’s IP address is not directly visible on the internet. We can call the IP address the postal address, which makes the data be received without any concern with the route it takes to reach the address.
Head to Head Comparison between Mac and IP Addresses (Infographics)
Below is the top 12 Comparison between Mac vs IP Addresses:
Key Differences between Mac and IP Addresses
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Mac vs IP Addresses:
1. Mac is Media Access Control, whereas IP is Internet Protocol.
2. Mac is the physical address, and IP is the logical address of the device.
3. Mac address identifies the device in the local network, and the IP address identifies the device in the global network.
4. Mac address is always a 6-byte hexadecimal address. The IP address is either IPv4 or IPv6, where IPv4 is 4-byte decimal, and IPv6 is a 16-byte hexadecimal address.
5. There will be only one Mac address for a device. The number of IP addresses of a device is determined by the number of networks it is connected to.
6. Mac address is unique to the device, but the IP address is not unique.
7. The device’s manufacturer gives Mac address, and Internet Service Provider provides an IP address.
8. Mac addresses cannot be hidden from the device, whereas the IP addresses can be hidden using the router.
9. Mac address appears in the Network Interface Layer, and the IP address appears in the Internet layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnections) model.
10. Mac address is hardware-oriented, and IP address is software-oriented.
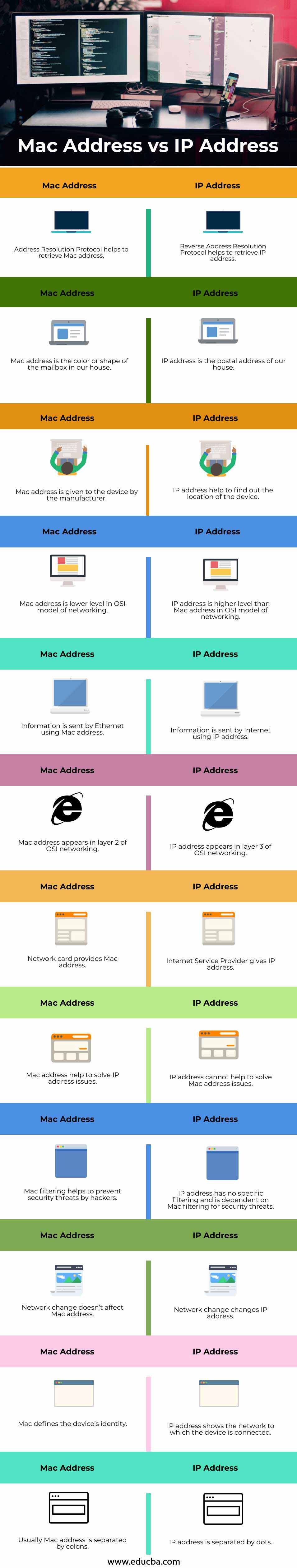
Comparison Table of Mac vs IP Addresses
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Mac vs IP Addresses:
|
Mac Address |
IP Address |
| Address Resolution Protocol helps to retrieve the Mac address. | Reverse Address Resolution Protocol helps to retrieve the IP addresses. |
| Mac address is the color or shape of the mailbox in our house. | The IP address is the postal address of our house. |
| Mac address is given to the device by the manufacturer. | IP address help to find out the location of the device. |
| Mac address is the lower level in the OSI model of networking. | The IP address is at a higher level than the Mac address in the OSI model of networking. |
| Information is sent by Ethernet using a Mac address. | Information is sent by the Internet using IP addresses. |
| Mac address appears in layer 2 of OSI networking. | The IP address appears in layer 3 of OSI networking. |
| The network card provides a Mac address. | Internet Service Provider gives IP address. |
| Mac address help to solve IP address issues. | IP addresses cannot help to solve Mac address issues. |
| Mac filtering helps to prevent security threats by hackers. | The IP address has no specific filtering and is dependent on Mac filtering for security threats. |
| Network change doesn’t affect the Mac address. | Network change changes IP address. |
| Mac defines the device’s identity. | The IP address shows the network to which the device is connected. |
| Usually, the Mac address is separated by colons. | The IP address is separated by dots. |
Both Mac address and IP address are important for a device to function efficiently in a network. While IP address functions more hardware-oriented, Mac address uniquely identifies the device in the local network.
Conclusion
Mac address physically connects the device to the network, and the IP address connects the device logically. The IP address helps in routing the data to the proper device that has a Mac address. IP address gives information about the system being connected to the network, whereas Mac does not. Communication locally is done by the Mac address. Globally the devices are identified by IP addresses. It’s good to have an understanding of both addresses.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Mac vs IP Addresses. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –