Updated April 15, 2023
Difference Between Mainframe vs Server
In Mainframe vs Server, mainframe, a class of computers handles a very large user base, a high volume of transactions, and provides reliable performance. It has abundant processing power and storage to manage robust data processing operations. It is usually deployed in 1. Big organization to manage enterprise-wide mission-critical ERP operations, 2. Banks to handle to trillion of transactions, 3. Back end operations of many digital applications. These computers are robust, rugged, reliable, secured, and available for nonstop 24×7 operations.
Server, It is a computer by hardware, connected in the local area network, wide area network, and internet. It serves its clients with data, specifically intended services using the software installed in it over the various networks. These servers are of multiple types, viz., Mail server, Web server, File server, Application server, Database server, Print server, proxy server, and Management server. The hardware part of these servers can be inexpensive commodity hardware, and the parts can be easily exchanged with parts from any other computers. These servers have minimum storage for storing boot files, and actual data is stored in shared external common storage. These servers are identified by the software loaded into to perform the specific services, not by hardware features.
Head to Head Comparison Between Mainframe vs Server (Infographics)
Below are the top 11 Comparisons between Mainframe and Server
Key Differences between Mainframe vs Server
Let us study some important key differences between Mainframe and Server:
Workloads
The mainframe is used in high volume data-crunching applications, Batch processing, OLTP applications, enterprise-wide deployments (ERP). Ideal for banking application which deals more number-crunching and high traffic of transactions and back end processing for Digital applications. A high level of transaction integrity is maintained in mainframe applications by ensuring all the transactions are committed properly, and all the tables are updated correctly. Consistency of data is paramount in applications where trillions of transactions and terabytes of data are handled. The server focuses more on the service it does for the clients’ machines connected to it rather than the number crunching and transaction processing. Multiple servers doing different functions share the workload. Web applications hosting, File hosting, DNS hosting, application hosting, HTTP services to manage user calls, Internet services are major workloads for the server.
Identity
A class of hardware identifies a mainframe, and they are branded as IBM Z series Z14, Z15 and IBM 1401, system/360, IBM 4341, etc. The mainframe computer is specified by its number-crunching power and data handling ability. The server is identified by the software loaded in it and the typical service that the software can do. Hardware is not a major indicator in the server, and a machine with the low-end specification is sufficient to function as a Server. Service is always tagged in a server’s identity like Application server, Database server, and Proxy server.
Load Factor
The mainframe is rugged in performance even in extreme conditions, as one of the components is overloaded. The mainframe’s performance is steady even if the memory is 80% full or the processor is loaded more. Many redundant features and no single point of failure features are well factored in mainframe design and making it a robust machine. Server performance will get impacted if any of the components are overloaded beyond an extent. Since these servers of commodity class, new servers can be added to the existing servers, and power can be augmented. Additional servers can be kept as standby to take care of failures, and automatic switching can be done easily as User data is kept out of these servers and stored in external storage. External storage has its own redundancies to manage failures.
Communication
Mainframe Components of mainframe computers are interconnected through high-speed channels, and there is a separate subsystem to manage internal input/output operations. This high-speed communication contributes to an overall improvement in the performance of mainframe computers. Server Communication speed is limited to the speed of the network it is connected to, be it LAN or WAN or the Internet.
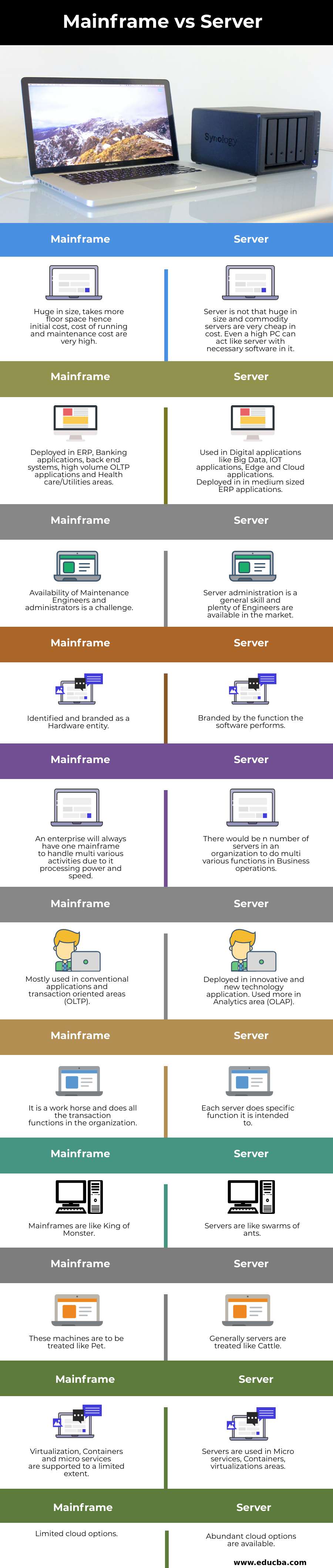
Comparison Table of Mainframe vs Server
Below is the comparison table:
|
Mainframe |
Server |
| Huge in size takes more floor space; hence initial cost, cost of running and maintenance cost are very high. | The server is not that huge in size, and commodity servers are very cheap in cost. Even a high PC can act as a server with the necessary software in it. |
| Deployed in ERP, Banking applications, back end systems, high volume OLTP applications, and Health care/Utility areas. | Used in Digital applications like Big Data, IoT applications, Edge, and Cloud applications. Deployed in medium-sized ERP applications. |
| The availability of Maintenance Engineers and administrators is a challenge. | Server administration is a general skill, and plenty of Engineers are available in the market. |
| Identified and branded as a Hardware entity | Branded by the function the software performs |
| An enterprise will always have one mainframe to handle multivarious activities due to its processing power and speed. | There would be n number of servers in an organization to do multi various functions in Business operations. |
| Mostly used in conventional applications and transaction-oriented areas (OLTP). | Deployed in innovative and new technology applications. Used more in the Analytics area (OLAP) |
| It is a workhorse and does all the transaction functions in the organization. | Each server does specific functions it is intended to. |
| Mainframes are like King of Monster | Servers are like swarms of ants. |
| These machines are to be treated like Pet. | Generally, servers are treated like Cattle. |
| Virtualization, Containers and microservices are supported to a limited extent. | Servers are used in Microservices, Containers, virtualizations areas. |
| Limited cloud options | Abundant cloud options are available. |
Conclusion
IT world is moving to Servers due to its low cost, flexibility, easy maintainability. Servers are ruling the show, and they are at the forefront in the digital world, and new technologies are getting developed with servers in mind for ultimate deployment.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Mainframe vs Server. Here we discuss the difference between Mainframe vs Server, key differences, and comparison table. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –