Updated May 2, 2023

Introduction to Management Styles Leadership
Management styles leadership is a very common word in today’s corporate world. Before going into details, we must first understand who a manager or a leader is:
- A manager is a person with a vision to resolve problems.
- He can make clear and effective decisions under pressure.
- He possesses excellent communication skills.
- A manager has the desire and passion for achieving the goals and objectives of the organization.
- He is well-informed, experienced, and knowledgeable about running an organization effectively.
Thus, we can say that managers have different management qualities and styles of leadership to achieve set goals and objectives. Now, what exactly do we mean by management styles leadership? A manager or a person holding a management position needs to perform numerous roles and functions in an organization. How he handles these different roles and responsibilities depends on the type of management styles, leadership skills, or strategies he adopts. Management styles are strategies, concepts, and theories which a manager adopts to enhance the work environment of an organization. In short, types of management styles leadership is a method one applies to overcome various challenges. It is characterized by the way one makes his decisions and guides his subordinates to perform at their level best.
Types of Management Styles
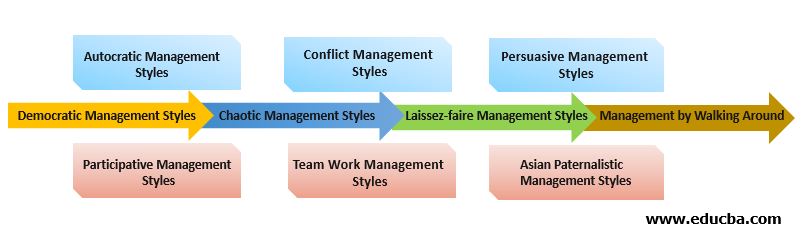
The 10 different types of management styles are as follows:
1. Autocratic
Here the manager prefers to take decisions independently by himself. Such decisions replicate the mindset, opinions, and personality of the decision-maker. In such a situation, subordinates have very little or no say. Autocratic management styles can further subdivide into:
- Directive autocrats: They prefer to take decisions single-handedly and also monitor the actions and work of their subordinates on their own.
- Permissive autocrats: They prefer to take their decisions independently but allow a bit of liberty to their subordinates as to how they will carry out the work or follow the decision.
These types are best in the time of crisis. When the decision from the higher-ups is unavailable due to certain reasons, the manager requires to take up the responsibility and give immediate orders. These orders must be obeyed immediately so that no further problems arise and the situation can be tackled efficiently. Such types of decisions are very common in the defense forces, paramilitary forces, and police forces. It is very effective in certain circumstances, like dealing with militant and terrorist encounters, controlling a mob, etc.
2. Conflict
Here too, the decisions are autocratic, but the decision is made by keeping in mind the interest of its employees. Conflict management styles have encouraged decision-making from the higher-ups and believe in developing a feedback system from the subordinates for the effective working of an organization. Conflict management styles bring motivation among the workforce as their social needs are taken care of, and they develop a sense of loyalty towards the management and organization. This style, on the one hand, can help develop a good relationship between the employer and the employees, indirectly enhancing their performance level. On the other hand, the downline may get used to taking orders from their higher-ups and become completely dependent on them. Restaurant managers and IT consultancies highly use these conflict management styles.
3. Persuasive
Here also, the decision-making is done by the manager. The manager controls the whole decision-making process but in a different way. He works in unison with his subordinates and tries to convince them that the decision is positively beneficial to them. Here too, the manager has his final say but does it through persuasion. This style has its own benefits. The task becomes easy to perform when the subordinates understand why they need to perform a task in the way the manager orders. In this way, the work is executed the way the leader plans it, but after the co-workers fully understand the logistics and reasons behind it.
An added advantage is that the leader can delegate some responsibilities to the subordinates to lower his burden. One disadvantage of this management style is that the subordinates lack creativity and initiative-taking quality and become dependent on their higher-ups, which may also affect the workforce’s overall performance. These types of management styles are common in the banking and insurance sector.
4. Democratic
Here the democratic management styles allow his subordinates to participate in the decision-making process. A consensus is developed before reaching any decision. High-level brainstorming and communication from the top to bottom and vice-versa are followed by a decision. Democratic management styles can be useful in developing competitive marketing strategies; the higher management can provide good information about the organization’s objectives, its profit and sales detail, and what they want from the new market strategy. The bottom-line people can pool in ideas and provide field-based information about shopping trends and habits of the customers. Although these democratic management styles are efficient to some extent, they can also lead to unwanted delays due to the brainstorming sessions and consensus-building process.
5. Chaotic
This is a modern technique in many organizations today. It believes in giving the workers full freedom to work. They can develop their own ideas and strategies to enhance their performance and the organization’s success. The higher-ups do not interfere in any way; they allow their employees to develop a sense of creativity and innovation. These types are best suitable for organizations working on research and innovation development, like pharmaceutical companies.
6. Laissez-faire
This management style emphasizes encouraging the subordinates to develop their own creative ideas and strategies to prosper in their respective fields. Here the higher management plays the role of a guide and advisor; they plunge into action whenever the need arises. They allow their subordinates to work out their own ways to tackle a problem or situation. The manager keeps himself informed about all the activities and interferes or guides whenever and wherever there is a bottleneck.
This management system develops a sense of responsibility and motivation among the workforce. They feel loyal to their organization. But in some cases, a delegation of work and initiative to take responsibility becomes difficult. This management style has effective usage in public sector companies. CEOs of car manufacturing companies use such a style. The CEO sets the sales, revenue, and cost objectives, and the bottom-line managers and employees decide their strategies on how they will fulfill these objectives.
7. Management by Walking Around
Management by Walking Around (MBWA) is a classic technique managers use. Here the manager encourages constant and frequent feedback from its employees. He tries to gather as much information about a situation or problem as possible and uses this information to tackle the problem and avoid any further crisis situations. This style is very efficient for developing objectives, processes, and policies related to the organization as a whole. This management style is limited to taking feedback from the workforce; the decisions depend on the manager’s will. Therefore it may lead to low motivation or initiatives from the workforce. This style can be much more effective if the manager intervenes only in high-level decision-making and leave the smaller issues to the subordinates. This will not only improve the performance of the subordinates, but they will take the initiative to handle problems on their own.
8. Participative
In these types of participative management styles, each worker or employee is assigned a particular type of work. The participative management style ensures that each employee understands his role and works on the project well. He makes them understand how each role played by each employee will bring efficiency and success to the project. Here the manager encourages constant questioning and feedback from his co-workers. Participative management styles ensure that each employee understands his work well and is on the right track regarding working strategies. He provides constant guidelines and assistance where and whenever required. The best example of these management style types is in the JFMs. Or the Joint Forest Management Committees, participative management styles, the executive body, and the general body members or the community people work together to protect the forest and its resources.
9. Team Work
This style encourages the employees and co-workers to pool their knowledge and experience to expedite the project’s work efficiently. It believes in teamwork and coordination building. It encourages solid communication between its team members and the higher-ups. This style emphasizes crisp, efficient presentation; and documentation. Here the manager appreciates and rewards his employees’ team spirit and efforts to encourage motivation among his team members. This management style can be a very efficient hospital setting, where each member has specific duties and responsibilities towards their clients.
10. Asian Paternalistic
In this style, decisions happen considering the benefits of the organization, its employees, and the benefits of the manager himself. Communication is downward, and this style is based on group harmony. This management style demands loyalty and hard work from its employees. The ultimate decision-maker is the manager who keeps into account the benefits he reaps, along with the benefits of the subordinates. Here the decisions are based on understanding what is good for the organization, staff, and its consumers or clients. One of the drawbacks of this system is that the employees depend on the higher-ups when addressing decision-making issues. They lack creativity and initiative-taking ability. Such management styles have wide usage in the oil and gas industries. Here the employees work at high-risk factors. Therefore, the company takes care of all their needs, for example, their accommodation, food, insurance, medical facilities, and so on.
Each type of these has its advantages and disadvantages. Depending on the situation, management professionals use a combination of styles to fulfill their goals and objectives. Apart from these management styles, they use other management strategies in accordance with the needs of the organization and its work. Other management strategies used by professionals are:
- Management by coaching and development
- Management by developing a competitive edge
- Management by developing different decision models
- Management by matrices, or by developing charts and graphics
- Management by organizational development
- Management by developing the performance of its workers
- Management by work simplification
A manager can use whichever management style he finds suitable to resolve a particular problem. But on the whole, he should focus on the profit and success of the organization, along with increasing his employees’ performance and work satisfaction. The perfect combination of positive and advantageous aspects of all management styles can lead to profit, success, and efficient organizational management.
While choosing a management style, the manager or leader should keep in mind the organization’s goals, objectives, values, and culture. It has been found that leaders who have used people-oriented, goal-oriented, and task-oriented management styles have been more successful in developing motivation, commitment, loyalty, profit, and efficiency in the organization. One should remember that management styles can succeed only when efficient managers or leaders handle them. They have proper knowledge about these styles and have the capability and enough experience to make them work so that the organization flourishes in a positive way.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further articles to learn more: