Updated July 7, 2023
Introduction to MATLAB Derivative of Function
MATLAB contains a variety of commands and functions with numerous utilities. This article focuses on how to use the MATLAB command ‘diff’ to calculate the derivative of a function. ‘diff’ command in MATLAB is used to calculate symbolic derivatives. The diff command takes a function, which we want to compute the derivative of, as an argument in its simplest form.
Understanding of Differentiation or Derivatives
Differentiation is a fundamental calculus tool that represents considerable small changes in quantities. Differentiation is a rate at which a function changes w.r.t one of its variables. It calculates the sensitivity to a change of an output value concerning a change in its input value.
For example, an object’s velocity is the derivative of the position of that moving object concerning time. The derivate Velocity here shows how quickly the object’s position changes when time moves. In mathematical terms, it can be shown as dx,dy,dz, etc. It can be written as f(x)/dy, where dy will represent the small change of f (x) with respect to x.
Now that we have refreshed our concepts of differentiation let us now understand how it is computed in MATLAB.
Syntax of derivative:
- diff (f)
- diff (f, var)
- diff (f, n)
- diff (f, var, n)
Examples of Derivative of Function in MATLAB
Now we will understand the above syntax with the help of various examples.
1. diff (f)
diff (f) will differentiate ‘f’ with the variable identified by symvar (f,1)
Here is an example where we compute the differentiation of a function using diff (f):
Lets us take a sine function defined as:
sin (x ^ 3)
Code:
syms f(x)
f(x) = sin (x ^ 3);
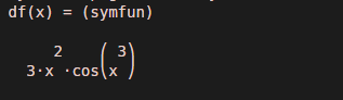
df = diff (f, x)Output:
The function will return the differentiated value of function sin (x ^ 3):
3 x^2 cos (x ^ 3)
2. diff (f, var)
diff (f, var) will differentiate ‘f’ w.r.t the variable passed as an argument (mentioned as ‘var’ in the command).
Here is an example where we compute the differentiation of a function using diff (f, var):
Let us take a sin function defined as:
sin (x * t ^ 4)
Code:
syms x t
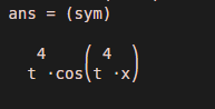
diff (sin (x* t ^ 4))Output:
The function will return the differentiated value of function sin (x * t ^ 4):
t ^ 4 cos(t ^ 4 x)
As we can notice, the function is differentiated w.r.t ‘t.’
3. diff (f, n)
diff (f, n) will compute the nth derivative (as passed in the argument) of the function ‘f’ w.r.t, the variable determined using symvar.
Here is an example where we compute the differentiation of a function using diff (f, n):
Let us take a function defined as:
4t ^ 5
We will compute the 3rd, 4th, and 5th derivative of our function.
Code:
syms t
d3 = diff (4 * t ^ 5, 3)
d4 = diff (4 * t ^ 5, 4)
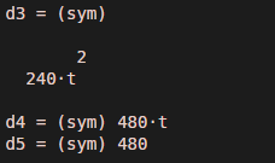
d5 = diff (4 * t ^ 5, 5)Output:
The function will return 3rd, 4th & 5th derivative of function 4t ^ 5 as below:
d3 = 240 t ^ 2
d4 = 480 t
d5 = 480
4. diff (f, var, n)
diff(f, var, n) will compute ‘nth’ derivative of the given function ‘f’ w.r.t, the variable passed in the argument (mentioned as ‘var’ in the syntax).
Here is an example where we compute the differentiation of a function using diff (f, var, n):
Let us take a function defined as:
x * sin (x * t)
Code:
syms x t
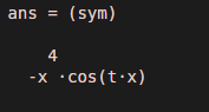
diff (x * sin(x * t), t, 3)Output:
The function will return 3rd derivative of function x * sin (x * t), differentiated w.r.t ‘t’ as below:
-x^4 cos(t x)
As we can notice, our function is differentiated w.r.t. ‘t’, and we have received the 3rd derivative (as per our argument). So, as we learned, ‘diff’ command can be used in MATLAB to compute the derivative of a function. We can also control the degree of derivative we want to calculate by passing ‘n’ (for nth derivative) as an argument.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MATLAB Derivative of Function” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.