Updated August 10, 2023
Introduction to Maya 3D Models
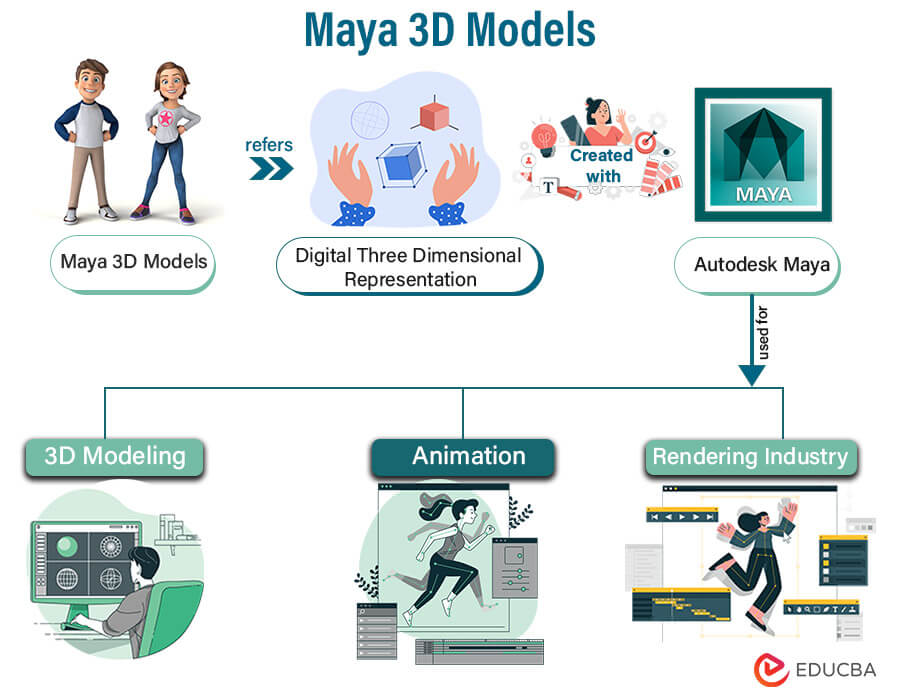
“Maya 3D model” refers to digital three-dimensional representations created with Autodesk Maya, a program frequently used in the 3D modeling, animation, and rendering industries. These models form the basis for making life-like characters, settings, and objects in various fields, such as film, gaming, architecture, and visual effects. Many modeling methods, including polygonal, NURBS, and subdivision surfaces, are available in Maya, each with advantages and uses. Using various Maya tools, artists can sculpt and perfect the models to attain the necessary level of complexity and detail.
The software also offers strong animation features for rigging and animating the models, enabling natural movement and interactions. It also supports a variety of rendering engines, allowing designers to produce stunning images for their projects. In general, Maya 3D models allow artists to let their imaginations run wild and vividly realize their thoughts.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Maya 3D Models
- Understanding 3D Modeling Concepts
- Importance of 3D Models in Maya
- Why Use Maya for 3D Modeling?
- Advantages of Using Maya 3D Models
- How to Create 3D Models in Maya?
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Tips and Tricks for Efficient 3D Modeling in Maya
- Advanced Techniques in Maya 3D Models
Key Takeaways
- 3D modeling involves creating digital representations of objects or scenes in three-dimensional space.
- Maya is a leading software used for 3D modeling, offering a wide range of tools and features.
- 3D models are essential for visualizing and simulating real-world objects, characters, and environments.
- Maya’s capabilities make it ideal for creating complex, detailed 3D models.
- The advantages of using Maya for 3D modeling include its extensive toolset, flexibility, and integration with other software.
Understanding 3D Modeling Concepts
Anyone who wishes to create, manipulate, and deal with three-dimensional objects in a digital environment must have a solid understanding of 3D modeling ideas. Understanding these essential ideas creates the foundation for productive and efficient 3D design, regardless of using 3D modeling software like Maya or any other tool.
The following are some essential 3D modeling ideas to comprehend:
- 3D Space: Work in a three-dimensional space with width, height, and depth while 3D modeling. This is distinct from the usual drawings or paintings’ two-dimensional spaces. It is crucial to comprehend how to move around and manipulate items in this 3D environment.
- Vertices, Edges, and Faces: 3D models comprise vertices, points, and edges that connect vertices, faces, and surfaces bounded by edges. These components determine the 3D models’ essential structure and shape.
- Mesh: The surface of a 3D model is defined by a mesh, which is a group of connected vertices, edges, and faces. It can be composed of quadrilaterals (quads) or triangles. For smooth deformations during animation and rendering, Mesh topology is essential.
- Primitive Objects: These models can be built from the ground up, such as cubes, spheres, cylinders, and cones. Modifications and combinations of simple objects are frequently used to build more complex structures.
- Polygonal Modeling: One of the most popular methods for 3D modeling, polygonal modeling entails using polygonal meshes to produce 3D models. It is appropriate for various applications thanks to its adaptability and simplicity.
- NURBS Modeling: In 3D modeling, non-uniform rational b-splines (NURBS) are mathematical surfaces and curves. NURBS modeling is perfect for producing slick, organic shapes like characters or automobile bodies.
- Sculpting: Digital sculpting uses sculpting brushes to shape 3D models, replicating the process of making sculptures out of clay. It can be used to create complex features and organic shapes.
- UV Mapping: Unwrapping the surface of a 3D object onto a 2D plane is known as UV Mapping. This enables the application of precise textures to the model, improving its appearance and realism.
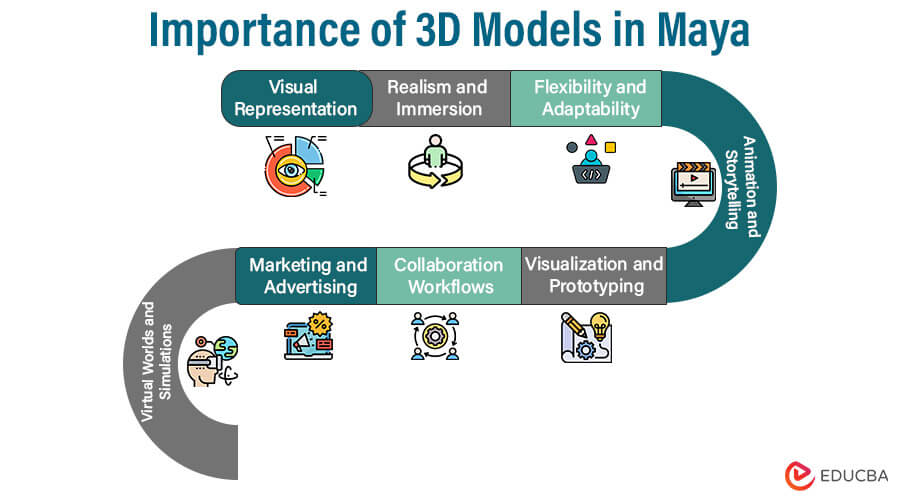
Importance of 3D Models in Maya
The importance of 3D models in Maya is derived from its basic function as the foundation for developing digital content. The flexible 3D computer graphics program Maya offers a variety of tools and functions for building, modifying, and animating 3D objects.
Maya relies heavily on 3D models for the following reasons:
- Visual Representation: Within Maya’s 3D, 3D models are used to visually represent virtual characters, environments, objects, and more. These models provide the creative thoughts of artists and designers in a physical form, allowing them to bring their conceptions and ideas to life.
- Realism and Immersion: Realistic 3D models are crucial for producing immersive and compelling experiences in industries like visual effects, video games, and movies. Maya gives artists the tools they need to create intricate, lifelike models, which enhances the final product’s authenticity and realism.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Maya’s 3D models are incredibly flexible and adaptive. Models are a flexible tool for iterating designs and exploring various concepts because artists can easily edit, relocate, and fine-tune them.
- Animation and Storytelling: In Maya animation is built on 3D objects to tell stories. By rigging and animating these models, artists may create emotive, dynamic individuals that serve as the focus of engrossing stories and storylines.
- Visualization and Prototyping: 3D models are invaluable for conceptualizing ideas and prototypes in architecture and product design. Because of Maya’s precise modeling capabilities, architects and designers may present their concepts and creations realistically and dynamically.
- Collaboration Workflows: Maya’s 3D models allow designers, animators, and other professionals to work effectively together. Teams can retain consistency and speed up the creative process using the same 3D files.
- Marketing and Advertising: 3D models are frequently employed in promotional efforts. Maya gives artists the tools to produce visually appealing product renderings and visualizations that show off items from various angles and viewpoints.
- Virtual Worlds and Simulations: Building 3D models is vital for creating virtual reality environments and simulations. Maya’s 3D modeling capabilities are used by sectors including gaming, virtual reality (VR), and scientific research to create convincing virtual environments and carry out accurate simulations.
Why Use Maya for 3D Modeling?
The following are the main justifications for choosing Maya for 3D modeling:
- Toolset in its Entirety: Maya offers a robust and extensive range of tools exclusively for 3D modeling. Film, animation, video games, architecture, and product design are just a few of the many sectors it serves.
- Polygon and NURBS Modeling: NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) and polygon modeling are both supported by Maya, enabling artists the freedom to design intricate surfaces.
- Workflow Efficiency: The software’s user-friendly interface and adaptable workspace increase artist productivity by letting them concentrate on the creative process rather than technical difficulties.
- Advanced Texturing and Shading: Maya has powerful tools for UV mapping, texture painting, and adding materials, allowing creators to give their 3D models realistic textures.
- Dynamics and Simulations: The dynamics system in Maya enables users to produce lifelike simulations of a variety of effects, such as cloth, hair, fluids, and particles, so increasing the overall realism of the scenes.
- Rendering Capabilities: Maya offers top-notch rendering solutions to display 3D models in all their beauty, whether using its own Arnold rendering engine or external renderers.
- Industry Standard: Professionals widely use Maya, enabling smooth collaboration and sharing of work between artists.
- Large User Base and Resources Online: Maya has a large user base and a wealth of online resources, offering helpful assistance, tutorials, and plugins.
Advantages of Using Maya 3D Models
Using Maya 3D models offers several advantages:
- Versatility: Artists may develop various 3D assets, such as characters, environments, vehicles, and more, using the versatile 3D modeling software Maya. Film, video games, architecture, and product design are just a few of the industries that its rich toolkit and skills make it appropriate.
- High-quality Rendering: Rendering of the highest caliber is possible with Maya thanks to its potent rendering tools, including the photorealistic Arnold renderer. This high-quality rendering is necessary for 3D scenes and animations to be visually attractive and lifelike.
- Animation Tools: Maya is renowned for its sophisticated animation capabilities, which make it a top choice for rigging and character animation. Artists can produce realistic movements and interactions between objects because of the support for keyframe animation, generative animation, and dynamic simulations.
- Industry Standard: Maya has long been a staple in the animation and visual effects fields. This indicates a sizable user base, copious amounts of documentation, and a wealth of internet resources, making it simpler for artists to locate assistance, instructions, and tools.
- Customization and Scripting: Maya’s Python scripting interface enables users to build unique tools and programs. With the help of this feature, artists can automate repetitive operations, create unique workflows, and expand the software’s functionality to suit their unique requirements.
- Collaboration: Maya offers several file types allowing animators, artists, and other team members to collaborate easily. This guarantees optimized production pipelines and efficient procedures for team-based projects.
- Rigging and Character Animation: Character rigging and animation are closely related because Maya’s powerful rigging tools make building intricate character rigs necessary for realistic and fluid character animations simpler. The animation process is simpler by including inverse kinematics (IK), restrictions, and skinning.
- Special Effects and Dynamics: Various tools are available in Maya to create special effects and dynamic simulations. Maya offers strong capabilities to enhance the realism and liveliness of 3D scenes, whether it is via modeling objects like fabric, fluids, hair, or particles.
How to Create 3D Models in Maya?
In Autodesk Maya, the animators and modelers generally create basic models or import complex 3d models into the program. Since Autodesk Maya is mostly used for smooth animations and rendering, the users create the 3D models on software such as Autodesk Max, AutoCAD, or Blender.
But some users also use Autodesk Maya for 3D modeling and Animation. To create 3d models in Maya, the users can use three basic functions or tools.
1. NURBS
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational Basis Splines) 3D modeling is based on creating smooth objects and is used to create arched surfaces with the help of the Bezier tool. The NURBS polymer modeling is commonly used to create interior and exterior designs and is also used in Mechanical Engineering to design automobile 3d models.
Below are the different steps to create 3D models in Autodesk Maya using NURBS:
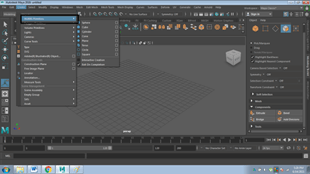
- Install and open Autodesk Maya
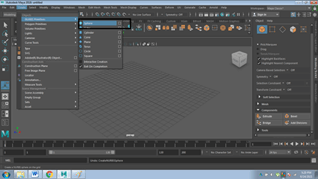
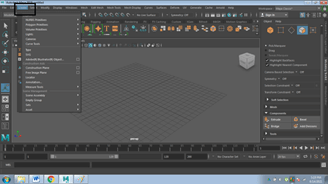
- Click on Menu Bar and Click CREATE, as shown in the image below
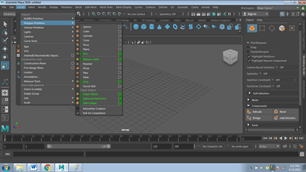
- Click on NURBS PRIMITIVES
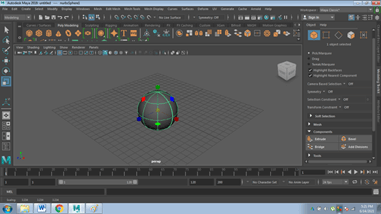
- Click on the object you wish to create.
- For example, we want a sphere, so click on it.
- Drag the mouse and create a sphere.
- Alternatively, you can also click on the Windows > UI Elements > Shelf and click on NURBS Primitives and select any object as required
2. POLYGON
The most basic and first step in creating any 3D model is with the help of Polygon Modeling. Polygon Modeling is based on simpler mathematical calculations and includes edges, vertices, and faces. The user can create simple models using shapes with this modeling function.
This is the best option for modeling when modifying or editing the object. The only setback of this modeling is that it works only with rough or hard edges. For smothering and curvy edges, the user should use NURBS modeling.
Below are the different steps to create models with Polygon Modeling:
- Install and open Autodesk Maya.
- Click on Menu Bar and Click CREATE, as shown in the image below
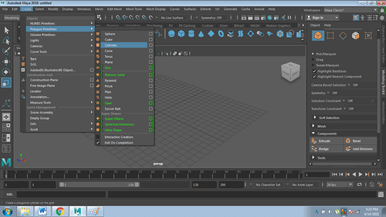
- Click on POLYGON PRIMITIVES.
- Click on the object you wish to create.
- For example, we want a cylinder, so click on it.
- Drag the mouse and create a cylinder.
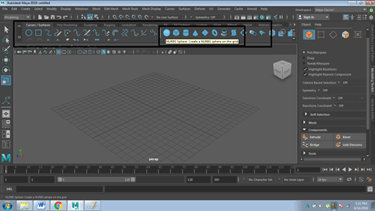
- The user can also use different tools from the OBJECTS PANEL to extrude, bevel, or bridge the surfaces accordingly.
- Alternatively, you can also click on Windows > UI Elements > Shelf and click on POLYGON Primitives and select any object as required.
3. SUBDIVISION SURFACES
These objects use both NURBS and Polygon modeling primitives. These objects have edges, vertices, and faces, but they have curves as NURBS. These objects are much more complicated to create on Maya.
With the help of these primitive tools, the user can create basic and complex models as required. In consideration, Autodesk Maya is expensive and considerate software to purchase only for creating 3D Models. So, designers sometimes download 3D models from online websites, import them into the software, and then create projects and animations with their help.
A huge collection of websites on the internet offers free and importable 3D models of various categories, such as characters, interiors, exteriors, and automobile models.
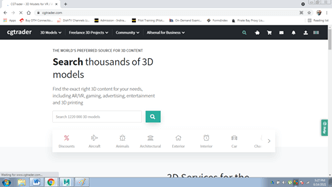
One of the websites that offer free 3D models is CG Trader. Following are the steps to download and import a 3d model on Autodesk Maya:-
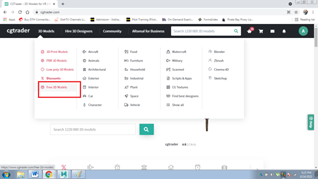
- Go to the website: www.cgtrader.com
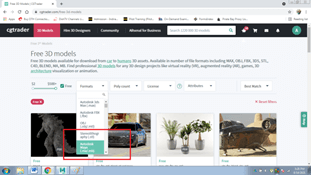
- Search for free 3D models and select the format of the model as shown below:-
- Save the model on the desktop
- Open Autodesk Maya
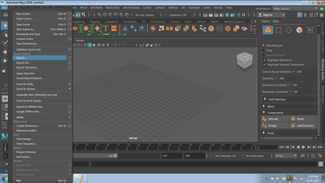
- Select Import from the file menu
- Select the source folder and import the model
- The model will be imported into Autodesk Maya.
- The model can be edited, scaled, or moved also.
Common Issues and Solutions
Here are some common Maya 3D modeling issues and their corresponding solutions:
1. Non-Manifold Geometry
- Problem: Surfaces with improperly connected edges, vertices, or faces are referred to as non-manifold geometry, which causes problems with mesh operations or rendering.
- Solution: Use Maya’s Cleanup or Mesh > Cleanup tools to find and correct non-manifold geometry. To ensure proper connections, modify vertex positions or merge vertices.
2. Holes and Gaps in the Mesh
- Problem: Gaps or holes in meshes might cause rendering artifacts or issues with smoothing and shading.
- Solution: To fill in spaces between vertices or edges, use the Append to Polygon tool. Alternatively, you can fix gaps in the mesh by using the Fill Hole tool.
3. Overlapping or Intersecting Geometry
- Issue: Geometry that overlaps or intersects might produce unfavorable rendering and animation results.
- Solution: Find and eliminate any duplicate or overlapping geometry. Use boolean operations or the Merge vertices tool to unite intersecting surfaces into a single strong mesh.
4. Edge or Face Normal Problems
- Issues: Shading difficulties and changes to the model’s appearance might be brought on by improperly oriented normals.
- Solution: The fix is to choose Normals > Reverse and flip the normals of the affected edges or faces. Activate Display > Polygons > Face Normals or Vertex Normals to view and adjust normals manually.
5. Cleaning Up Topology
- Issue: Poorly organized topology might cause unanticipated deformation when rendering and animating.
- Solution: To improve the mesh’s topology, use modeling tools in Maya like Quad Draw or Target Weld. Aim for evenly spaced polygons and edge loops.
6. Dealing with Non-Smoothed Surfaces
- Issue: Even with smooth shading selected, some surfaces may not appear smooth.
- Solution: Check for irregular vertex placements or non-planar faces as a solution. Vertex pairs that are too near one another should be merged, and any unintended creases or sharp edges should be avoided.
Tips and Tricks for Efficient 3D Modeling in Maya
Effective Maya 3D modeling will help you produce high-quality models faster and streamline your process.
The following advice will help you be more effective:
- Master Maya’s User Interface: Become familiar with Maya’s user interface, hotkeys, and navigational tools. You’ll save time if you know where to look and how to access the key modeling tools rapidly.
- Use Hotkeys and Custom Shortcuts: Use keyboard shortcuts for frequently used commands by learning and utilizing hotkeys and custom shortcuts. Make shortcuts for programs you frequently use but may not have already.
- Customize Your User Interface: Set up your UI to maximize your workflow. Organise tools used frequently together and keep customized layouts for particular activities.
- Modeling Toolkit: Use Maya’s modeling toolkit, which offers a collection of simplified modeling tools that speed up the modeling process.
- Non-Destructive Workflow: Use non-destructive modeling approaches like modifiers, deformers, and history whenever possible. This makes it simple to make modifications without having to start over.
- Quad Draw: The tool can retopologize your models and produce neat topology. It aids in preserving polygon flow and edge loops.
- Marking Menus: Customise the marking menus in Maya to gain rapid access to frequently used modeling tools. By doing this, you can navigate toolbars and menus faster.
- Snapping: To correctly align vertices, edges, or objects, use the snapping settings. Snapping facilitates accurate modeling and lessens the demand for human modifications.
- Reference Pictures: Import reference pictures into your project to direct your modeling process. As you work, it helps to retain shapes and proportions.
Advanced Techniques in Maya 3D Models
Maya 3D models with advanced approaches have more intricate and specialized characteristics that let artists create 3D works with realistic and sophisticated effects.
Let’s explain each of these advanced techniques:
1. Sculpting and Displacement Maps
Similar to sculpting real clay, Maya sculpture includes directly manipulating the vertices of a 3D model with sculpting brushes. This method helps enhance the surface of a model, adding little details and creating organic shapes. Contrarily, displacement maps are grayscale textures that alter a model’s geometry according to the map’s values. Artists may add high-resolution details to their models without adding more polygons by combining sculpting and displacement mapping.
2. Character Rigging and Skinning
The technique of character rigging entails building a digital skeleton (rig) for a 3D character so they may move and be posed flexibly and naturally. The rigging process entails adding joints (bones) to the model and specifying how those joints affect the surrounding geometry. To ensure that the character’s skin deforms properly while the rig is animated, a method known as “skinning” involves allocating the influence of each joint to specific vertices. For realistic character animation, proper rigging and skinning are crucial.
3. Particle Systems and Dynamics
Particle systems simulate and manage swarms of tiny objects or particles in a 3D scene. These particles can represent a variety of natural occurrences, including abstract elements, snowflakes, sparks, and showers. With Maya’s powerful particle systems, artists may create dynamic effects like smoke, flames, explosions, etc. To create realistic simulations, these particle systems interact with other elements and forces in the scene.
4. Fluid and Smoke Simulation
Maya has robust fluid simulation tools let artists produce realistic fluid effects, including liquids, smoke, clouds, and water. To simulate fluids, researchers must solve complex mathematical equations. Still, Maya’s fluid solver gives users control over variables like viscosity, density, and turbulence, resulting in realistic and striking results.
5. Cloth Simulation
Using cloth simulation, artists can design realistic fabric and cloth behavior for clothing or other cloth-like objects. Maya’s cloth simulation system applies the cloth’s stiffness, elasticity, and friction qualities to provide realistic-looking movement and interactions with actors and the environment. Character clothing, flags, curtains, and other fabric-related items frequently use cloth simulation.
6. Fur and Hair Systems
Maya’s fur and hair systems let artists give realistic hair and fur to people, animals, and other scene elements. To specify the size, length, density, and behavior of the hair/fur strands, these systems employ a variety of controls. The simulations account for forces, collisions, and gravity, enabling realistic and dynamic animations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Maya 3D is a well-known and often-used program in the 3D graphics business. Professionals in various creative fields like it because of its extensive toolkit for modeling, animation, and rendering. Maya makes collaborating and creating effective workflows simple because of its easy integration into production pipelines and support for industry-standard formats.
The software’s ongoing updates and strong user base guarantee it stays at the forefront of the industry’s technological innovations. While Maya’s complexity may be intimidating to newcomers, its strength and adaptability make it a crucial tool for producing appealing visual content, including animated films, video games, architectural visualizations, and product designs. Maya 3D’s status as a top 3D program remains solid and dependable as it develops and adapts to shifting demands.
FAQs
Q1. What file formats does Maya support for 3D models?
Ans: The file extensions.ma (Maya ASCII),.mb (Maya Binary),.fbx (Autodesk FBX),.obj (Wavefront OBJ),.dae (Collada), and others can be imported and exported using Maya. The exact use case and the software you use influence your chosen file format.
Q2. Are there any royalty-free Maya 3D models available?
Ans: Yes, a lot of artists offer 3D models that can be used in many projects for free or under a creative commons license. Before utilizing any 3D model, review the licensing terms and conditions to ensure you adhere to the artist’s requests.
Q3. Can I use Maya 3D models for commercial purposes?
Ans: The license that a Maya 3D model is made accessible under will determine the usage rights that come with it. While some models may have limitations on commercial use, others may be freely usable for both private and public purposes. To prevent copyright problems, always review the licensing details provided by the model’s creator.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Maya 3D Models” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.