Updated July 6, 2023
What is a Mixed Economic System?
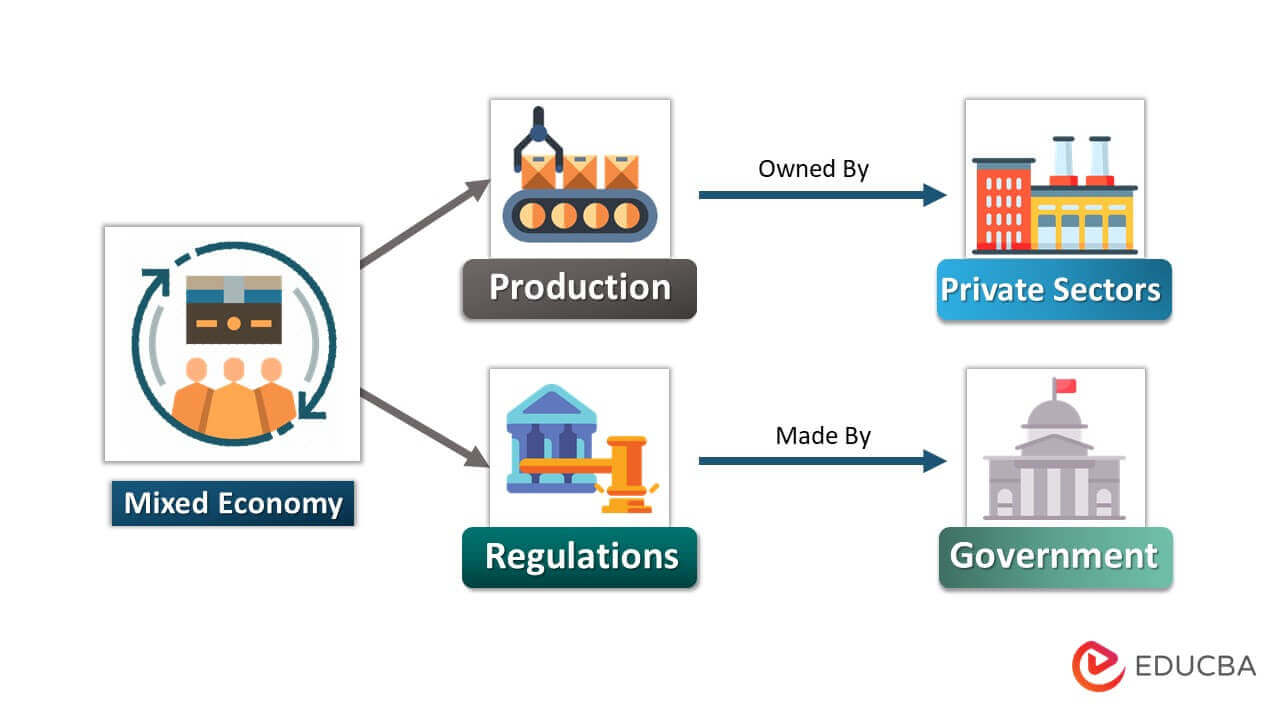
A mixed economic system combines capitalism (private-owned sectors) and socialism (government-owned industries).
For Example, Wales, a country in the southwest of Great Britain, has incorporated a mixed economic system over the last 21 years. Because of mixed economies, there has been an improvement in the country’s employment rate.
A mixed economic system in a country protects private properties and allows a certain level of financial freedom. It will enable governments to intervene in economic activities to achieve various social aims.
Key Highlights
- Mixed economies maintain private ownership of most of the means of production while the government intervenes through regulations.
- Mixed economies specifically socialize industries that are considered essential or produce public goods.
- Some socialistic and free-market elements organize a mixed economy, which lies on a continuum between pure socialism and pure capitalism.
- All known old and modern economies are examples of mixed economies, even though some economists have evaluated the economic effects of various forms of mixed economy.
How Does a Mixed Economic System Work?
A mixed economic system takes on the characteristics of a planned economy and a market economy, i.e., a capitalist and a socialist system. The public and private sectors co-exist in a mixed economic system.
In a capitalist system, the government incentivizes companies to make money by finding ways to maximize efficiency and minimize costs. Here, the government does not own any company or land. Instead, it sets policies regulating the market and providing infrastructure for business owners. The government controls taxes and regulations and does not interfere with business operations. It provides public goods and collects taxes to create more social welfare.
Moreover, in a socialist system, The private sector can decide the use of capital and earn profits. Private enterprises in the market economy can set up businesses and make profits. The supply and demand of the market determine the prices of goods and services and the allocation of resources.
Examples
#1: United States
The United States is a mixed economy, with the federal government spending 38.9 % of its GDP as a share in the development of education, health care, agriculture, and food sectors.
#2: United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is a mixed economy, with the central government spending 47.3% of its GDP on the UK economy. The government provides subsidies for buying houses and has state-run industries that offer jobs to people who work in those industries.
Features
- The government plays a vital role in this type of system because it oversees the companies that operate on its behalf. The government controls prices, wages, and other factors affecting business operations.
- Industries that the government does not own are still subject to oversight from local officials who ensure that profits go back into the community rather than into foreign accounts or other tax havens.
- There is usually some form of social safety the government provides during hard times. They may even offer jobs where there are layoffs because they want people to have options if they need them.
- In terms of business, state-owned enterprises are typically monopolies meaning that only one company in the country provides a service; there is no competition. Because of this, government-owned companies are not profit-driven in the same way that private companies are.
- Government-owned companies focus on providing services to people and increasing their quality of life as much as possible.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| They are suitable for the environment. | It is hard to maintain a balanced economy. |
| It’s much easier to get things done when there is a mix of different types of economies. | It is hard to establish a good relationship between the countries involved in this type of relationship. |
| It allows for greater equality between different types of people, businesses, and various groups within society. | Companies from different countries have to compete with one another. |
| It makes it easier for people to get what they need because there is more opportunity for everyone’s needs to be met by someone else. | The countries involved have to work together to set up their policies, which can be difficult if they have different political views. |
| It’s a system that allows for the free market and government intervention in certain areas, such as health care and education. | People have to pay more for their goods and services because they are not benefiting from government subsidies or incentives. |
| It allows for the creation of large-scale infrastructure projects that would only be possible with public funding. | It can result in inefficient use of resources and a lack of focus on long-term goals. |
| As everyone feels participating in their country’s political life, it fosters a sense of community among citizens. | Contrary to a pure market economy, it is more likely to spark conflict between various social groupings. |
| It allows the government to create jobs by funding public-sector employment. | It can lead to an unequal distribution of wealth between different groups within society, leading to social division and unrest. |
Final Thoughts
A mixed economic system can be a successful way to achieve economic growth and prosperity. The key is maintaining a balance between the private and public sectors. If not, you could end up with an overly centralized system that does not allow innovation or change.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is meant by a mixed economy?
Answer: A mixed economy is a country’s economic system with both public and private ownership of the means of production. The government controls some aspects of the economy while allowing businesses to be more entrepreneurially creative.
Q2. What country uses a mixed economy?
Answer: Many countries use a mixed economy, including Germany, France, Japan, Russia, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
Q3. What are the three advantages of a mixed economy?
Answer: Mixed Economy ensures that it distributes income fairly and impartially. It also provides employment and job security in the country. The country has no monopoly as both public, and private sectors participate in the economic activities.
Q4. What are the disadvantages of having a mixed economy?
Answer: Because of a mixed economy, there is more emphasis on profit at the expense of the citizen’s welfare. There is usually a high level of mismanagement and corruption. Due to a mixed economy, the efficiency is low as the state is involved.
Q5. Why is a mixed economy better than capitalism?
Answer: Mixed economies permit private participation in production, allowing healthy competition that may result in profit. They also contribute to public ownership in manufacturing, which addresses social welfare needs.
Recommended Articles
We hope you find this EDUCBA guide on “Mixed Economic System” helpful. For more information on Economy-related topics, EDUCBA recommends these articles.