Updated March 6, 2023

Difference Between Mobile Apps vs Websites
Mobile apps are applications that are designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones or mobile phones. Websites are web applications that are run on computer devices such as Laptops or Personal Computers. Mobile applications are developed using native cross-platform frameworks to make them compatible across all types of devices. Mobile apps are developed in such a way that they can be easily handled or adjusted to the smaller screen-sized displays for portable devices. Mobile apps are easier to use, and nowadays, they have gained a lot of popularity and is being used by many users where it has portability and can be used at any time. Mobile apps are easily scalable as per the device and screen size, such as Mobile, Smartphones of different screen sizes, tablets, and different screen sizes. The mobile apps basically come from different flavors, such as from different producers like Android from Google or iOS from Apple or Blackberry or a few other cross platforms apps. Here we have discussed Mobile Apps vs Websites.
Websites are web applications that can be opened directly from any web browser using any laptop or personal computer, and even they can be opened in mobile browsers that are compatible and easier to scale the size of the screen or application into the display. The applications developed for the sake of web-based users are more compared to the mobile as it provides a wide variety of options and feasible for different operations.
Head to Head Comparison Between Mobile Apps and Websites (Infographics)
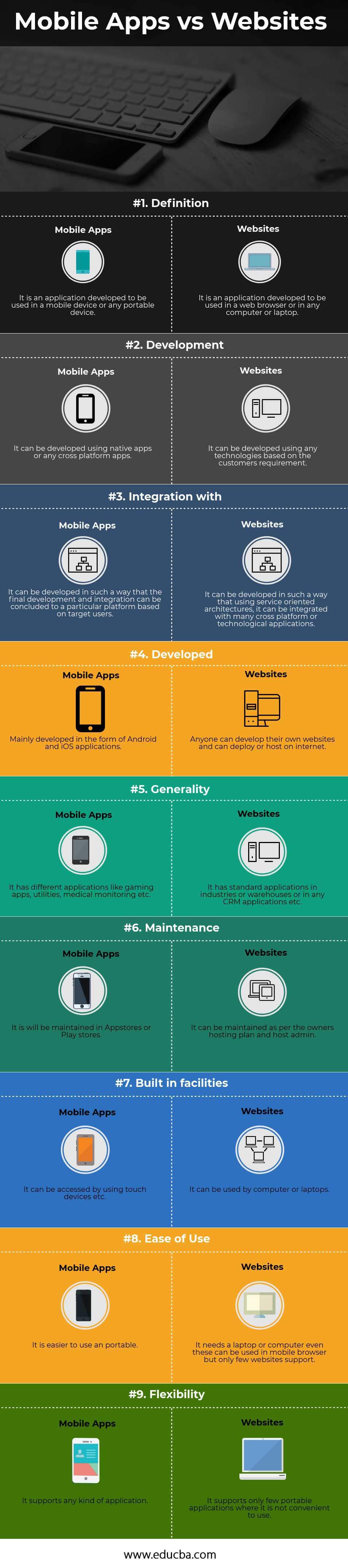
Below are the top 9 comparisons of Mobile Apps and Websites:
Key Differences Between Mobile Apps and Websites
Both Mobile Apps and Websites are popular choices in the market. Let us discuss some of the major Difference Between Mobile Apps vs Websites:
- Mobile Apps are easy to use, compatible with a number of devices, easily upgradable, easily be shareable or downloadable, whereas Websites are not that easier to use as mobile apps are.
- Mobile Apps life cycle is usually smaller where mostly the updates will be released every week or sometimes for even a single day to support several features or bugs or security, whereas Websites have a longer life cycle where they do not need any changes or fixes as per the development plan where it requires immediate changes only in the case of major functionality issues.
- Mobile Apps are less expensive, whereas Websites are more expensive.
- Mobile Apps are easier to maintain, whereas Websites are a bit different to maintain and support their change releases.
- Mobile Apps can easily be brought to more customers in a shorter time, whereas, in the case of Websites, it is not easier.
- Mobile Apps’ initial development and deploying or publishing takes longer time and effort and is easier to maintain once its first version is deployed, whereas, in the case of Websites, it is normal in all the phases of its life cycle.
- Mobile Apps have navigation features, whereas Websites do not have such a feature.
- Mobile Apps are being used recently by every business owner in order to reach most of the customers, whereas Websites are also being used but with normal features or functionality where they are mostly concentrating and making it mandatory for a mobile app.
- Mobile Apps help in retaining the customer for a longer time and can provoke the customers to its businesses by sending push notifications to the customer, whereas Websites have less familiarity with these types of features.
- The number of people who are buying online through mobile devices got increased by 30%, whereas in the case of Websites, it remained the same almost.
Mobile Apps and Websites Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison among Mobile Apps and Websites:
| The basis of comparison |
Mobile Apps |
Websites |
| Definition | It is an application developed to be used in a mobile device or any portable device. | It is an application developed to be used in a web browser or on any computer or laptop. |
| Development | It can be developed using native apps or any cross-platform apps. | It can be developed using any technology based on the customer’s requirement. |
| Integration
with |
It can be developed in such a way that the final development and integration can be concluded to a particular platform based on target users. | It can be developed in such a way that using service-oriented architectures, it can be integrated with many cross-platform or technological applications. |
| Developed | Mainly developed in the form of Android and iOS applications. | Anyone can develop their own websites and can deploy or host on the internet. |
| Generality | It has different applications like gaming apps, utilities, medical monitoring, etc. | It has standard applications in industries or warehouses or in any CRM applications etc. |
| Maintenance | It is will be maintained in App stores or Play stores. | It can be maintained as per the owner’s hosting plan and host admin. |
| Built-in facilities | It can be accessed by using touch devices etc. | It can be used by computers or laptops. |
| Ease of use | It is easier to use a portable. | It needs a laptop or computer; even these can be used in a mobile browser, but only a few websites support it. |
| Flexibility | It supports any kind of application. | It supports only a few portable applications where it is not convenient to use. |
Conclusion
Mobile apps are popular nowadays as the number of Smart Phones users is becoming more and more and provides a variety of features through the mobile apps themselves. The native apps will be developed normally to develop either Android or iOS or any other based on the requirement, whereas web-based application is based only on a single development model. Mobile apps have ba boilerplate code to develop and are easier to develop apps. Even web-based apps have ready-to-use production-grade applications to develop a new website easily.
Mobile apps have a lot of applications, such as utilities, transport, games, etc., to fulfill the daily life requirements of many customers, whereas website apps are less required in terms of portability. In terms of gaming and portable applications such as instant cab booking, QR payments at Point of Sales, or any other outdoor activities where websites can’t be easily accessed, their mobile apps have greater benefits. Ultimately, the requirement of end-users and the number of target customers can be decided to whether to develop a mobile app or website.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the highest distinction among Mobile Apps vs Websites. Here we have discussed Mobile Apps vs Websites head-to-head comparison, a key difference, and infographics and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –