Updated July 10, 2023
Introduction to Mobile IP
Mobile IP is sweet thing; you will be amazed by its significance and benefits. So let’s begin our friendship with “Mobile IP.” Mobile + IP, these two words together are a boon to mobile networking today, without which we can’t even imagine using cell phones and data transfer in them. Let’s know-how:
Mobile, in simple terms, as you all know, means being able to move freely or being portable. For example, a ‘mobile bed’ is a bed that can be folded and freely taken along, essentially a movable bed. The bed remains the same without changing shape or size when you take it anywhere. You keep the bed in your bag & you travel. Mobile IP maintains the same IP regardless of location and keeps all other connection and identification details intact, allowing you to take the IP along.
As your portable bed resides in your bag, your IP resides in your cell phone or any of your digital gadgets connected to a network like the Internet or Intranet. The unchanging constant IP is the core meaning of Mobile IP, the IP being so faithful that even while you travel around or change networks, it remains as it is. Ok, now let’s begin with some questionnaires, and you will love your unnoticed long-time pal, Mobile IP, because of its huge help, which it has given you for a long time.
- Does your movie stop buffering while traveling, and does your location changes from one city to another?
- Did you ever notice that it’s not just you who is traveling but your mobile to travel along with you, but it never says, “Oops? My connection is lost & I am out of network L !!! “
- Does your call disconnect when you are talking to your buddies or your siblings while you are on a train or bus?
The answer to questions no. 1 & 3 is a huge NO 99% of the time. Thanks to. Mobile IP, our connection savior. This is the benefit of Mobile IP: it always helps you STAY CONNECTED to the network. Let us learn more about our fantastic buddy who helps us silently without telling us.
Components of Mobile IP
Here are some essential components that are included in the following mobile IP:
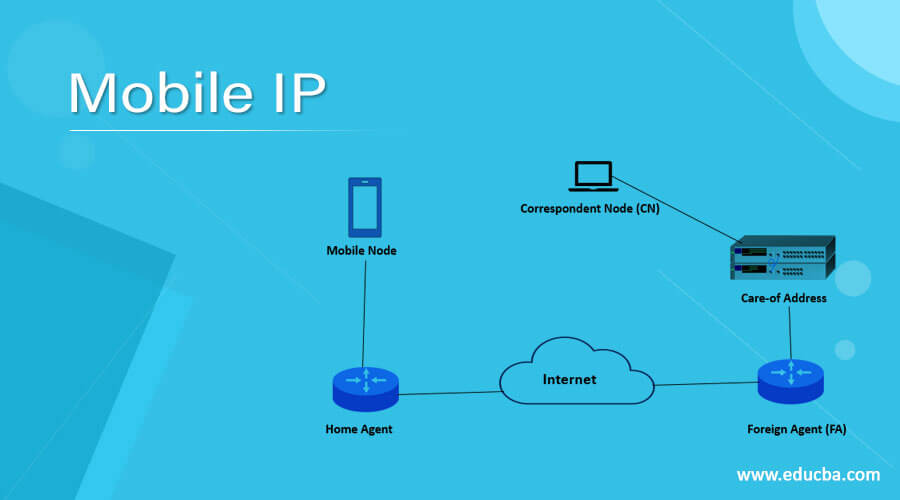
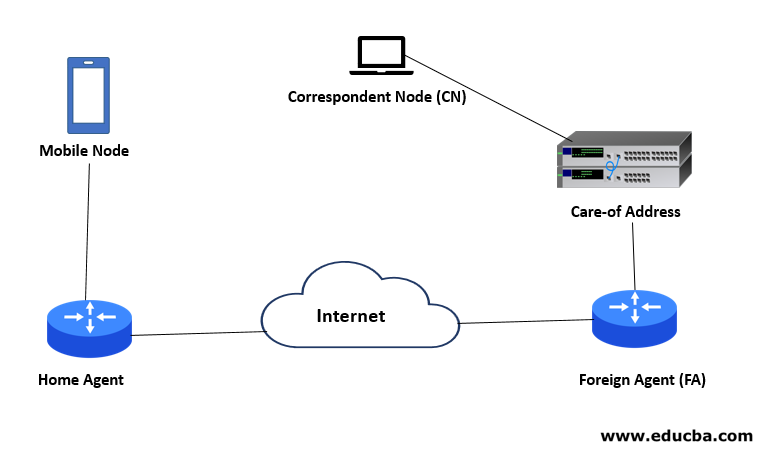
1. Mobile Node
Your devices like a laptop, cell phone, i-pad, etc.
2. Home Agent
Your mobile device is connected to a router located on your home network.
3. Foreign Agent (FA)
- Router to which your mobile device is connected.
- When you are away from your home network, your device uses this agent to send/receive data to and from the HA (Home agent).
- Registers you as a foreigner in the foreign network similar to when you enter a new country, you are registered by a foreign country (as a newcomer) as well as your resident country (as a visitor to a foreign country with all details saved where you are going & why).
4. Care-of Address
- When you take your mobile device outside of its home network (MyHN) & enter a new network zone, your device is assigned a CoA, i.e. care-of address, which tells your home network your current location and that you belong to the family “MyHN.”
- It is usually the IP of the foreign agent.
- For example, when you want to go to a foreign country, you must tell all your care-of details, i.e. details of your home country and everything, to the VISA office and embassy. After you reach a foreign country, they send all the details to your home country where you have arrived, and your ID is, for example, ID-001, so this ID is your care-of address.
5. Correspondent Node (CN)
- It is the node to which your device corresponds (a web server).
- It communicates with your device.
Working on Mobile IP
The explanation below breaks down the three phases that comprise the process:
1. Agent Discovery
- Whenever you enter a network, your device needs to know which network it is, a home network or a foreign network.
- For this, the home agent (HA) & foreign agent (FA) advertise their services so that your device can see those advertisements and discover which one is in which network zone.
- Your mobile node, i.e., your device determines its current point of attachment; if it fails to do so, it attempts to send messages to the agents (HA / FA) to send their advertisements.
2. Registration
- This happens when your device enters a foreign network.
- Your device registers itself by sending its care-of address to its home router/agent via the foreign agent or directly via a collocated care-of address (CCoA), a temporary IP address assigned to it.
- The home router sends the response to your device via FA or directly to CCoA to deliver the data packets.
- The device must register its current location before the expiry of the authenticated request’s registration time.
- Great! They added you to their visitor lists.
- After your registration is successful & authenticated, the foreign and home agents add your device to their visitor lists.
3. Tunneling
- A tunnel is a secure path from HA to FA that ensures the successful delivery of packets to your device.
- Your device sends packets using its home IP address but shows it is always on its home network.
- Reverse tunneling resolves packet drops by establishing a mechanism where the Foreign Agent sends packets back to the Home Agent upon receiving them from the device.
Benefits
- Stay connected & online always (99% efficiency)
- It makes you seamlessly connected to a network always wherever you are, whenever you are.
- No geographical barriers.
- No modification to the home IP address of your device
- Feel safe; they can track your mobile node without changing the IP address.
- Auto-switch & register to a new network zone. You must have noticed that your mobile network automatically “Welcomes” you when you enter a new city; that’s the power of Mobile IP.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Mobile IP. Here we have discussed the basic concept and components of mobile IP, working, and its benefits. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –