Updated June 9, 2023
Difference Between Modem vs Router
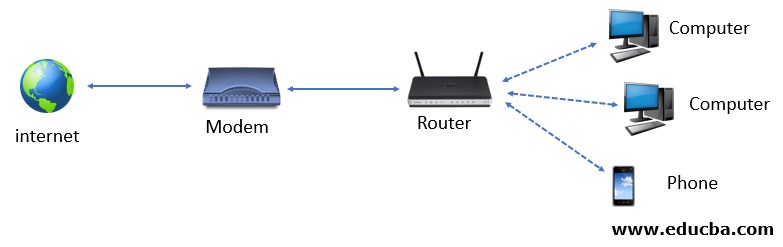
The following article provides an outline for Modem vs Router. A Modem is called a modulator and demodulator. The modem device receives the computer’s digital signal, modulates it, and sends the signal as an analog signal to telephone lines. It can also demodulate the signal in the same process. The modem behaves as a translator between the internet available in public and the computer network. Without a modem, the computer cannot access the internet. The modem transmits the data in packet forms in the data link layer. And its purpose of bringing the information received from the internet to the computer. It does not scan or screen the data packets received. For a single computer connection, the Modem itself can be connected using an Ethernet port and its cable, which connects to the Internet.
Illustration of Modem connected to Router:
Routers are devices that route the data from one LAN to another LAN. The data packets are forwarded between networks. Router carries packets and typically forwards from one router to another through internet working to the destination by managing the traffic and directing the packets through the internet. Routers can connect two or more different networks. Routers work in a manner where only authorized machines are allowed to connect other systems. It also keeps track of activity by logging into files.
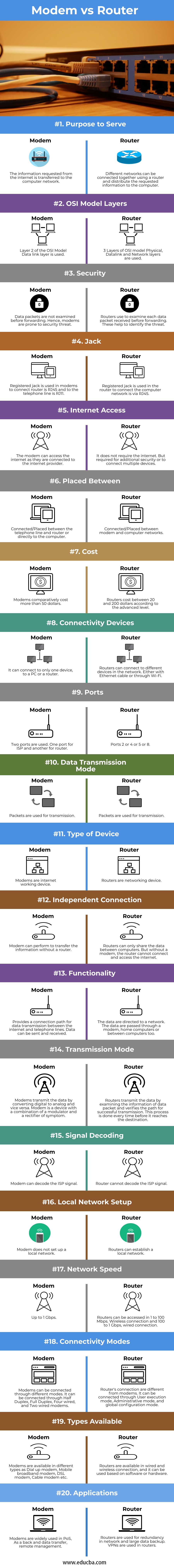
Head to Head Comparison between Modem vs Router (Infographics)
Below are the top 20 comparisons between Modem vs Router:
Key Differences Between Modem vs Router
Let us discuss some key differences between Modem vs Router:
- The router helps connect its device to various networks. The modem device converts the digital to an analog signal called a modulator and converts the analog to a digital called a demodulator.
- The router’s responsibility is to distribute the information received from one computer to others requested in the network. Where Modem has a responsibility to carry the information from the internet to the requested network, and the router does rest.
- When a computer performs an upload on the internet, the modem helps convert digital signals to the analog of the telephone line; download operation is performed opposite in modem. The modem does not analyze the signals received. Where the router analyzes the destination field of a data packet and reads its physical address, then it routes the packet to the specified destination.
- A router is operated on three layers of the OSI model – Physical, Datalink, and Network layer, where the Modem is operated on the Data link layer only.
- Modems can be connected to the computer or network to the public internet. Where the router only directs the traffic in the network by sending packets to specified devices.
- The router checks the packet every time before sending its destination. The firewall implemented in the router helps the computer network from threatening. Where the modem just transfers the data packet without any examination and prone to threat easily.
- Router lies between the modem and computer networks. Modem lines between telephone lines and router.
Modem vs Router Comparison Table
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Modem vs Router:
| Parameters | Modem | Router |
| Purpose to Serve | The information requested from the internet is transferred to the computer network. | Different networks can be connected together using a router and distribute the requested information to the computer. |
| OSI Model Layers | Layer 2 of the OSI Model Data link layer is used. | 3 Layers of OSI model Physical, Datalink and Network layers are used. |
| Security | Data packets are not examined before forwarding. Hence, modems are prone to security threats. | Routers use to examine each data packet received before forwarding. These help to identify the threat. |
| Jack | Registered jack is used in modems to connect router is RJ45, and the telephone line is RJ11. | Registered jack is used in the router to connect the computer network is via RJ45. |
| Internet Access | The modem can access the internet as it are connected to the internet provider. | It does not require the internet. But required for additional security or to connect multiple devices. |
| Placed Between | Connected/Placed between the telephone line and router or directly to the computer. | Connected/Placed between modem and computer networks. |
| Cost | Modems comparatively cost more than 50 dollars. | Routers cost between 20 and 200 dollars according to the advanced level. |
| Connectivity Devices | It can connect to only one device, to a PC or a router. | Routers can connect to different devices in the network. Either with Ethernet cable or through Wi-Fi. |
| Ports | Two ports are used. One port for ISP and another for a router. | Ports 2 or 4 or 5 or 8. |
| Data Transmission Mode | Packets are used for transmission. | Packets are used for transmission. |
| Type of Device | Modems are internet working device. | Routers are networking device. |
| Independent Connection | The modem can perform to transfer the information without a router. | Routers can only share the data between computers. But without a modem, the router cannot connect and access the internet. |
| Functionality | Provides a connection path for data transmission between the internet and telephone lines. Data can be sent and received. | The data are directed to a network. The data are passed through a modem, home computers or between computers too. |
| Transmission Mode | Modems transmit the data by converting digital to analog and vice versa. A modem is a device with a combination of a modulator and a rectifier of symptoms. | Routers transmit the data by examining the information of the data packet and verifies the path for successful transmission. This process is done every time before it reaches the destination. |
| Signal Decoding | The modem can decode the ISP signal. | A router cannot decode the ISP signal. |
| Local Network Setup | The modem does not set up a local network. | Routers can establish a local network. |
| Network Speed | Up to 1 Gbps. | Routers can be accessed in 1 to 100 Mbps. Wireless connection and 100 to 1 Gbps, wired connection. |
| Connectivity Modes | Modems can be connected through different modes. It can be connected through Half Duplex, Full Duplex, Four wired, and Two wired modems. | Router’s connection is different from modems. It can be connected through User execution mode, Administrative mode, and global configuration mode. |
| Types Available | Modems are available in different types as Dial up modem, Mobile broadband modem, DSL modem, Cable modem etc. | Routers are available in a wired and wireless connection, and it can be used based on software or hardware. |
|
Applications
|
Modems are widely used in PoS, As a back and data transfer, remote management. | Routers are used for redundancy in network and large data backup. VPNs are used in routers. |
Conclusion
The basic functionality of routers and modems are discussed with their operation mode and working principle. The router and modem can be combined as a single device and used as a hybrid device. This is called as a gateway and is provided by specific providers only.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Modem vs Router. Here we also discuss the Modem vs Router key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –