Updated April 7, 2023
Difference Between MPLS vs Internet
MPLS and the Internet are two of the core options customers examine for connectivity across numerous locations of an Enterprise. Though MPLS connectivity is a secure and very solid proposition at a premium cost, the Internet is another low-cost option that businesses may investigate, although it comes with certain drawbacks. MPLS, as well as Internet networks, enable full mesh communication across sites, allowing each location to connect to every other location via MPLS or the Internet, allowing for direct site-to-site contact. Both MPLS and Internet networks can be ended on a variety of layer 1 mediums, including T1, Ethernet, DSL, wireless, cable, and fiber also.
Head to Head Comparison between MPLS vs Internet (Infographics)
Below are the top 12 differences between MPLS vs Internet:
Key Differences between MPLS vs Internet
Some of the key differences between MPLS vs Internet are:
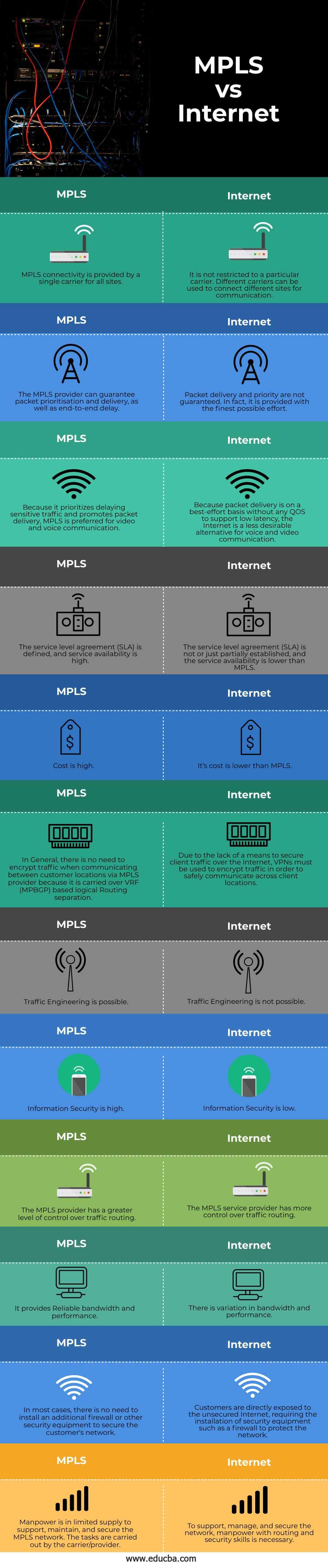
- MPLS connectivity is provided by a single carrier for all sites. Whereas on the internet, It is not restricted to a particular carrier. Different carriers can be used to connect different sites for communication.
- The MPLS provider can guarantee packet prioritization and delivery, as well as end-to-end delay. On the other hand, on the internet, Packet delivery and priority are not guaranteed. In fact, it is provided with the finest possible effort.
- Because it prioritizes delaying sensitive traffic and promotes packet delivery, MPLS is preferred for video and voice communication. Whereas Because packet delivery is on a best-effort basis without any QOS to support low latency, the Internet is a less desirable alternative for voice and video communication.
- In MPLS, the service level agreement (SLA) is defined, and service availability is high. While on the internet, the service level agreement (SLA) is not or just partially established, and the service availability is lower than MPLS.
- The cost of MPLS is high and the internet’s cost is lower than MPLS.
- In General, there is no need to encrypt traffic when communicating between customer locations via MPLS provider because it is carried over VRF (MPBGP) based logical Routing separation while Due to the lack of a means to secure client traffic over the Internet, VPNs must be used to encrypt traffic in order to safely communicate across client locations.
- In MPLS, Traffic Engineering is possible where on the internet, Traffic Engineering is not possible.
- Information Security is high in MPLS. The Internet has Information Security is low.
- The MPLS provider has a greater level of control over traffic routing whereas the internet provider has more control over traffic routing.
- It provides Reliable bandwidth and performance. Whereas There is variation in bandwidth and performance.
- In MPLS, In most cases, there is no need to install an additional firewall or other security equipment to secure the customer’s network while Customers are directly exposed to the unsecured Internet, requiring the installation of security equipment such as a firewall to protect the network.
- In MPLS, Manpower is in limited supply to support, maintain, and secure the MPLS network. The tasks are carried out by the carrier/provider whereas To support, manage, and secure the network, in the internet, manpower with routing and security skills is necessary.a
MPLS vs Internet Comparison Table
Let us discuss the top comparison between MPLS vs Internet:
|
Sr. No |
MPLS |
Internet |
| 1 | MPLS connectivity is provided by a single carrier for all sites. | It is not restricted to a particular carrier. Different carriers can be used to connect different sites for communication. |
| 2 | The MPLS provider can guarantee packet prioritization and delivery, as well as end-to-end delay. | Packet delivery and priority are not guaranteed. In fact, it is provided with the finest possible effort. |
| 3 | Because it prioritizes delaying sensitive traffic and promotes packet delivery, MPLS is preferred for video and voice communication. | Because packet delivery is on a best-effort basis without any QOS to support low latency, the Internet is a less desirable alternative for voice and video communication. |
| 4 | The service level agreement (SLA) is defined, and service availability is high. | The service level agreement (SLA) is not or just partially established, and the service availability is lower than MPLS. |
| 5 | Cost is high | The cost is lower than MPLS |
| 6 | In General, there is no need to encrypt traffic when communicating between customer locations via MPLS provider because it is carried over VRF (MPBGP) based logical Routing separation. | Due to the lack of a means to secure client traffic over the Internet, VPNs must be used to encrypt traffic in order to safely communicate across client locations. |
| 7 | Traffic Engineering is possible. | Traffic Engineering is not possible. |
| 8 | Information Security is high. | Information Security is low. |
| 9 | The MPLS provider has a greater level of control over traffic routing. | The MPLS service provider has more control over traffic routing. |
| 10 | It provides Reliable bandwidth and performance. | There is variation in bandwidth and performance. |
| 11 | In most cases, there is no need to install an additional firewall or other security equipment to secure the customer’s network. | Customers are directly exposed to the unsecured Internet, requiring the installation of security equipment such as a firewall to protect the network. |
| 12 | Manpower is in limited supply to support, maintain, and secure the MPLS network. The tasks are carried out by the carrier/provider. | To support, manage, and secure the network, manpower with routing and security skills is necessary. |
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MPLS vs Internet. Here we also discuss the MPLS vs Internet key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –