Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to Multidimensional Database
A Multidimensional Database is a type of Database Management system, which can be categorized as an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP). The multidimensional data stored in this database are applied for Analysis and Reporting resolutions that serves as primary input for business decision-making processes. The basic actions carried out on a Multidimensional database as a part of OLAP are Roll-up, Drill-down, Slice & Dice, in order to retrieve the required data from the database, where data is organized in the form of multidimensional cubes.
Relational Database
It stores data in a two-dimensional table format as rows and columns. The below tables shows the example of the relational database. The data is stored as a record in a row and each record divided into columns.
| Item | Store Location | Quantity |
| Paper, A4 | Chennai | 40 |
| Chocolate, Munch | Delhi | 5 |
| Paper, A3 | Delhi | 89 |
| Chocolate, 5Star | Chennai | 100 |
Examples of Multidimensional Array
Below are the examples of the multidimensional array:
MDB – Multidimensional Database: It is a type of database that has the data warehouse and OLAP (online analytical processing). MDB can create the inputs from the relational database and relational database can access the data from the database using SQL (structured Query Language). The OLAP which can access the data from the multidimensional database is known as MOLAL (Multidimensional Online Analytical Processing). Multidimensional Database Management System (MDDBMS) is the ability to rapidly process data, so we can quickly get the answer.
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing): The technology is the use of many BI (Business Intelligence) operations. And it is a powerful technology for data discovery, reports, analytical calculations, and predictive analysis planning.
OLAP for Multidimensional Analysis
- OLAP is using for business which is running in multidimensional activities and it supports business intelligence to do analysis from the various data sources. It allows the analyst to do analytical from many different sources at the same time. Many OLAP application includes business processing, reports, analytical, forecasting, predictions and so on. The measurement can take place in each dimension. When there is multidimensional data from the multiple data sources it can be analysis by using the three operations Roll-up, Drill-Down, Slicing, and Dicing.
- Take an example for an organization that is running as product manufacturing operations, they have to maintain the product sales based on the product category, customer list, time and so on. In such a way, the time plays a major role by measuring the month-on-month, year-on-year, etc, it is maintained in the x-axis and the product category is separated in the same x-axis by the difference the sales rate in the y-axis.
- Now we can easily do the analysis for our business to make improvements and predictions for our sales. The analyst needs to look at all dimensions to create a more effective analysis to target regular customers. That is the reason OLAP plays a vital role in multidimensional operations.
Data Warehousing
- A data warehousing is also known as an enterprise data warehouse. It is collecting and managing data from various sources for reporting and data analysis, considering business intelligence insights. It can act as a centralized repository and integrating data from one or more sources. Data warehousing involves data cleaning, data integration, and data consolidations.
- Take an example of a departmental store that has a large amount of data about the products. When we look at the specific product is available or how many counts left, we need to design a query to transform data into information which is available for users
Two-Dimensional Data Array
Below is the detail explanation of the two-dimensional data array:
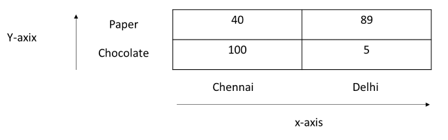
The data in the previous example is shown here as the 2×2 matrix. In this below figure, the store location is represented in x-axis and Item in the y-axis
Each axis in the multi-dimensional array is called as dimension, the dimensions are store location and item. It contains two positions each
- Store location = Chennai and Delhi
- Item = Paper and Chocolate
Each entry within the dimension is called a position. The areas are plotted as the quantity of paper and chocolates in each store location.
Multi-dimensional data is easy to see the representation of the array rather than a relational database. The two-dimensional database is easy to understand that there are two dimensions item and store location and each dimension contains two positions. For example, the quantity of information for chocolate is groped into one row and can be easily totaled.
The array format the information about a number of dimensions and positions within each dimension and also it can be an easy analysis method. When we store the data in an array format, we can easily do the analysis, import and export data very quickly.
Three Dimensional Data Array
Below is the detail explanation of the three-dimensional data array:
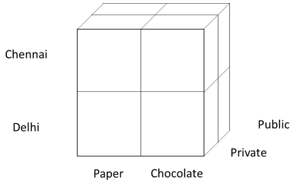
When we extend the relational database by adding the third dimension to the data set is represented as a Three Dimensional relational table. From the above array table, we’ll add the dimension “Customer”. The dimension can be two possibilities “Public” and “Private”. By adding one dimension with the two-dimension can extend the number of rows in the table. Where we extend the length of the table it is difficult to handle the data so that’s why the multidimensional structure plays a vital role.
| Item | Store Location | Customer | Quantity |
| Paper, A4 | Chennai | Public | 40 |
| Chocolate, Munch | Delhi | Private | 5 |
| Paper, A3 | Delhi | Public | 89 |
| Chocolate, 5Star | Chennai | Private | 100 |
Four-Dimensional Data Array
Below is the detail explanation of the four-dimensional data array:
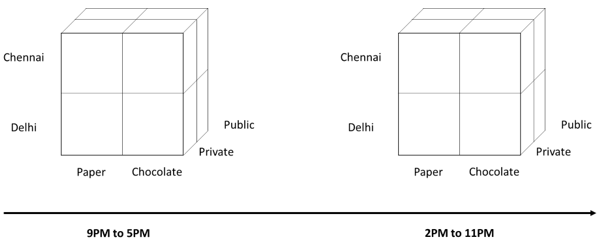
The three-dimensional can be extended to four-dimension by adding one more dimension as opening time. The four-dimensional array is difficult to understand, so a similar figure by adding each as opening time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Multidimensional Database
Advantages of Multidimensional Databases
Some of the advantages in Multidimensional database are:
- Easy Maintenance: It is easy to handle and maintain
- Increased Performance: The performance is much better than that of normal databases such as the relational database.
- Better Data Presentation: The data in a multi-faceted and contains many different factors. The data presentation is great distance superior to conventional databases.
Disadvantages of Multidimensional Databases
Below line explain the disadvantages of multidimensional databases:
One of the disadvantages in multidimensional databases is that quite complex and it would take professionals to understand and analyze the data from the database.
Conclusion – Multidimensional Database
Now in this article, we have learned what is about Multidimensional database, OLAP, Data warehousing, advantage and disadvantage of a multi-dimensional database.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Database. Here we discuss examples, two, three, four-dimensional data array with its advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more-