Updated April 18, 2023

Introduction to Multiplexer
The multiplexer has another name called data selector in electronics. Hence, from the name, it can be perceived that it selects data from a source. The multiplexer selects data from different analog and digital signal inputs given to the source and gives this signal to an output line, and hence the result is produced as a combination of digital and analog signals. Select lines are given to the multiplexer, and it selects the signal only from those lines. These signals are mostly low-speed, and they are combined and transmitted at higher speeds than input signals.
What is Multiplexer?
- It is a device used to transmit digital or analog signals of low speed from different input sources to a medium with high transmitting speed as a single output signal. This medium can be a single device or a single medium. Hence, we can say that multiplexer is a multi-input single-output device used to improve the efficiency of communication systems. The transmission conductor used can be a fiber optic cable or a copper wire, depending on the output device.
- Generally, a demultiplexer is used along with a multiplexer. This helps to verify and single out the signals received by the output device. This works as a single combined device and is usually termed a multiplexer. The multiplexer’s single output is received by the single input in demultiplexer, analyzed, and transmitted so that the receiver understands the circuit well in the system.
- When analog signals are taken into consideration, a multiplexer with time division is needed so that separate analog signals are selected, combined, and made into a high amplitude analog signal. This makes the process less complicated due to the usage of a time-division multiplexer. In a similar fashion, digital signals are received, combined, and transmitted as constant bandwidth signals of high amplitude. A time-division multiplexer can be used as analog signals, and the input signals are multiplexed into a high rate data stream that can be used in the output device.
Types of Multiplexer
They are easily divided into two types based on the type of signals they combine and transmit.
1. Analog multiplexer is the device that converts only analog signals. These signals are translated based on wavelength and frequency.
Hence wavelength multiplexer and frequency multiplexer are the two types derived from the analog multiplexer.
a. Wavelength Division Multiplexer: The data with various wavelengths are passed through a single medium. This helps to determine the frequency of the medium. If the wavelength is increased, the frequency is decreased and vice versa. Prism can be used as output for these kinds of the multiplexer as the application of prism is to convert different wavelengths into a single output. Hence, this prism becomes the input for the demultiplexer. An example is optical signals with different wavelengths of lights that are passed through a single optical fiber that helps in the communication of devices and data transmission. Both the directions are used for the transmission of data in the fiber optic cable.
b. Frequency Division Multiplexer: This is the frequent multiplexer in analog multiplexing. Various frequencies are used to combine the data as a single output. The bandwidth is divided into different frequency bands, and all these carry different signals to the output signal. A very common example is radio and television signals. Different signals of multiple frequencies are transmitted into the air at a time in radio. FDM helps to get the output from these signals.
2. Digital multiplexer are devices that combine and convert digital signals. Data is available as bits, and these are in the form of discrete signals.
Digital multiplexers are divided into different types.
Time Division Multiplexers: Independent signals are transmitted and received in the channel path so that they are divided into slots. Each message has a slot, and the receiver understands and combines them.
TDM is divided into two types.
- Synchronous TDM: The link or input signal is divided into time slots, and it is fixed. These slots depend on the number of connections, and it is proportional. Samples are taken, and they are similar for all the inputs received. The same slot is given to all the devices in synchronous TDM. And the slots are allocated even though the input signals are empty.
- Asynchronous TDM: The difference between synchronous and asynchronous TDM is that the sampling rate is different, and the time clock cannot be used for all the signals. If the timeslot receives nothing from the input device, it can be used for the next set of signals. This cannot be done in Synchronous TDM.
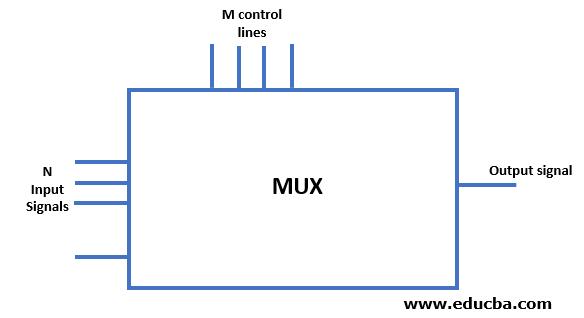
Block Diagram
Given below is the block diagram of Multiplexer:
Many inputs are received, and one output is given in multiplexer. This multiplexer receives an n input signal and gives only a single output signal. The single output signal is the result of the control lines used in the device. These control lines do the combination and transmission, due to which four input signals are turned to one output signal.
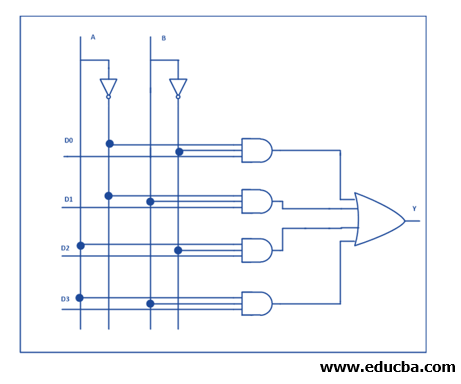
The 4-to-1 multiplexer can be shown in a similar fashion. 4 inputs, 2 control lines, and one output are the specialty in this multiplexer. Output always depends on the control values used in the device. The whole control of the system is in the control lines as it decides which input line has to be selected and which input data has to be transmitted to the output device. We might have done this experiment in the lower classes to get the desired output.
When only the upper AND gate is enabled and all other gates are disabled, the D0 signal is transmitted to the output device. Similarly, when the second AND gate are enabled, and all others are disabled, the D1 signal is transmitted to the output device. In a communication system, efficiency can be increased in different ways, and the use of a multiplexer is one method of transmission of high-speed data. Time and bandwidth can be selected for the better communication purpose. Also, it can be used to implement Boolean functions in the signals to use it as functions of multivariable.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multiplexer. Here we discuss the introduction; what is a multiplexer? Types and block diagrams, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –