Introduction to Mutual Fund
Mutual Fund is an establishment that pools money from various investors and invests that money into financial instruments and securities like stocks, bonds, debt instruments, etc. The combination of all these investments together is called a portfolio.
Investors who invest money in mutual funds will get shares representing ownership in the portfolio proportionate to their investment.
Explanation
A Mutual fund is a professionally managed fund. It pools money from investors to purchase securities. Mutual fund investment is open to both retail investors and institutional investors. The key benefits of investing in mutual funds are their diversification, that professionals manage them, that investments are made after proper research, and that they are liquid investments. The fund managers charge some management fees, which come as an additional expense compared to independent investment.
Features of Mutual Fund
- Professionals manage a Mutual fund. The fund managers do complete research and analysis before investing in securities or instruments. On investment, they monitor the portfolio and its performance.
- A Mutual fund popular for its diversification. It invests in various securities and instruments in a range of companies and different industries. By diversification, the risk in the portfolio reduces.
- Mutual fund shares are available at a relatively lower price than independent investment in equities as the portfolio is a total issue in multiple units to investors.
- A Mutual fund is a liquid investment, it can easily redeem at any time, and the shares will redeem at the current net asset value (NAV) with some redemption fees.
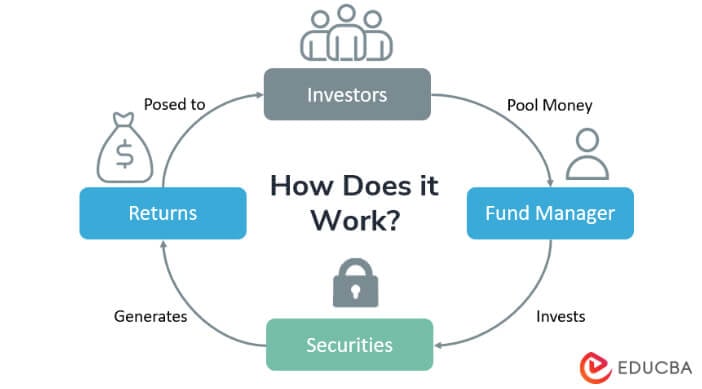
How Does Mutual Fund Work?
Portfolio managers manage mutual funds. Investors who want to invest in the capital market and other securities, and if they lack the knowledge and skillset, choose to invest in mutual funds as it manages the professionals who have experience in investment, and they do proper research before investing. Investors get the shares of mutual funds, giving good returns to investors in the form of capital appreciation and income yield.
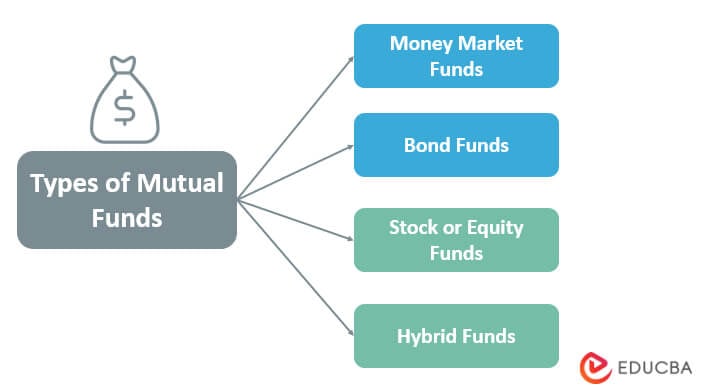
Types of Mutual Funds
Below are the following types:
1. Money Market Funds
Money market funds invest money in money market instruments. It invests in short-term fixed-income securities. Investors predominantly choose money market funds as a substitute for bank deposits, but it is not as secure as bank deposits as the government does not guarantee these investments.
2. Bond Funds
Bond funds invest in fixed-income securities or debt instruments. This fund mainly generates fixed income for the investors, and the investment money is secure also as it is a low-risk investment. Various bond funds differ from the bond issuer (Government, Corporate, Municipal, etc.) and time period (Short-term, Intermediate, and long-term).
3. Stock or Equity Funds
Stock or equity funds are an investment in the shares of the corporates in the capital market. The stock funds are also diversified as the portfolio predominantly consists of shares from different companies, industries, growth stocks, income stocks, strong valuation companies, high market cap companies, etc. This fund has more risk than other funds, and the value of mutual fund shares is subject to market risk and volatility.
4. Hybrid Funds
Hybrid funds invest both in stocks and bonds. They balance the risk and returns by investing in different securities. It is structured as funds of funds as hybrid funds invest in other mutual funds that invest in securities. The ideal proportion of equity and bond is fixed to get good returns and manage the portfolio’s risk.
How to Make Money from Mutual Funds?
There are various funds in mutual funds. An Investor needs to choose the right fund based on their return expectation and risk appetite. They are many portfolio managers with a track record of their investments and the returns generated. Investors can compare and choose the fund manager who meets their expectations.
Structure of Mutual Funds
The primary structure of mutual funds is as follows.
A) Open-End Funds
Open-end mutual funds are willing to buy back (Redeem) their shares from investors based on the net asset value (NAV) computed on the day of redemption based on the market price of the securities in the portfolio. Open-end mutual funds shares are sold daily to investors’ value depending on the net asset value.
B) Unit Investment Trusts (UIT)
The trust issues unit investment trusts at the time of creation and issues them to investors for a specific period. It also gives the option to the investors to redeem the shares at any time. Investors can redeem the shares upon termination of the trust. Any portfolio manager does not manage this fund as the securities in the portfolio and the holding time are pre-determined at the time of the trust creation.
C) Closed-End Funds
Closed-end funds are issued to investors only once at the time of the creation of funds through an Initial public offering (IPO) and then listed on the stock exchange. An Investor can exit the fund only by selling the shares in the market, and they cannot sell them back to the mutual fund. The IPO through which the fund shares are issued can list the shares either at a premium (i.e.) more than the NAV or at a discount (i.e.) less than NAV.
D) Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF)
Exchange-traded funds (ETF) combine both open-end and closed-end funds. They have a structure similar to open-end funds but trade on the stock exchange. The arbitrage mechanism keeps the trading price of ETF close to the net asset value.
Benefits of Mutual Fund
Below are some of the advantages:
- It has a diversified portfolio by holding various securities in various companies and industries, and diversification reduces its risk.
- It offers high liquidity to investors as they can redeem the mutual fund shares at any time for their net asset value.
- It is managed by professionals with the required knowledge and skillset in investments and supervises the portfolio’s performance.
- Small investors who cannot directly invest in shares and equities can easily purchase mutual fund shares priced at a lower value.
- It has its own regulations, and governmental institutions also regulate it.
- It operates completely transparently to investors, reporting all the information to them.
Drawbacks of Mutual Fund
Below are some of the advantages:
- It charges management fees, Which is an additional expense to investors.
- Investors cannot control the investment plan of the portfolio managers as they don’t have the option to decide on the investments.
- Mutual funds are also subject to market risk, varying from fund to fund. The growth and income yield from investments is not predictable.
- It is also a fixed investment plan and cannot customize according to investor needs.
Conclusion
A mutual fund is a good investment for small investors who cannot directly invest in securities in the capital market. It is also helpful for investors who lack experience and knowledge of investment. It is not possible to do complete research like how professionals do. Investors can invest either in SIP plans or lump sum plans. SIP plans are an excellent regular investment, and the investors can enjoy the value appreciation of investment and income generated from funds.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Mutual Funds. Here we discuss the introduction, types of mutual funds, and their advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –