Updated May 26, 2023

Introduction to MySQL Flush Log
Flush log is used to flush individual logs like Binary, general, error logs, etc. There is a command-line interface provided by the mysql admin utility for flush operations, using commands such as flush-logs, flush-status, flush-hosts, flush-privileges, and flush-tables.
To execute the log flushing statements or commands, we need to connect to the server with the account which has “RELOAD” Privilege.
Flushing the binary log creates a new binary log file. Whereas flushing the general query log closes and reopens the log file. The same goes for the slow query log and error log; it just closes and reopens the log file.
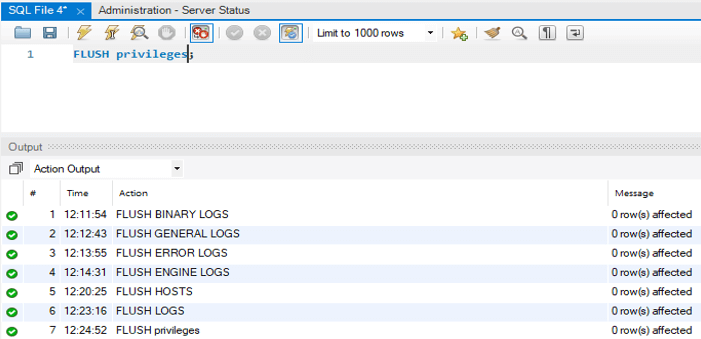
Syntax
Below is the syntax for the flush: –
FLUSH [NO_WRITE_TO_BINLOG | LOCAL] {
[flush_option] [, flush_option] ...
| [tables_option]
}Below is the syntax for flush tables: –
FLUSH TABLEStbl_name;
FLUSH TABLES tbl_name [, tbl_name], TABLES WITH READ LOCK;Here the flush_option and tables_options are as below:
- flush_option: BINARY LOGS, DES_KEY_FILE, ENGINE LOGS, ERROR LOGS, GENERAL LOGS, HOSTS, SLOW LOGS, STATUS, LOGS, PRIVILEGES, QUERY CACHE, etc.,
- tables_options: tables_option: TABLES, Multiple tables: – TABLES tbl_name [, tbl_name], TABLES WITH READ LOCK, Multiple tables: – TABLES tbl_name [, tbl_name] … WITH READ LOCK, TABLES tbl_name [, tbl_name] … FOR EXPORT
How does MySQL Flush log file work?
The flush statement works as below:
Before flushing the logs, it is always a good practice to back up the log files in some directory.
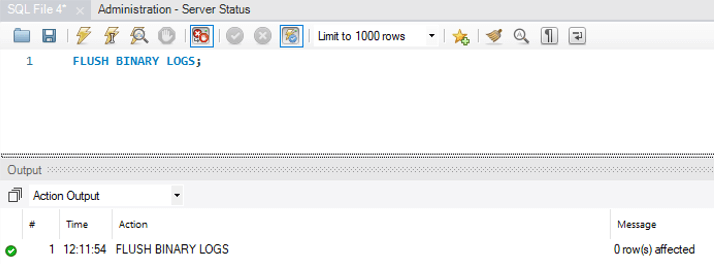
1. Flush Binary logs
It is used to close and reopen the binary log files where the server is writing.
Code:
FLUSH BINARY LOGS;Output:
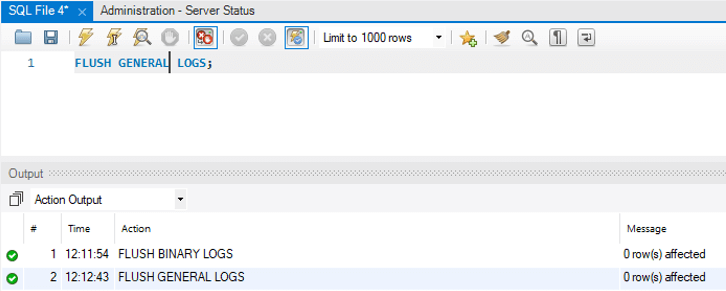
2. Flush General logs
It is used to close and reopen the general log files where the server is writing.
Code:
FLUSH GENERAL LOGS;Output:
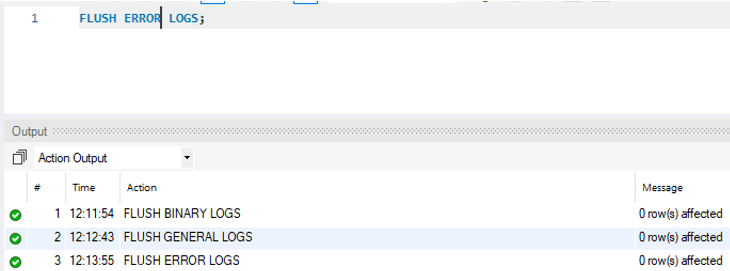
3. Flush Error logs
It is used to close and reopen the error log files where the server is writing.
Code:
FLUSH ERROR LOGS;Output:
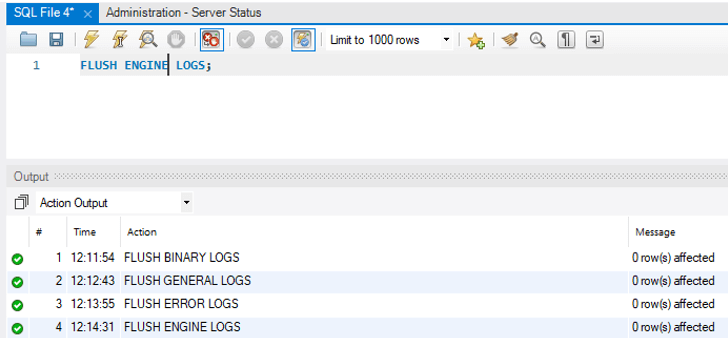
4. Flush Engine logs
It is used to close and reopen the storage engine log files.
Code:
FLUSH ENGINE LOGS;Output:
5. Flush DES_KEY_FILE
This option is used at the server startup time to load the DES keys from the “DESC_KEY_FILE.”
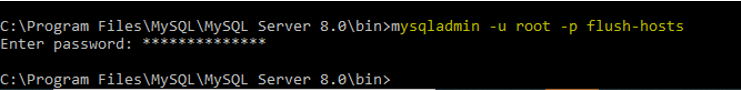
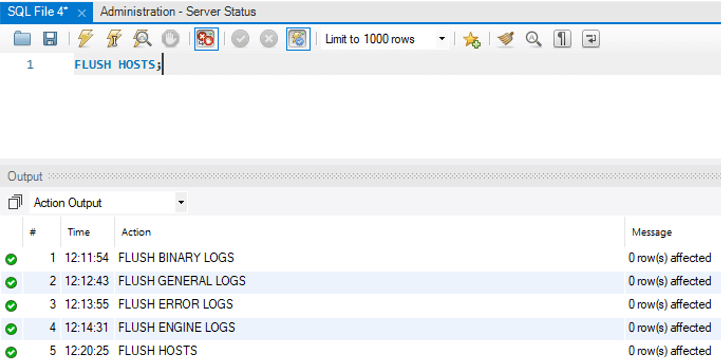
6. Flush Hosts
It is used to flush all the information from the host cache.
Code:
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-hosts /* -- to flush all host information --*/Output:
Or
Workbench level Syntax: –
FLUSH HOSTS;Output:
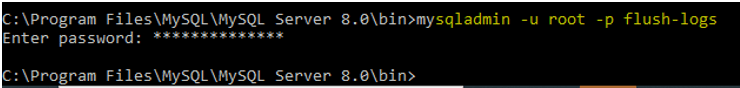
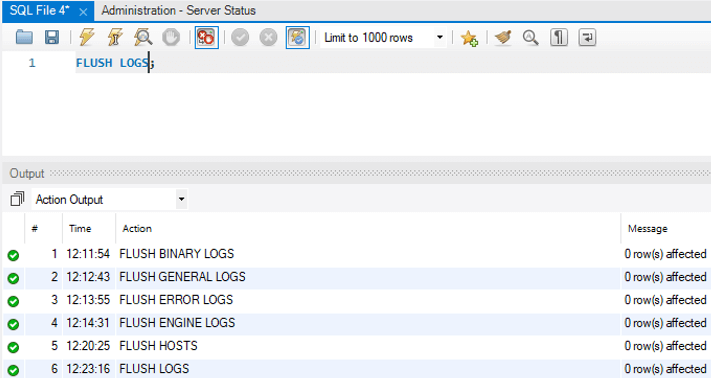
7. Flush Logs
It is used to flush all information logs.
Code:
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-logs /* -- to flush all logs --*/Output:
Or
Code – Workbench level
FLUSH LOGS;Output:
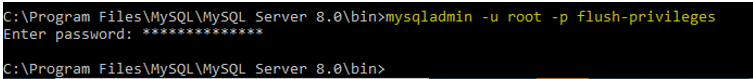
8. Flush Privilege
It is used to reload the grant tables.
Code:
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-privileges /* -- to reload all grant tables --*/Output:
Or
Code – Workbench level
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Output:
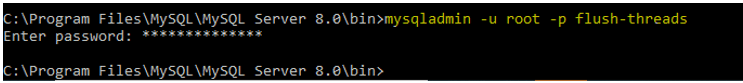
9. Flush threads
It is used to flush all the thread cache.
Code:
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-threads /* -- to flush all threads --*/Output:
10. Flush Query cache
It is used to defragment the query cache.
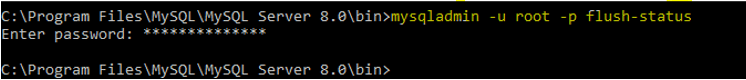
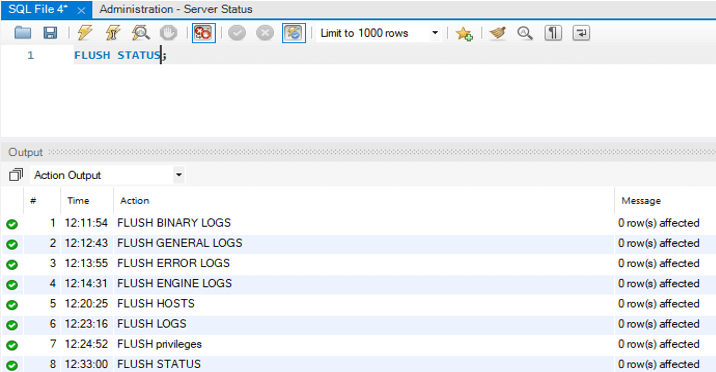
11. Flush STATUS
It is used to clear the status variables.
Code:
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-status /* -- to clear all status variables --*/Output:
Or
Code – Workbench level
FLUSH STATUS;Output:
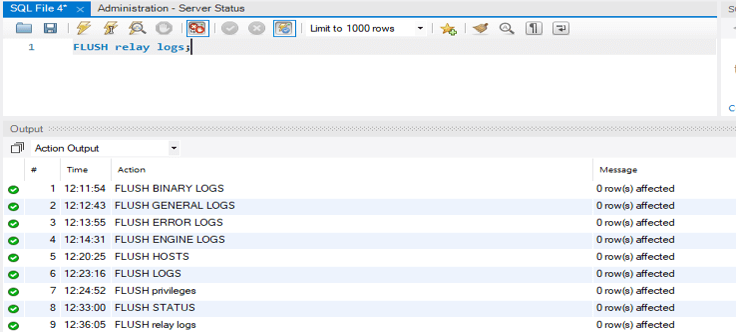
12. Flush Relay logs
You can use it to close and reopen the relay log files that the server is writing to.
Code:
FLUSH RELAY LOGS;Output:
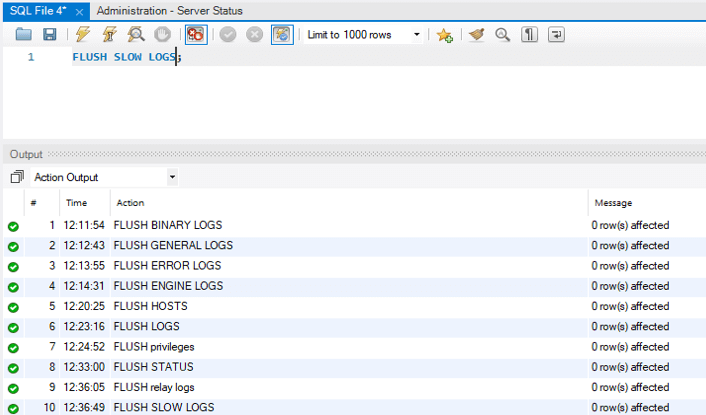
13. Flush Slow logs
You can use it to close and reopen the slow log files that the server is writing to.
Code:
FLUSH SLOW LOGS;Output:
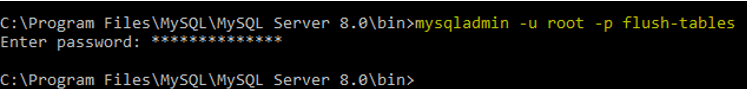
14. Flush Tables
You can use it to flush all the tables based on the lock condition.
Code:
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-tables /* -- to flush all tables --*/Output:
Code:
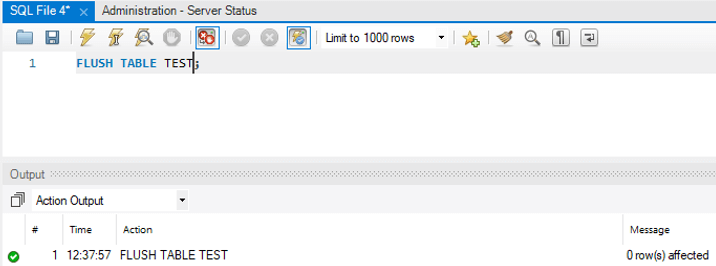
FLUSH TABLE TBL_NAME;
EG: -
FLUSH TABLE TEST;Output:
Example
Now let us check the flush option by using the below statement: –
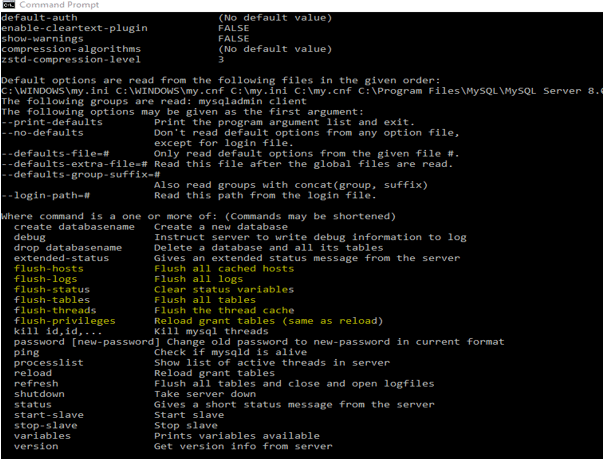
mysqladmin -help;Output for flush would be as below:
- flush-hosts- Use to Flush all cached hosts.
- flush-logs- Use to Flush all logs.
- flush-status- Use to Clear status variables.
- flush-tables- Use to Flush all tables.
- flush-threads- Use to Flush the thread cache.
- flush-privileges- Use to Reload grant tables.
Let us see the screenshot of the command “mysqladmin -help” output. Below is the screenshot that represents the same. There are many help options other than the flush shown in the screenshot below.
Output:
Conclusion
- The Flush log command flushes individual logs such as Binary, General, Error logs, etc. You can perform the flush operation using “mysqladmin” for hosts, logs, status, tables, threads, and privileges.
- To execute the log flushing statements or commands, we need to connect to the server with the account which has “RELOAD” Privilege.
- Flushing the binary log creates a new binary log file. Whereas flushing the general query log closes and reopens the log file. The same goes for the slow query log and error log; it just closes and reopens the log file.
- We can’t use the Flush statements in the store functions or triggers. We may use it in stored procedures. The functions or triggers should not call this procedure in turn.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Flush Log” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.