Updated May 25, 2023

Introduction to MySQL Repair Table
MySQL Repair Table is to repair the corrupted table. This repair table doesn’t work for all the storage engines. Usually, we might never get to use the “Repair table”, but when a disaster occurs, we get the data back from the “MyISAM” table. We need a few privileges like SELECT and INSERT for the table. It works only for the “MyISAM” storage engine and not the “InnoDB” storage engine. So we need to change the storage engine to “MyISAM”. It’s always a good measure to take the backup of the table before performing the “Repair Table” as it might cause data loss. We have the options of Quick, Extended, and USE_FRM applicable and defined at the syntax level. Let’s discuss the “Repairable” and the example in this session.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of MySQL Repair Table
REPAIR[NO_WRITE_TO_BINLOG|LOCAL]
TABLEtable_name1[,table_name2]... [table_nameN]
[QUICK][EXTENDED][USE_FRM]How does MySQL Repair Table work?
Let us see how MySQL Repair Table.
Code:
REPAIR[NO_WRITE_TO_BINLOG|LOCAL]
TABLEtable_name1[,table_name2]... [table_nameN]
[QUICK][EXTENDED][USE_FRM]Here if we consider each option and its use:
- NO_WRITE_TO_BINLOG | LOCAL: By default, the Binary log is where the server writes the “Repair Table” for the replication slaves. We specify the option “NO_WRITE_TO_BINLOG” or Local to suppress the logging.
- QUICK: If we specify the “QUICK” option, we are trying to repair only the “index” file, not the data file. It is done by myisamchk –recover –quick.
- EXTENDED: It creates one index at a time with sorting instead of creating row by row. It can be done by myisamchk –safe –recover.
- USE_FRM: If the MYI index file is missing or the header is corrupted. This option tells us not to trust the.MYI information and re-create the information from the data dictionary. It can’t be done by myisamchk.
Now let us create the table, alter the storage engine, and create a “repair table”.
Code:
CREATE TABLE LOAN_TABLE(
LOAN_NO VARCHAR(25)PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(25),
AMOUNT INTEGER(10),
AP_DATE DATE
);Inserting data into the loan_table table:
Code:
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('3A341','Ram', 189000,'2018-09-08');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('4E251',' Ravi', 125000,'2018-09-09');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('1R121',' Santosh', 169000,'2018-09-10');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('53RT1',' Samuel', 139560,'2018-09-11');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('2RR31',' Kartika', 188756,'2018-09-12');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('8PP91',' Donald', 122568,'2018-09-13');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('0PK91',' Donald Parker', 135684,'2018-09-14');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('7JI81',' Danny', 190000,'2018-09-15');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('OWE31',' Harsh', 164988,'2018-09-16');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('PPL11',' Blue park', 127568,'2018-09-17');
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('R34E1','chai', 156000,'2018-09-18');
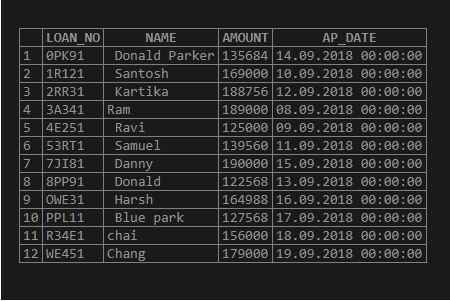
INSERT INTO LOAN_TABLE VALUES ('WE451','Chang',179000,'2018-09-19');Now let us select the table:
select * from LOAN_TABLE;Output:
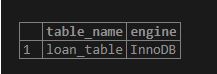
Here below query is used to check the storage engine for the specified table.
Code:
select table_name, engine from information_schema.tables where table_name='loan_table';Output:
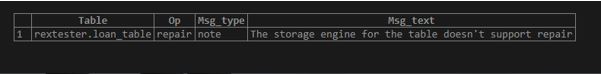
Here it is, “InnoDB”. So when we create the repair table for this storage engine table, it throws an error:
Code:
REPAIR TABLE LOAN_TABLE;Output:
Alter the table storage engine to “MyISAM” and then try to create the “repair table”.
Code:
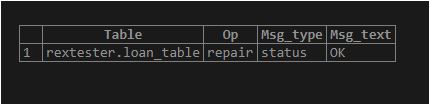
ALTER TABLE LOAN_TABLE ENGINE='MyISAM';Now let us create the “repair table” for the loan_table;
REPAIR TABLE LOAN_TABLE;Output:
Here from the output, we can see that it has four columns Table, Op, Msg_type, and Msg_text.
| Column_name | Description |
| Table | It specifies the name of the table |
| Op | Always “Repair” |
| Msg_type | It can be status, error, info, or warning |
| Msg_text | It consists of the message |
Examples to Implement MySQL Repair Table
Now let us create another table:
Example #1
Code:
create table Weather_temperature
(
Days date,
London Float (5,2),
New_York Float (5,2),
India Float (5,2),
America Float (5,2),
Africa Float (5,2),
China Float (5,2),
Australia Float (5,2)
)ENGINE=MyISAM; /* -- Storage engine as “MyISAM” instead of default one “InnoDB” -*/Now let us insert the data into the table as below:
Code:
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-01', 36.7, 34.6, 39.1, 39.8, 34.1, 29.0, 37.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-02', 31.7, 39.6, 31.1, 32.8, 40.0, 39.0, 34.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-03', 32.7, 38.6, 38.1, 31.8, 45.2, 34.0, 32.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-04', 33.7, 37.6, 32.1, 36.8, 49.1, 31.0, 37.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-05', 34.7, 36.6, 37.1, 34.8, 49.7, 36.0, 39.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-06', 35.7, 35.6, 33.1, 30.8, 49.2, 33.0, 31.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-07', 36.7, 34.6, 34.1, 33.8, 48.9, 38.0, 39.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-08', 37.7, 23.6, 35.1, 39.8, 45.5, 36.0, 33.7 );
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-09', 28.7, 30.6, 36.1, 32.8, 49.9, 30.0, 37.7 );
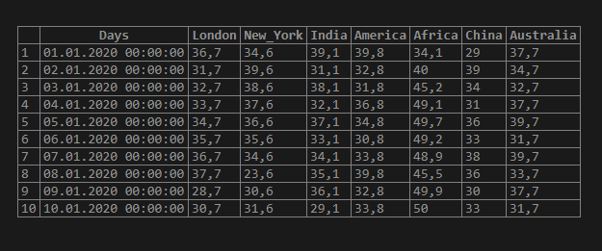
insert into weather_temperature values ('2020-01-10', 30.7, 31.6, 29.1, 33.8, 50.0, 33.0, 31.7 );Now let us select the table and see the output:
SELECT * FROM WEATHER_TEMPERATURE;Output:
Example #2
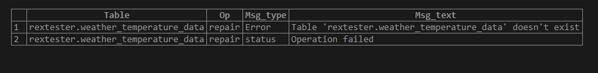
We have created the table with the storage engine as “MyISAM”. So the repair table will be executed without any error:
Code:
REPAIR TABLE WEATHER_TEMPERATURE_DATA QUICK extended;Output:
Conclusion
MySQL Repair Table is for the repairs of the corrupted table. This repair table doesn’t work for all the storage engines. It works only for the “MyISAM” storage engine and not the “InnoDB” storage engine. So we need to change the storage engine to “MyISAM”. It’s always a good measure to take the backup of the table before performing the “Repair Table” as it might cause data loss. We have the options of Quick, Extended, and USE_FRM applicable and defined at the syntax level.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Repair Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.