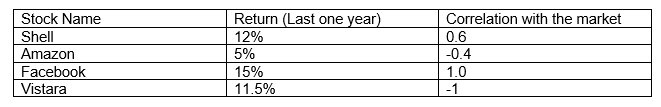Updated July 26, 2023
Overview of Negative Correlation example
A negative correlation is a statistical measure used to describe the relationship between two variables. A negative correlation happens when one variable increases when the other decreases and vice versa. Portfolio managers use assets with such characteristics to diversify the portfolio and decrease or mitigate the risk.
Examples of Negative Correlation
Examples of Negative Correlation are as Follows:
Negative Correlation – Example #1
Let us look at an example. Let’s assume a portfolio manager invests in the financial industry sector. But in the past few months, the prices of these stocks have been falling due to changes made by the Fed. According to his analysis, the shares will tumble further and might also lead to a crash. He is not looking at selling these stocks and wants to keep them as per his client’s long-term goal.
But he realizes that he has not diversified his portfolio or managed any risk. So he thinks of using assets negatively correlated with the financial industries. Assets that have a negative correlation with stocks are gold. The portfolio manager then sells some of his investments in the financial sector and buys gold to exploit the negative correlation.
If he is not keen on selling a part of his portfolio, the portfolio manager can hedge his risk. A negative correlation can also be used for hedging, mitigating the risk. The manager can take offsetting positions; in this case, for example, he can put options on the financial services stocks or even sell call options. Both of these are considered negatively correlated assets.
Negative Correlation – Example #2
Lara is an investor looking to add shares of Amazon or Apple to her portfolio. Her portfolio mainly tracks the stocks from the S&P 500. Before buying it, she wants to do some analysis and look at stocks that will help her diversify her portfolio and, most importantly, not increase the systematic risk of her portfolio. He plans to look at the correlation between these stocks to fulfill this.
He finds the prices of the last three years and calculates the correlation. The correlation of Apple with the index is -0.9, while her portfolio is -0.7. On the other hand correlation of Amazon with the index is 0.9, while with her portfolio, it is 0.2
Looking at the above, Lara adds Apple to her portfolio based on the negative correlation.
Negative Correlation – Example #3
The instructor gives a finance student a sample of the risk and return of multiple stocks and asks them to determine which one will be the best for their investor if they are allowed to advise them. His client’s main goal is to mitigate risk and diversify his portfolio. He also has exposure to oil prices.
He is looking at multiple factors in parallel, like risk, return, and correlation. Below is the list of stocks he has to select from
He looks at all these stocks and observes that the stocks with the highest two returns, i.e. 12% and 15%, positively correlate with the portfolio. He wonders if this is the right choice. However, he observes that the correlation of Facebook with the market is 1.0, which is perfectly correlated. Then he looks at the market performance of the last year of the S&P 500.
Looking at the numbers, he understands the market had a good last year due to a positive global outlook. However, according to him, the current market conditions do not look the same. So if he buys Facebook and looks at the perfectly positive correlation, he concludes that when the market falls, this stock’s price will also get hampered. He, therefore, does not choose Facebook to invest in
Next, he looks at Shell; he knows that the client has exposure to oil prices. With choosing this company, there will be no diversification benefits. Keeping that aside, he checks for the correlation. The correlation of 0.6 means that when the market increases, the stock prices increase and vice versa. Looking at both these factors, he does the select shell.
Next, he looks at Vistara; even though the return is not the highest but can provide great diversification benefits. First, since it is an airline company when it is negatively correlated to oil exposure, and second, the correlation with the market is -1, which means that when the market price goes up, the stock price goes down. These things perfectly match his objective, so he selects Vistara.
Negative Correlation – Example #4
In this example, let us look at some real-world scenarios of negative correlation.
The most common example is the price of the bonds and interest rates. As the interest rate increases, the price of the bond falls. The fixed-interest bonds become worthless in this case, but the money price has already increased.
One more classic example would be the price of oil and oil producers (BP, Shell). This is negatively correlated to the price of airline companies.
The above ones are logical and can be related; however, there are some different ones too. For example, The price of the potato chip makers vs the price of the potato. The oil price vs the share price of consumer discretionary companies. One logic can be that as the prices fall, there is more income on hand or discretionary income for consumers to buy cosmetics and other products.
Another example is the price of the dollar vs the price of the debt of the emerging market. When the price of USD rises, the ability of the emerging market countries to repay their debt back falls, which in turn increases the chances of default. The correlation may not be perfectly negatively correlated.
Conclusion
There are both pros and cons of using the correlation method. However, decisions mustn’t be taken in isolation, and a decision should be based on the results of all the methods.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Negative Correlation Example. Here we discuss the definition and top 4 examples of negative correlation, along with a detailed explanation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –