Updated July 18, 2023
Definition of Negotiable Instruments
Negotiable Instruments refer to a signed document that contains a promise by a person being the payer to pay a certain amount of money to the specified person or the assignees being the payee either on demand or at a specified date in the future.
The instrument is said to be negotiable since it can be freely transferred from one person to another, and the transferee of the instrument gets a clear title to the said instrument.
Importance of Negotiable Instruments
Negotiable instruments are issued by parties to fulfill their payment obligations. They serve as a guarantee that the person making and signing such a document as the payee shall be under an obligation to pay the specified amount of money to the mentioned person or the assignees, or the holder of the instrument at a certain future date or at demand. The holder can transfer the document to another person by signing the endorsement, and such another person shall get the legal title for such an instrument and be entitled to claim money from the person who had signed in the capacity of the payer. The holders usually make these endorsements to meet their debt obligations.
Characteristics of Negotiable Instruments
The presence of the following features can characterize negotiable instruments:
- Transferrable: These instruments can be easily transferred by the holder to another person either by delivery or by making a lawful endorsement. If the payee is not mentioned in the instrument, then the transfer can be made by mere delivery. If the payee is mentioned, then the transfer has to be made by endorsement in the name of another person or assignee, or bearer.
- Right to Receive Payment: If the negotiable instrument is not honoured on the specified date and the holder of the instrument doesn’t get the payment, then the holder becomes entitled to take legal action against the payer. This applies even if the instrument was not initially issued to the holder but instead transferred.
- Title of Transferee: The transferee of the negotiable instrument gets a clear title to the instrument and is known as a “holder in due course”. This means that the title of such a transferee who acquired the instrument by legal means shall not be affected due to the flaw or illegality in the title on account of the transferor or any other previous holder.
Examples
Some of the common examples of negotiable instruments include
- Cheques
- promissory notes
- bills of exchange
- demand drafts, etc.
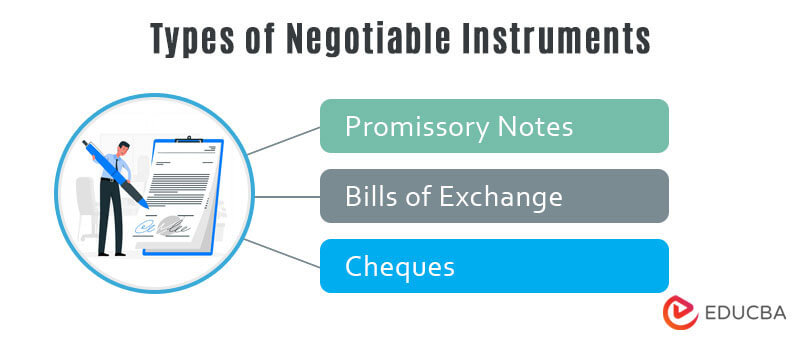
Types of Negotiable Instruments
Negotiable instruments can be broadly classified into three types, namely promissory notes, cheques, and bills of exchange.
1. Promissory Notes
These are the instruments that are signed by the payer and contain a promise to pay a certain amount of money to another person, or his/her order, or to the bearer of the instrument at a certain date. The promise to pay shall be unconditional, failing which the note shall not be called a promissory note. The person making the note is known as the maker, and the person to whom the such note is being made is called the payee. For example, A makes a promissory note in writing to B stating that I shall pay $10,000 to B on 30.11.2020 and sign the same.
2. Bills of Exchange
Bills of exchange contain a direction or an order made by the maker of the instrument instructing a certain person to pay a specified amount of money to another person, or his/her order, or to the bearer of the instrument at a specified date. The person making the instrument is known as a drawer, and the person on whom the such instrument is drawn is known as the drawee or the acceptor. The payee may or may not be the drawer. For example, A draws a bill of exchange to B in which it’s written that “Kindly pay to the bearer $10,000 on 30.11.2020 and oblige”.
3. Cheques
Cheques are the bill of exchanges that are drawn by the person making such cheques on the specific bank, instructing the bank to pay a certain amount of money to a person mentioned therein on demand. The person signing the cheque and making an instruction to the bank is known as the drawer, the bank becomes the drawee, and the person to whom payment is to be made is known as the payee.
Requirements for Negotiable Instruments
- Certainty in Time of Payment: The time at which the payer will make the payment shall be certain and determinable, even if it is not any specific date. It should mention either the specified date or a determinable event upon which the payment shall be made. The payee can mention that the amount will be paid on 31.10.2020, after 3 months, after the death of Mr X or on-demand, and so on.
- Definite Amount: The amount to be paid shall be clearly mentioned without any ambiguity, and an instrument without any definite amount shall be invalid.
- Unconditional Payment: The promise or instruction to pay shall be unconditional, and the payment shall not be subjected to any condition or upon the occurrence or non-occurrence of any uncertain event.
- Written Instrument: The instrument has to be in writing, and the oral instruments have no legal validity.
- Signed by Maker: The person making such a negotiable instrument shall sign the same anywhere on the instrument and appoint an authorized representative to sign the same.
- Payable in Money: The mode of payment shall be money only, and non-monetary payments shall not form part of negotiable instruments. Such as the payment can’t be made in bonds, shares, gold coins, and so on.
Conclusion
Negotiable instruments are vital to the economy and as recognized globally as a medium of payment. They can be freely transferred from one person to another, which makes them more useful, and parties can use them to meet their payment obligations. However, due care shall be taken when writing a negotiable instrument, especially when the same is made payable to a bearer as a person acquiring the same by unfair means can try to misuse the instrument, and legal actions can take some time thereafter.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Negotiable Instruments. Here we also discuss the definition and characteristics of negotiable instruments along with types and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –