What is Neuromarketing?
Neuromarketing is the study of how our brain responds to marketing. It helps businesses create ads and products that connect emotionally with consumers.
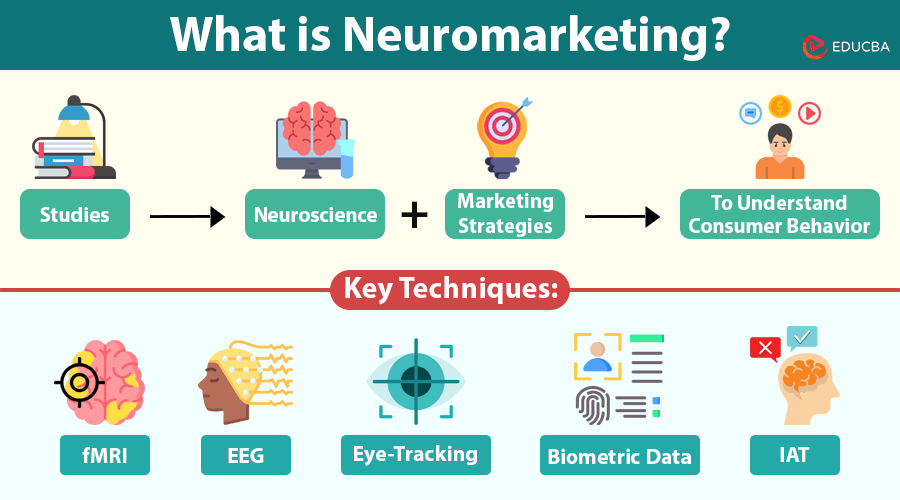
Neuromarketing is a cutting-edge field that merges neuroscience and marketing strategies to understand consumer behavior on a deeper, often subconscious, level. It uses tools and techniques from neuroscience to study how consumers respond to marketing stimuli like advertisements, product designs, and branding. The ultimate goal is to help businesses craft more effective marketing campaigns by analyzing the brain’s emotional and cognitive reactions. Unlike traditional marketing, which focuses on rational decision-making, neuromarketing focuses on emotional drivers.
The Science Behind Neuromarketing
Neuromarketing relies on neuroscience tools and psychological research to gain insights into consumer behavior. Here are some key concepts:
- Brain Activity and Consumer Behavior: The brain constantly processes information, and when a consumer interacts with a brand, their brain reacts in various ways. Neuromarketing uses advanced tools to track these reactions, including brain activity, eye movements, and emotional responses.
- Emotional vs. Rational Decisions: Neuroscientific research confirms emotions are crucial in shaping decision-making. Consumers often make decisions based on emotional triggers, even when they believe they are acting rationally. Neuromarketing focuses on tapping into these emotions to influence purchasing decisions.
- Cognitive Biases: Cognitive biases are consistent patterns of deviation from rational thinking in judgment and decision-making. Neuromarketing leverages these biases to craft messages and ads that align with how consumers’ brains are wired to think, thus increasing the likelihood of influencing behavior.
Key Techniques in Neuromarketing
Neuromarketing employs a variety of sophisticated tools and techniques to gain insights into consumer behavior. These methods help capture data on brain activity, eye movement, and physiological responses that reveal how people react to advertisements, products, and brands.
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI): It tracks brain activity by monitoring variations in blood flow.fMRI scans allow researchers to observe which brain areas activate in response to specific marketing stimuli. For example, fMRI can help determine if an advertisement triggers an emotional response or engages the rational thought process.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): EEG tracks electrical activity in the brain, giving real-time data on how the brain responds to stimuli. By analyzing patterns of brain waves, EEG can identify emotional reactions, attention levels, and cognitive engagement when exposed to different types of marketing content.
- Eye-Tracking: Eye-tracking technology tracks where a person’s gaze lands and for how long. Marketers use eye-tracking to understand which elements of an advertisement, website, or product packaging attract the most attention. This helps optimize the design and positioning of key elements to maximize consumer engagement.
- Biometric Data: Biometric tools, such as heart rate monitors, skin conductance sensors, and facial expression analysis, measure physical reactions to stimuli. For instance, increased heart rate or skin conductance can indicate heightened emotional arousal, which may correlate with positive or negative reactions to marketing messages.
- Implicit Association Tests (IAT): IATs are psychological tests that measure implicit attitudes by analyzing reaction times. In neuromarketing, IATs uncover consumers’ unconscious associations with brands, products, and advertisements. This helps marketers design campaigns that align with consumers’ hidden preferences and biases.
The Role of Neuromarketing in Modern Business Practices
Neuromarketing applies to various aspects of marketing and business strategies. Here is how companies typically use it:
- Advertising: Neuromarketing techniques help identify which ads elicit emotional responses from consumers. For example, an emotional ad might evoke happiness or nostalgia, leading to better recall and higher engagement. By understanding what captures attention and triggers emotions, brands can craft compelling advertisements that evoke the desired emotional reaction.
- Product Design: Brands use neuromarketing to optimize product design, ensuring that it appeals to consumers emotionally. This includes everything from the colors used on packaging to the shape and texture of products. For example, blue is often associated with trust, while red can stimulate excitement and urgency.
- Branding: Neuromarketing helps companies understand how consumers perceive brands. Using brain imaging and other tools, companies can refine their branding strategies to create a stronger, more emotional connection with their audience. For example, logos with simple, bold designs tend to be more memorable and elicit stronger emotional responses than complex, detailed logos.
- Pricing Strategy: Understanding how consumers react to different price points allows companies to optimize pricing. Neuromarketing has shown that consumers often respond more positively to prices just below whole numbers (e.g., $9.99 instead of $10.00).
Psychological Triggers in Neuromarketing
The table below highlights some of the most effective psychological triggers used in neuromarketing and how they shape marketing strategies.
| Psychological Trigger | Description | Application in Marketing |
| Scarcity | The principle is that people are more likely to act when they perceive a limited availability. | Limited-time offers, flash sales, “only X items left” notifications. |
| Authority | People are more likely to trust and follow authority figures. | Celebrity endorsements or expert recommendations. |
| Reciprocity | When someone does something for us, we feel compelled to return the favor. | Offering free samples, discounts, or gifts in exchange for customer loyalty. |
| Social Proof | People often look to others to determine how to behave, especially in uncertain situations. | Customer testimonials, social media likes, reviews, and shares. |
| Consistency | Once someone commits to something, they are more likely to act consistently with that commitment. | Subscription models or signing up for a newsletter encourages consistent interaction. |
Real-World Examples
Several global brands have successfully implemented neuromarketing strategies to enhance their marketing efforts:
- Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi: A famous fMRI study showed that when participants were unaware of the brand, their brain activity indicated a preference for Pepsi. However, when researchers told participants they were drinking Coca-Cola, their brain’s emotional centers showed higher engagement, proving the power of branding.
- Netflix’s Thumbnails & Personalized Content: Netflix uses neuromarketing insights to test different thumbnails and content previews, selecting those that generate the highest engagement based on user responses.
- Amazon’s One-Click Purchase: Amazon optimizes its shopping experience by reducing friction in the buying process and leveraging insights from neuromarketing to make transactions feel effortless.
- Google’s Color Testing: Google once experimented with 41 shades of blue for advertising links to determine which color generated the most clicks, demonstrating the power of small psychological cues in marketing.
Ethical Considerations
While neuromarketing has proven highly effective, it raises ethical concerns. The main issue revolves around manipulating consumer behavior, especially when it involves unconscious decision-making.
- Manipulation of Consumers: Neuromarketing’s ability to influence emotions and decisions raises the question of whether it is ethical to manipulate consumers’ subconscious minds. Companies could use these insights to create highly persuasive campaigns that may push consumers toward decisions they would not otherwise make.
- Privacy Concerns: Neuromarketing techniques like brain scans and facial recognition rely on collecting sensitive data. Privacy concerns exist, especially when consumers are unaware that their reactions are being tracked and analyzed.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children, for example, are more susceptible to emotional appeals in advertisements. Marketers must be cautious when targeting vulnerable populations to ensure that manipulative tactics do not unduly influence them.
- Informed Consent: For neuromarketing to stay ethical, companies must inform consumers about the methods used to study their behavior. Transparency is key in maintaining trust between brands and consumers.
The Future of Neuromarketing
As technology advances, so does the potential of neuromarketing, opening up new possibilities for understanding consumer behavior. Here are a few predictions for the future:
- Integration with AI: Artificial intelligence will enhance neuromarketing by analyzing vast amounts of real-time data. AI can analyze consumer behavior patterns and predict future buying decisions with remarkable accuracy, enabling the creation of highly personalized marketing campaigns.
- Increased Personalization: Neuromarketing will enable brands to create hyper-personalized experiences. By understanding individual consumer preferences deeper, companies can craft tailored messages, offers, and experiences that resonate with their audience.
- More Immersive Experiences: Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) are poised to play a bigger role in neuromarketing. Brands could create immersive shopping experiences that directly engage the senses and trigger emotional responses.
Final Thoughts
Neuromarketing is reshaping the marketing landscape by providing deeper insights into consumer behavior. Businesses can craft more effective, emotionally engaging marketing campaigns by understanding how the brain reacts to different stimuli. As the field evolves, neuromarketing will provide even more advanced techniques for businesses to enhance their marketing strategies and establish stronger consumer connections.
Recommended Articles
We hope this in-depth guide to neuromarketing helps you understand how neuroscience can transform your marketing strategies. Check out these recommended articles for more insights into consumer behavior and marketing innovation.
